Imagine this: you've spent weeks meticulously crafting a set of high-performance components from a specialty alloy. The heat-treatment cycle in your vacuum furnace runs perfectly—temperature, pressure, and duration are all precisely to spec. You pull the batch out, and it looks flawless.
But then, testing reveals a disaster. The parts are brittle. They fail quality control for microscopic contamination. They're completely unusable. All that time, effort, and expensive material have been wasted. And the most frustrating part? You have no idea why it happened.
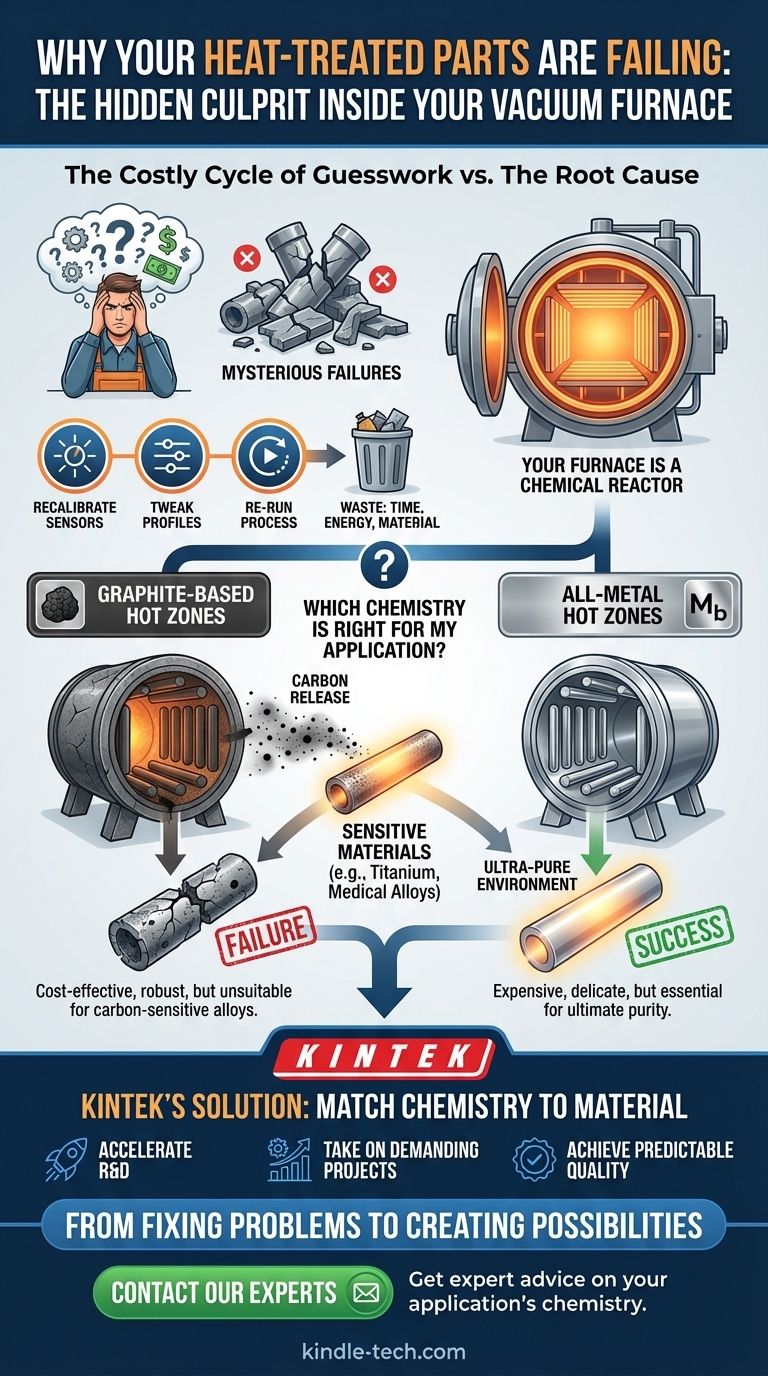
The Costly Cycle of Guesswork
If this scenario sounds familiar, you're not alone. When faced with these mysterious failures, most labs and engineering teams begin a frantic troubleshooting process.
- You recalibrate the temperature sensors.
- You tweak the heating and cooling profiles.
- You try to pull an even deeper vacuum.
- You re-run the process, hoping for a different outcome.
