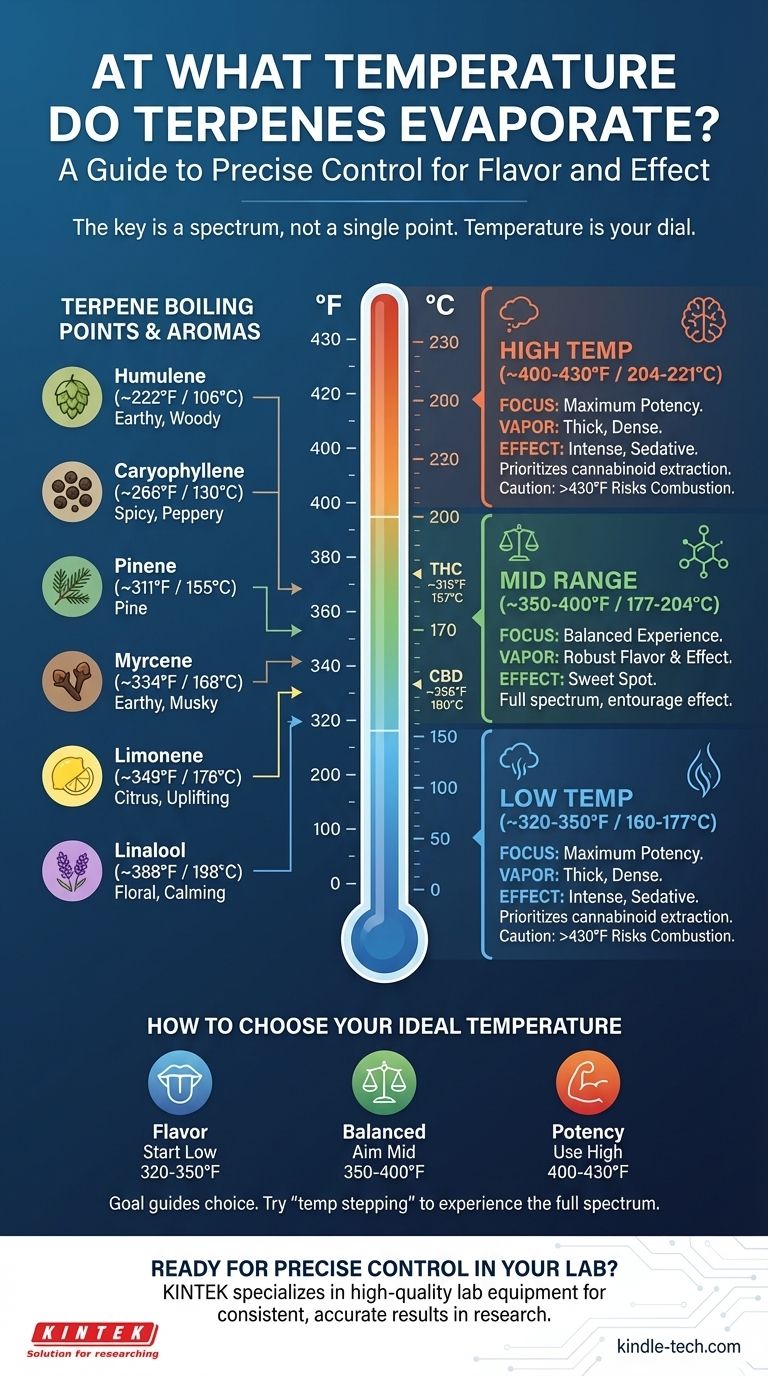
The short answer is there is no single temperature. Terpenes are a diverse class of aromatic compounds, and each one has a unique boiling point, beginning to evaporate at temperatures as low as 222°F (106°C). Most of the desirable terpenes in cannabis vaporize across a wide spectrum, generally between 310°F and 400°F (155°C and 204°C).
The core principle is not to find one "correct" temperature, but to understand that temperature is a dial you can use to control your experience. Lower temperatures preserve delicate flavors, while higher temperatures prioritize the activation of cannabinoids like THC and CBD.

Why Boiling Points Are the Key to Control
The temperature you choose directly dictates which compounds are released from your material and which are left behind or destroyed. This is the fundamental concept behind vaporization.
The Impact on Flavor
Terpenes are responsible for the distinct aromas and flavors of different cannabis strains—from the citrus notes of limonene to the piney scent of pinene. Many of the most volatile and flavorful terpenes have low boiling points, meaning they evaporate first.
