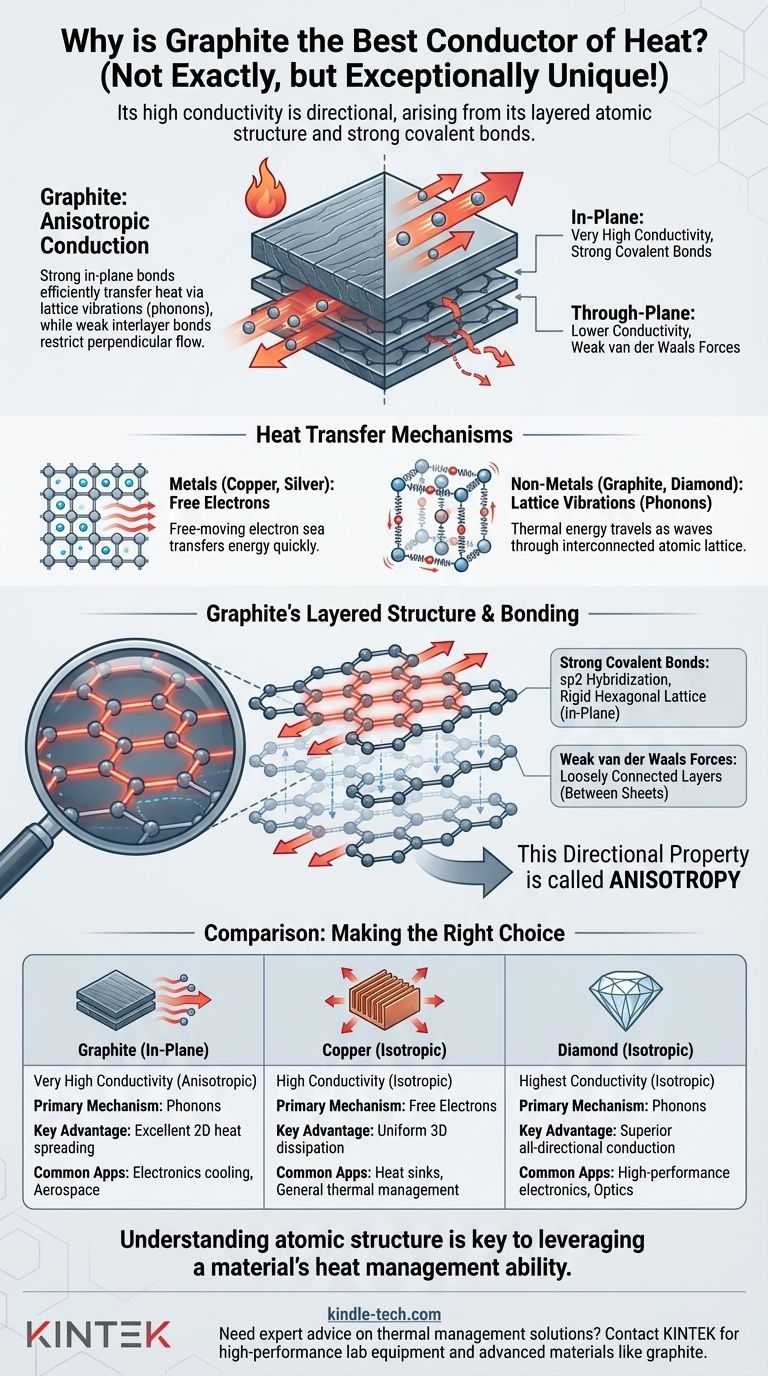
While an excellent thermal conductor, graphite is not actually the best. Its reputation comes from its unique ability to conduct heat exceptionally well in specific directions, often rivaling metals like copper. This high conductivity is a direct result of graphite's layered atomic structure and the strong chemical bonds within those layers.
Graphite's high thermal conductivity is not a simple fact, but a directional property. It arises from strong in-plane atomic bonds that efficiently transfer heat via lattice vibrations (phonons), while weak bonds between its layers restrict heat flow in the perpendicular direction. This directional behavior, known as anisotropy, is the key to understanding its thermal performance.

How Heat Moves Through a Solid
To understand graphite, we first need to understand the two primary mechanisms for heat transfer in a solid material.
The Role of Free Electrons
In metals like silver, copper, and aluminum, the outer electrons of the atoms are not tied to any single atom. They form a "sea" of free-moving electrons.
When one part of the metal is heated, these electrons gain kinetic energy and move rapidly, colliding with other electrons and atoms to quickly transfer that energy throughout the material. This is a highly efficient process, making metals excellent thermal conductors.
The Role of Lattice Vibrations (Phonons)
In non-metals like graphite and diamond, there are very few free electrons. Heat is transferred primarily through lattice vibrations.
