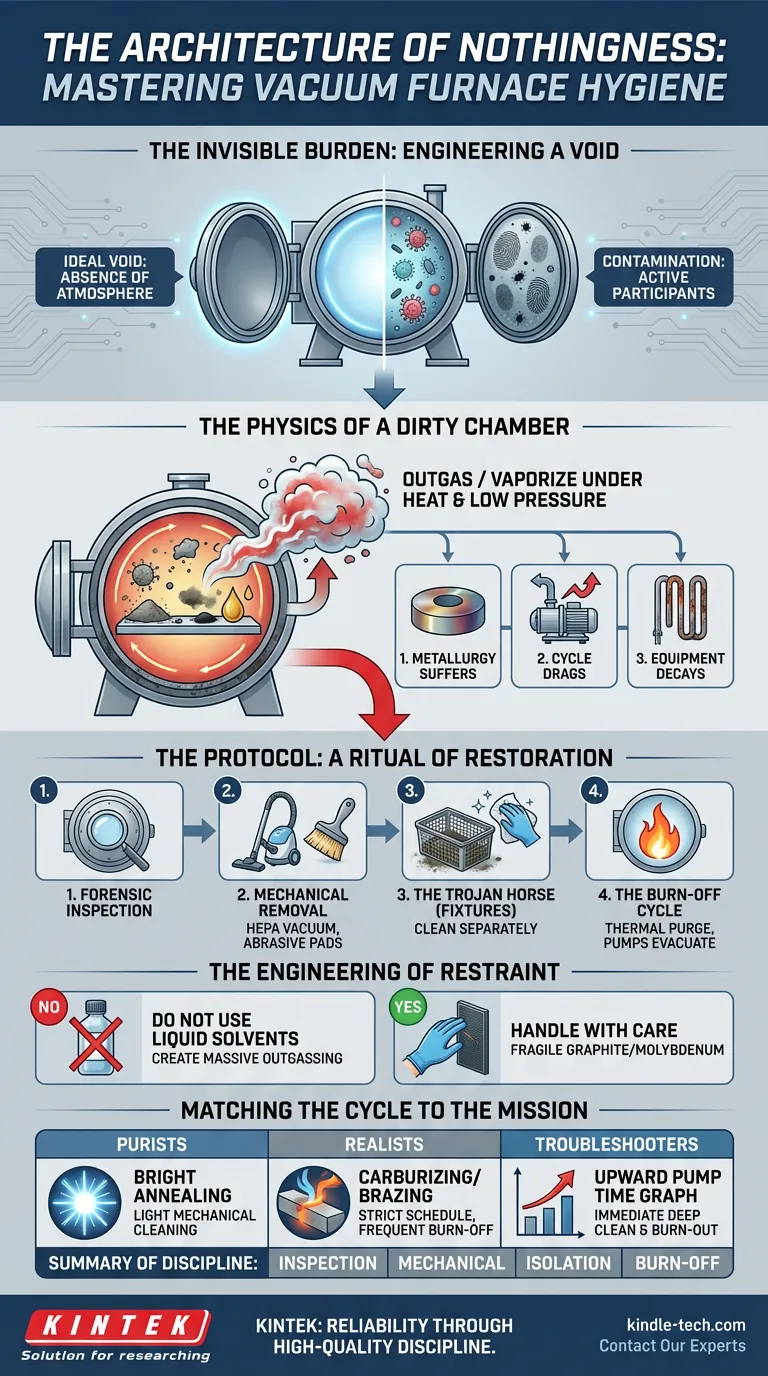
The Invisible Burden
In the world of thermal processing, "nothingness" is the most expensive commodity you buy.
When you operate a vacuum furnace, you are paying for the absence of atmosphere. You are engineering a void where chemistry can happen without interference.
But nature abhors a vacuum.
Every fingerprint, every speck of soot, and every drop of residual oil is not merely "dirt." In the high-temperature, low-pressure environment of a hot zone, these contaminants become active participants in your process. They are variables you didn't account for.
Cleaning a vacuum furnace is not about aesthetics. It is a battle against thermodynamics.
The Physics of a Dirty Chamber
We often think of contamination as static—dust sitting on a shelf.
Inside a vacuum furnace, contamination is dynamic.
When heat is applied under low pressure, residues do not just sit there. They outgas. They vaporize. Contaminants that are solid at room temperature turn into a chaotic cloud of vapor that your vacuum pumps must struggle to remove.