If your temperature is too high, these delicate compounds are instantly vaporized or even destroyed, resulting in a harsh, generic "toasted" taste.
The Impact on Effect
Cannabinoids like THC and CBD also have their own boiling points (THC: ~315°F/157°C; CBD: ~356°F/180°C). Furthermore, terpenes work synergistically with cannabinoids in what is known as the entourage effect.
This theory suggests that terpenes can modulate the effects of cannabinoids. For example, the terpene linalool may enhance calming effects, while limonene might contribute to a more uplifting experience. By controlling temperature, you influence which combination of compounds you inhale, thereby tailoring the overall effect.
A Guide to Common Terpene Boiling Points
Below are the approximate boiling points for some of the most common terpenes found in cannabis. Remember that vaporization is a gradual process that begins well below the actual boiling point.
Humulene: ~222°F / 106°C
Known for its earthy, woody, and spicy notes, also found in hops.
Caryophyllene: ~266°F / 130°C
Delivers a spicy, peppery aroma and is the only known terpene that also acts as a cannabinoid.
Pinene: ~311°F / 155°C
This is the most common terpene in the natural world, offering a distinct pine aroma.
Myrcene: ~334°F / 168°C
Characterized by an earthy, musky, and slightly fruity scent, similar to cloves.
Limonene: ~349°F / 176°C
Provides the bright citrus aroma found in lemons, oranges, and juniper.
Linalool: ~388°F / 198°C
Best known for the floral scent of lavender, it is associated with calming and relaxing effects.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Low vs. High Temperatures
Choosing a temperature involves a direct trade-off between flavor and potency. There is no universally "best" setting; the ideal temperature depends entirely on your goal.
The Case for Low-Temperature Vaping (~320-350°F / 160-177°C)
At these lower settings, you primarily vaporize the terpenes with the lowest boiling points.
This range is ideal for maximizing flavor preservation. The vapor will be lighter and more aromatic, allowing you to experience the full, nuanced profile of the strain. The effects may feel more subtle and clear-headed.
The Case for Mid-Range Vaping (~350-400°F / 177-204°C)
This range is often considered the "sweet spot" for a balanced experience.
You vaporize a broader spectrum of terpenes while also fully activating key cannabinoids like THC and CBD. You get a good mix of robust flavor and noticeable effects, making it a popular all-around choice.
The Case for High-Temperature Vaping (~400-430°F / 204-221°C)
Pushing into higher temperatures prioritizes maximum cannabinoid extraction.
The vapor will be thicker and much denser, and the effects will be more pronounced and sedative. However, you will sacrifice almost all of the delicate terpene flavors, and the taste will be significantly less pleasant. Be cautious, as temperatures above this range risk combustion, which destroys many compounds and creates harmful byproducts.
How to Choose Your Ideal Temperature
Your goal should guide your choice. Start low and gradually increase the temperature during a session ("temp stepping") to experience the full spectrum of available compounds.
- If your primary focus is flavor: Begin in the 320-350°F (160-177°C) range to savor the most delicate aromatic notes.
- If your primary focus is a balanced effect: Aim for the 350-400°F (177-204°C) sweet spot for a comprehensive blend of flavor and cannabinoid activation.
- If your primary focus is maximum potency: Use a higher setting around 400-430°F (204-221°C), understanding that you will trade flavor for intensity.
Ultimately, precise temperature control empowers you to customize your experience to meet your exact needs.
Summary Table:
| Terpene | Boiling Point (°F / °C) | Common Aroma/Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Humulene | ~222°F / 106°C | Earthy, Woody |
| Caryophyllene | ~266°F / 130°C | Spicy, Peppery |
| Pinene | ~311°F / 155°C | Pine |
| Myrcene | ~334°F / 168°C | Earthy, Musky |
| Limonene | ~349°F / 176°C | Citrus, Uplifting |
| Linalool | ~388°F / 198°C | Floral, Calming |
Ready to achieve precise temperature control in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including reliable heating and vaporization tools essential for consistent and accurate results in cannabis research and analysis. Ensure the integrity of your terpene and cannabinoid profiles with our trusted solutions.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect equipment for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What is a rotary kiln reactor? A Guide to Industrial Thermal Processing
- What is the meaning of rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- What are the equipment for pyrolysis laboratory? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Research
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker



















