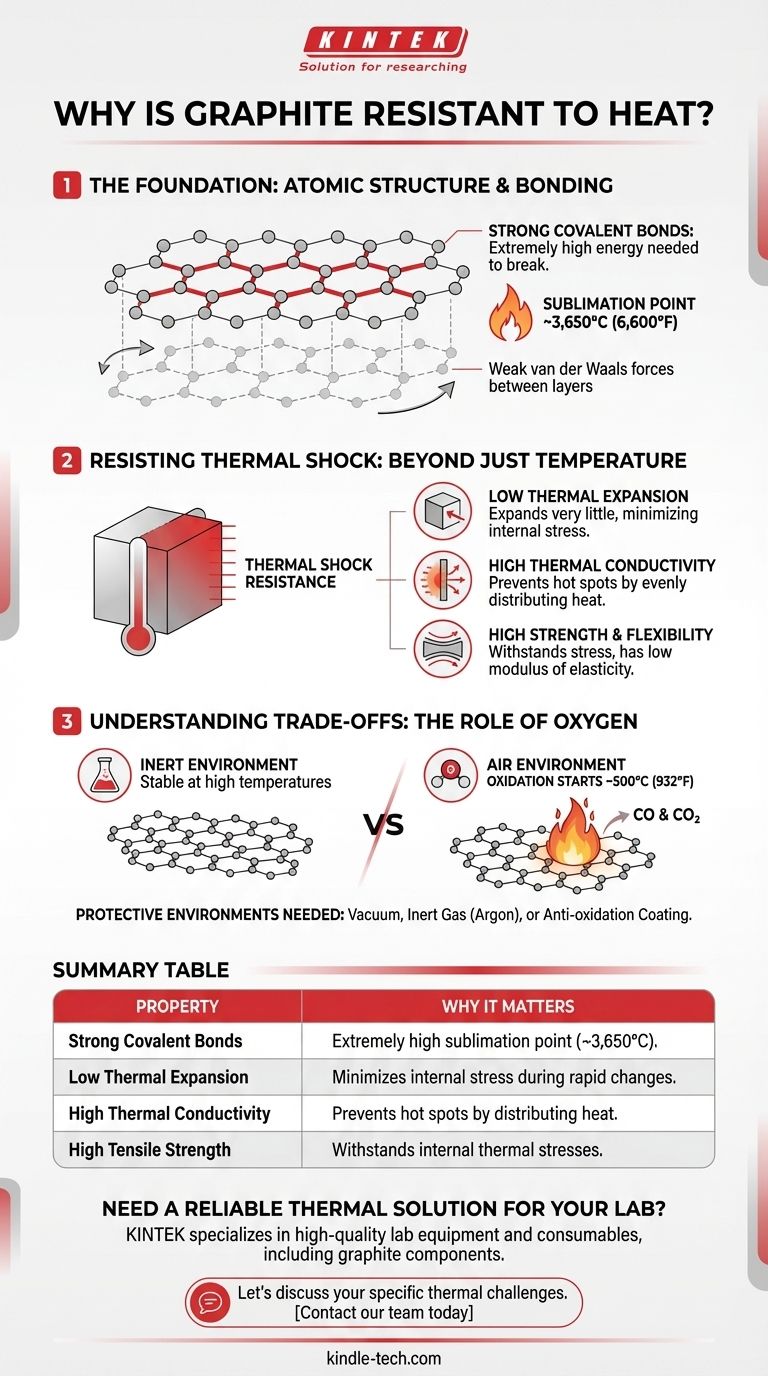
The fundamental reason for graphite's heat resistance lies in its unique atomic structure. The carbon atoms within its layers are linked by extremely strong covalent bonds, which require a tremendous amount of thermal energy to break apart. This results in an exceptionally high sublimation point and an ability to maintain structural integrity at temperatures where most metals would be liquid.
The term "heat resistance" involves two distinct concepts: the ability to withstand a high temperature without melting and the ability to survive rapid changes in temperature without cracking. Graphite excels at both due to its powerful atomic bonds and a unique combination of thermal properties that prevent internal stress.

The Foundation: Atomic Structure and Bonding
To understand graphite's thermal performance, we must first look at how its carbon atoms are arranged. Its properties are a direct result of its internal structure.