If the pumps lose that battle, three things happen:
- The Metallurgy Suffers: The vapor redeposits onto your pristine workpieces. This leads to discoloration, surface blemishes, or compromised structural integrity.
- The Cycle Drags: A dirty chamber has a higher "gas load." The pumps have to work harder and longer to reach the desired vacuum level, driving up energy costs and cycle times.
- The Equipment Decays: At high temperatures, certain contaminants become chemically aggressive. They attack the graphite insulation and metallic heating elements, leading to premature—and expensive—failure.
The Protocol: A Ritual of Restoration
Cleaning is a systematic discipline. It requires a methodical approach that prioritizes mechanical removal over chemical intervention.
Here is the blueprint for restoring the void.
1. The Forensic Inspection
The process begins only after the furnace has cooled and vented.
Open the door and look. You are looking for the story of the last few cycles. Is there soot from a dirty process? Are there oil films from improperly cleaned parts?
Identify the enemy before you attack it.
2. Mechanical Removal
This is the heavy lifting. Using a HEPA-filtered vacuum, remove loose dust and debris.
For adhered films, use soft, non-metallic brushes or abrasive pads (like Scotch-Brite™). The goal is to dislodge the contaminant without scarring the surface beneath it.
Work from the top down. Gravity is your ally here.
3. The Trojan Horse (Fixtures)
The grids and baskets that hold your parts are often the dirtiest items in the shop.
If you clean the chamber but ignore the fixtures, you are reintroducing contamination the moment you load the next batch. Remove these components and clean them aggressively outside the furnace. Isolate the mess.
4. The Burn-Off Cycle
Mechanical cleaning removes what you can see. The "Dry Run-Out" removes what you can't.
By running the empty furnace at high temperatures under vacuum, you force remaining microscopic oils and water vapor to vaporize. The pumps then evacuate this gas.
It is a thermal purge. It resets the baseline of the machine.
The Engineering of Restraint
How you clean is as important as the act itself. In our rush to solve problems, we often create new ones.
The Solvent Trap There is a temptation to use liquid solvents to wipe down the interior. Do not do this.
Solvents soak into porous insulation and microscopic crevices. During the next run, they will boil off, creating massive outgassing that can overwhelm your pumps and ruin the load.
The Fragility of Strength Graphite insulation and Molybdenum heating elements are incredibly capable at high temperatures, but they are brittle at room temperature.
A wire brush or a heavy hand can snap a heating element or gouge insulation. Treat the hot zone with the gentleness required by a surgical theater.
Matching the Cycle to the Mission
Not all processes require the same level of vigilance. Your maintenance schedule should reflect your reality.
- The Purists: If you run sensitive processes like bright annealing, you need a routine of light mechanical cleaning.
- The Realists: If you perform vacuum carburizing or braze oily parts, you are fighting a heavier war. You need a strict schedule involving frequent burn-off cycles.
- The Troubleshooters: If your pump-down times are drifting upward, stop immediately. A deep clean and burn-out is usually the cure.
Summary of Discipline
| Step | The Action | The Physics |
|---|---|---|
| Inspection | Visual check for soot/oil. | Identifying the gas load source. |
| Mechanical | HEPA vacuum and soft abrasion. | Physical removal of potential vapor. |
| Isolation | Cleaning fixtures separately. | Preventing cross-contamination. |
| Burn-Off | High-temp vacuum run (empty). | Thermodynamic vaporization of residue. |
The KINTEK Standard
Reliability is not an accident. It is the result of high-quality equipment maintained with high-quality discipline.
At KINTEK, we understand that your furnace is the heart of your production line. Whether you need robust lab equipment or the consumables to keep them running at peak efficiency, we provide the solutions that support scientific rigor.
Do not let contamination dictate your results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Bottom Discharge Graphitization Furnace for Carbon Materials
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
Related Articles
- Temperature Control Requirements for Laboratory Small High-Temperature Resistance Furnaces
- Maximizing Efficiency and Precision with Vacuum Graphite Furnaces
- Optimizing Performance with Graphite Vacuum Furnaces: A Comprehensive Guide
- Biomass Pyrolysis An Effective Means of Producing Biofuels
- Unveiling Vacuum Graphite Furnaces: Performance, Applications, and Expert Insights




