Think of the atoms in a solid as being connected by springs. Heating one end makes the atoms there vibrate more intensely. These vibrations travel through the interconnected atomic lattice as waves, similar to a sound wave. These waves of thermal energy are called phonons. The stronger and more rigid the "springs" (atomic bonds), the more efficiently phonons can travel.
The Unique Structure of Graphite
Graphite’s thermal properties are a direct consequence of its atomic arrangement. It is an allotrope of carbon, meaning it has the same atoms as diamond but they are bonded together differently.
A Tale of Two Bonds: Strong vs. Weak
Graphite is composed of stacked sheets of carbon atoms. Each sheet is a one-atom-thick layer of what we now call graphene.
Within each sheet, every carbon atom is bonded to three others by extremely strong covalent bonds (sp2 hybridization). These bonds form a hexagonal lattice that is incredibly stiff and stable.
However, the bonds between these sheets are very weak van der Waals forces. The layers are not rigidly connected and can easily slide past one another, which is why graphite feels slippery and is used as a lubricant.
In-Plane vs. Through-Plane Conduction
This dual-bond structure creates two very different paths for heat.
When heat is applied along the plane of a graphene sheet (in-plane direction), the strong covalent bonds allow phonons to travel with extreme speed and minimal resistance. This results in exceptionally high thermal conductivity in that direction.
When heat must travel from one sheet to another (through-plane direction), it has to cross the weak van der Waals gap. Phonons do not transfer efficiently across this weak link, leading to much lower thermal conductivity—often 100 times lower than the in-plane value.
Anisotropy: The Defining Characteristic
This directional dependence of a property is called anisotropy. Graphite is highly anisotropic. It is a fantastic conductor in two dimensions (along the sheets) but a relatively poor conductor in the third dimension (between the sheets).
This is why a block of graphite will feel hot on one side almost instantly if you heat the other side, but it will take much longer for the top to get hot if you heat the bottom.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Graphite vs. Other Conductors
Correcting the initial premise, it's crucial to see where graphite stands in relation to other materials.
Comparison with Diamond
Diamond, another carbon allotrope, is the best known natural thermal conductor. Its carbon atoms are all connected by strong covalent bonds (sp3 hybridization) in a rigid, three-dimensional tetrahedral lattice.
There are no weak links. Phonons can travel with incredible efficiency in any direction. This makes diamond an isotropic conductor (uniform in all directions) and superior to graphite's best-case conductivity.
Comparison with Metals (Silver & Copper)
The best metallic conductors, like silver and copper, benefit from the highly efficient heat transfer of free electrons.
While the in-plane thermal conductivity of high-quality pyrolytic graphite can exceed that of copper, metals have the advantage of being isotropic. They conduct heat equally well in all directions, making them more predictable and suitable for applications where heat needs to dissipate uniformly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The choice of a thermal material depends entirely on the specific engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is one-directional heat spreading: High-purity pyrolytic graphite sheets are an exceptional choice for moving heat rapidly away from a source (like a CPU) along a single plane.
- If your primary focus is uniform, multi-directional heat dissipation: Isotropic materials like copper, aluminum, or diamond are superior for tasks where heat needs to be conducted away evenly in all directions.
- If your primary focus is balancing cost, weight, and performance: Aluminum and specialized graphite composites are often the go-to materials for general-purpose thermal management in electronics and aerospace.
Ultimately, understanding a material's atomic structure and bonding is the key to predicting and leveraging its ability to manage heat.
Summary Table:
| Property | Graphite (In-Plane) | Copper | Diamond |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Very High (Anisotropic) | High (Isotropic) | Highest (Isotropic) |
| Primary Mechanism | Lattice Vibrations (Phonons) | Free Electrons | Lattice Vibrations (Phonons) |
| Key Advantage | Excellent 2D heat spreading | Uniform 3D dissipation | Superior all-directional conduction |
| Common Applications | Electronics cooling, aerospace | Heat sinks, general thermal management | High-performance electronics, optics |
Need expert advice on thermal management solutions for your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including advanced materials like graphite for precise thermal control. Whether you're developing next-generation electronics or require reliable heat management in research, our team can help you select the ideal materials for your specific application. Contact us today to optimize your lab's thermal performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is graphite used for heat transfer? For Superior In-Plane Thermal Conductivity
- What are the disadvantages of using graphite? Key Limitations in High-Tech Applications
- At what temperature does graphite melt? Understanding Its Extreme Phase Change
- Why is the thermal conductivity of graphite so high? Unlock Superior Heat Transfer with Its Unique Structure
- Why graphite has high thermal conductivity? Unlock Superior Heat Management with Its Unique Structure



