Strong Covalent Bonds
Graphite consists of layers of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. Within each layer, every carbon atom is bonded to three others through strong covalent bonds. These are the same types of bonds found in diamond.
Breaking these bonds requires immense energy, which is why graphite does not melt at atmospheric pressure but instead sublimates (turns from a solid directly to a gas) at an extremely high temperature, around 3,650°C (6,600°F).
A Tale of Two Bonds
While the bonds within each layer are incredibly strong, the forces holding the layers together (van der Waals forces) are very weak. This is why layers can slide past each other, making graphite an excellent lubricant, but it is the strength within the layers that provides its thermal stability.
Resisting Thermal Shock: Beyond Just Temperature
Many materials can withstand high heat but will fracture when the temperature changes too quickly. This failure is called thermal shock. Graphite is exceptionally resistant to it.
Thermal shock occurs when different parts of a material expand or contract at different rates, creating internal stress that exceeds the material's strength.
Low Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
One of graphite's most important properties is its very low coefficient of thermal expansion. This means that when it gets hot, it expands very little.
Because it doesn't try to change its size drastically, it generates significantly less internal stress compared to materials like ceramics or metals during rapid heating or cooling.
High Thermal Conductivity
Graphite is an excellent thermal conductor. It efficiently moves heat throughout its structure, preventing the formation of "hot spots."
This ability to quickly even out the temperature across the material means there are no severe temperature gradients to cause differential expansion and stress in the first place.
High Strength and Flexibility
Despite being known as a soft material, graphite possesses high tensile strength, especially as temperatures increase. It can withstand the internal stresses that do manage to build up.
Furthermore, it has a low modulus of elasticity, meaning it isn't perfectly rigid or brittle. It has a slight amount of "give," allowing it to flex under thermal stress rather than shattering.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Role of Oxygen
No material is perfect, and graphite's primary weakness at high temperatures is its interaction with the environment.
Oxidation in Air
While graphite is exceptionally stable in a vacuum or inert atmosphere, its performance changes dramatically in the presence of oxygen.
Graphite will begin to oxidize, or burn, in air at temperatures starting around 500°C (932°F). This chemical reaction consumes the graphite, turning it into carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide gas.
The Need for Protective Environments
This limitation means that for ultra-high-temperature applications like furnace components or rocket nozzles, graphite must be used in a vacuum, an inert gas atmosphere (like argon), or be protected by a special anti-oxidation coating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When evaluating graphite, your operating environment is as important as the temperature itself.
- If your primary focus is stability in an inert environment: Graphite is one of the best materials available due to its extremely high sublimation point, which is a direct result of its strong covalent bonds.
- If your primary focus is surviving rapid heating and cooling cycles: Graphite's combination of low thermal expansion, high thermal conductivity, and good strength makes it exceptionally resistant to thermal shock.
- If you are operating in an oxygen-rich environment above 500°C: You must account for graphite's susceptibility to oxidation and either provide a protective atmosphere or choose a different material.
By understanding these distinct properties, you can effectively leverage graphite's incredible thermal strengths while respecting its environmental limitations.
Summary Table:
| Property | Why It Matters for Heat Resistance |
|---|---|
| Strong Covalent Bonds | Provides an extremely high sublimation point (~3,650°C). |
| Low Thermal Expansion | Minimizes internal stress during rapid temperature changes. |
| High Thermal Conductivity | Prevents hot spots by evenly distributing heat. |
| High Tensile Strength | Withstands internal thermal stresses, especially at high temperatures. |
Need a reliable thermal solution for your lab?
Graphite's unique properties make it ideal for high-temperature processes, but its performance depends on the right application and environment. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including graphite components designed for furnaces and other thermal systems. Our experts can help you select the right materials to enhance your lab's efficiency and safety.
Let's discuss your specific thermal challenges. Contact our team today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Bottom Discharge Graphitization Furnace for Carbon Materials
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is the thermal conductivity of graphite so high? Unlock Superior Heat Transfer with Its Unique Structure
- How is synthetic graphite manufactured? A Deep Dive into the High-Temperature Process
- Does heat affect graphite? The Crucial Role of Atmosphere in High-Temp Performance
- Is a graphite melting point high or low? Discover Its Extreme Thermal Resilience
- Is graphite affected by heat? Discover Its Remarkable Strength and Stability at High Temperatures


















