In principle, no. A hydraulic press cannot press anything. While its power is immense, it is ultimately a machine with finite limits defined by its design, the materials it is built from, and the laws of physics. Its ability to crush an object is a direct contest between the force it generates and the material's inherent strength.
The question is not whether a hydraulic press is powerful, but rather what defines its limits. Its capability is determined by a simple battle: the force generated by the press versus the compressive strength of the target object, all constrained by the structural integrity of the press itself.

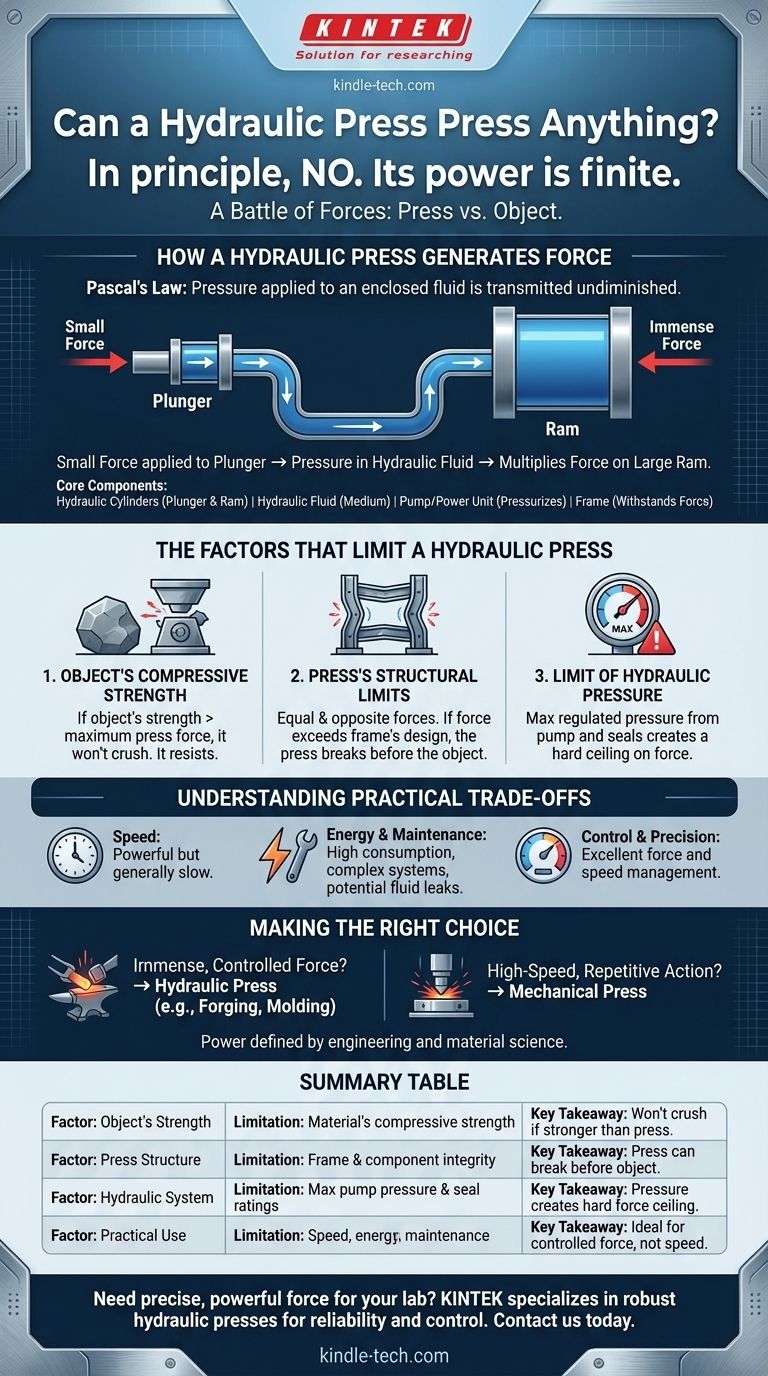
How a Hydraulic Press Generates Force
To understand a press's limits, we must first understand its power source. The entire mechanism is an application of a fundamental principle of fluid dynamics.
The Principle of Pascal's Law
A hydraulic press operates on Pascal's Law, which states that pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted undiminished to every portion of the fluid and the walls of the containing vessel.