Each attempt consumes more energy, more time, and more material. Yet the results remain inconsistent. This isn't just a technical problem; it has serious business consequences. Project deadlines are missed, R&D budgets are exhausted by trial-and-error, and your reputation for delivering reliable, high-quality components is put at risk.
The reason these common fixes fail is that they are treating the symptoms, not the disease. The true source of the problem is often hidden in plain sight: the very materials your furnace is made of.
The Root Cause: Your Furnace Is a Chemical Reactor, Not Just an Oven
The fundamental mistake many make is thinking of a vacuum furnace as a simple, inert box that just gets hot. The reality is that at extreme temperatures, a vacuum furnace is an active chemical environment. The materials used to construct its internal "hot zone" can—and do—interact with the parts you are treating.
This is the core of the issue, and it boils down to one critical choice in furnace design.
Graphite vs. All-Metal: A Tale of Two Chemistries
Virtually all vacuum furnace hot zones are built using one of two material systems:
-
Graphite-Based Hot Zones: These are the industry workhorses. Made from graphite fiberboard and felt, they are robust, durable, and cost-effective. They are perfect for the vast majority of heat-treating processes for common steels and many other alloys. The catch? At high temperatures, graphite can release microscopic carbon particles. For most applications, this is harmless. But for certain materials—like titanium, medical-grade implants, or specific nickel superalloys—this carbon acts as a contaminant, embedding into the metal's structure and fundamentally altering its properties, often making it brittle.
-
All-Metal Hot Zones: Built from refractory metals like molybdenum or tungsten, these are the "cleanrooms" of the heat-treating world. These metals are incredibly stable at high temperatures and do not shed reactive particles. They create an ultra-pure environment. The catch? They are more delicate and significantly more expensive than graphite.
Your unexplained failures are not random. They are often the direct result of a chemical incompatibility: you are processing a carbon-sensitive material inside a graphite-based furnace. No amount of process tweaking can change this fundamental chemical reaction.
The Right Tool for the Right Chemistry
To permanently solve this problem, you don't need to become a master of trial-and-error. You need to make the right choice from the start by matching your furnace's internal chemistry to your material's needs.
The question isn't "which furnace is better?" but "which furnace chemistry is right for my application?"
This is where the design philosophy behind KINTEK's laboratory equipment becomes critical. We recognize that a furnace is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Our product line is built on a deep understanding of this material science.
- Our graphite-based vacuum furnaces are engineered for durability and efficiency, providing a cost-effective solution for general-purpose heat treating of steels and non-sensitive alloys.
- Our all-metal vacuum furnaces are designed to provide the ultimate in purity, ensuring that when you process reactive and sensitive materials like titanium or medical-grade alloys, the results are clean, uncontaminated, and perfectly meet specifications.
We've designed our equipment to be the embodiment of the solution. By offering both options, we empower you to select the right tool based on the underlying science, eliminating the risk of contamination from the very beginning.
From Fixing Problems to Creating Possibilities
When you eliminate the guesswork of material compatibility, you do more than just solve a frustrating problem. You unlock a new level of operational certainty and innovation.
- Accelerate R&D: Move confidently from material development to production-quality parts without the fear of mysterious contamination derailing your progress.
- Take on Demanding Projects: Pursue contracts in aerospace, medical devices, or advanced electronics, knowing you have the right equipment to handle materials with the strictest purity requirements.
- Achieve Predictable Quality: Scale up production with the assurance that every batch will meet the same exacting standards, dramatically improving yield and reducing waste.
Instead of spending your time diagnosing past failures, your team can focus on pushing the boundaries of what's possible.
Your projects involve unique materials and face specific challenges. A five-minute conversation about your application's chemistry can save you weeks of frustration and thousands of dollars in wasted resources. Let our specialists help you navigate the trade-offs and ensure your next heat treatment cycle is a success from the start. To get expert advice tailored to your needs, Contact Our Experts.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
Related Articles
- The Symphony of Silence: Molybdenum and the Architecture of the Vacuum Hot Zone
- Why Your Brazed Joints Are Inconsistent—And the Fix Isn't in the Furnace
- Your Vacuum Furnace Hits the Right Temperature, But Your Process Still Fails. Here’s Why.
- Your Furnace Hit the Right Temperature. So Why Are Your Parts Failing?
- The Art of Absence: Why Advanced Materials Demand Vacuum Furnaces




