The press uses two connected cylinders of different sizes: a small one called the plunger and a large one called the ram.
When a small amount of force is applied to the plunger, it creates pressure in the hydraulic fluid. This pressure is transmitted equally throughout the fluid, acting on the much larger surface area of the ram. This multiplies the initial force, generating the immense power the press is known for.
The Core Components
Several key components work together to achieve this force multiplication:
- Hydraulic Cylinders: The plunger and ram are the heart of the system, responsible for applying and multiplying the force.
- Hydraulic Fluid: This is the medium that transmits the pressure from the plunger to the ram. It must be incompressible to work effectively.
- Pump / Power Unit: This unit, often electric, is what initially pressurizes the hydraulic fluid, driving the entire operation.
- Frame: This is the steel skeleton of the press. Its sole job is to withstand the colossal forces being generated internally.
The Factors That Limit a Hydraulic Press
The fantasy of a press that can crush anything runs into three hard physical realities. An object will fail to be pressed if it can successfully challenge any of these limits.
1. The Object's Compressive Strength
Every material has an inherent compressive strength—the maximum pressure it can withstand before it deforms or breaks.
If the compressive strength of an object is greater than the maximum force the press can generate, the object will not be crushed. It will simply resist the force and remain intact.
2. The Press's Structural Limits
A hydraulic press generates equal and opposite forces. As the ram pushes down on the object, the object pushes back up on the ram with the same force.
This immense force is contained by the press's frame. If the force required to crush an object exceeds what the steel frame, cylinders, or seals are designed to handle, the press itself will fail—potentially catastrophically. The machine will break before the object does.
3. The Limit of Hydraulic Pressure
The system has a maximum regulated pressure. The hydraulic pump can only generate a certain amount of pressure, and the seals and hoses are only rated to contain that pressure.
Attempting to exceed this can cause fluid leaks or a complete failure of the hydraulic system. This regulated pressure creates a hard ceiling on the total force the ram can ultimately deliver.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
Beyond raw power, hydraulic presses have practical limitations that define their use in industrial and scientific settings.
Speed of Operation
Hydraulic presses are powerful but generally slow. Moving the large volume of fluid required to actuate the main ram takes time. For applications requiring high-speed repetition, a mechanical press is often a better choice.
Energy Consumption and Maintenance
Generating high hydraulic pressure consumes a significant amount of energy. Furthermore, these are complex systems that require regular maintenance. The potential for hydraulic fluid leaks is a constant concern, posing both an operational and an environmental risk.
Control and Precision
While limited in speed, a key advantage of hydraulic systems is their exceptional control. The force and speed can be precisely managed throughout the entire stroke, which is critical for technical applications like forming complex parts or preparing delicate lab samples.
Making the Right Choice for the Task
Understanding these limits is key to using a hydraulic press effectively. It is not an unstoppable force but a highly specialized tool for applying controlled, immense pressure.
- If your primary focus is applying immense, controlled force: A hydraulic press is the ideal tool for tasks like forging metal, molding plastics, or pressing material samples where raw power and precision are paramount.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, repetitive action: A mechanical press is likely a better solution, as it sacrifices some force and control for much faster cycle times.
Ultimately, a hydraulic press is a powerful instrument, but its power is defined and contained by the principles of engineering and material science.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Limitation | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| Object's Strength | Material's compressive strength | Object won't crush if it's stronger than the press's force. |
| Press Structure | Frame and component integrity | The press can break before the object does. |
| Hydraulic System | Maximum pump pressure and seal ratings | System pressure creates a hard ceiling on force. |
| Practical Use | Speed, energy consumption, maintenance | Ideal for controlled force, not high-speed repetition. |
Need precise, powerful force for your lab or production line?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust laboratory equipment, including hydraulic presses designed for reliability and precise control. Whether you're molding materials, preparing samples, or conducting research, our solutions are engineered to meet your specific needs while operating safely within their designed limits.
Let our experts help you select the perfect press for your application. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover the KINTEK difference in performance and support.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- 30T 40T Split Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability
- What is the advantage of KBr? Unmatched IR Transparency for Precise Spectroscopy
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy



















