Yes, you can both solder and braze stainless steel, but it requires a specific approach that differs from joining mild steel. The key to a successful joint is not the process itself, but how you prepare the surface and manage the environment to overcome the material's inherent properties.
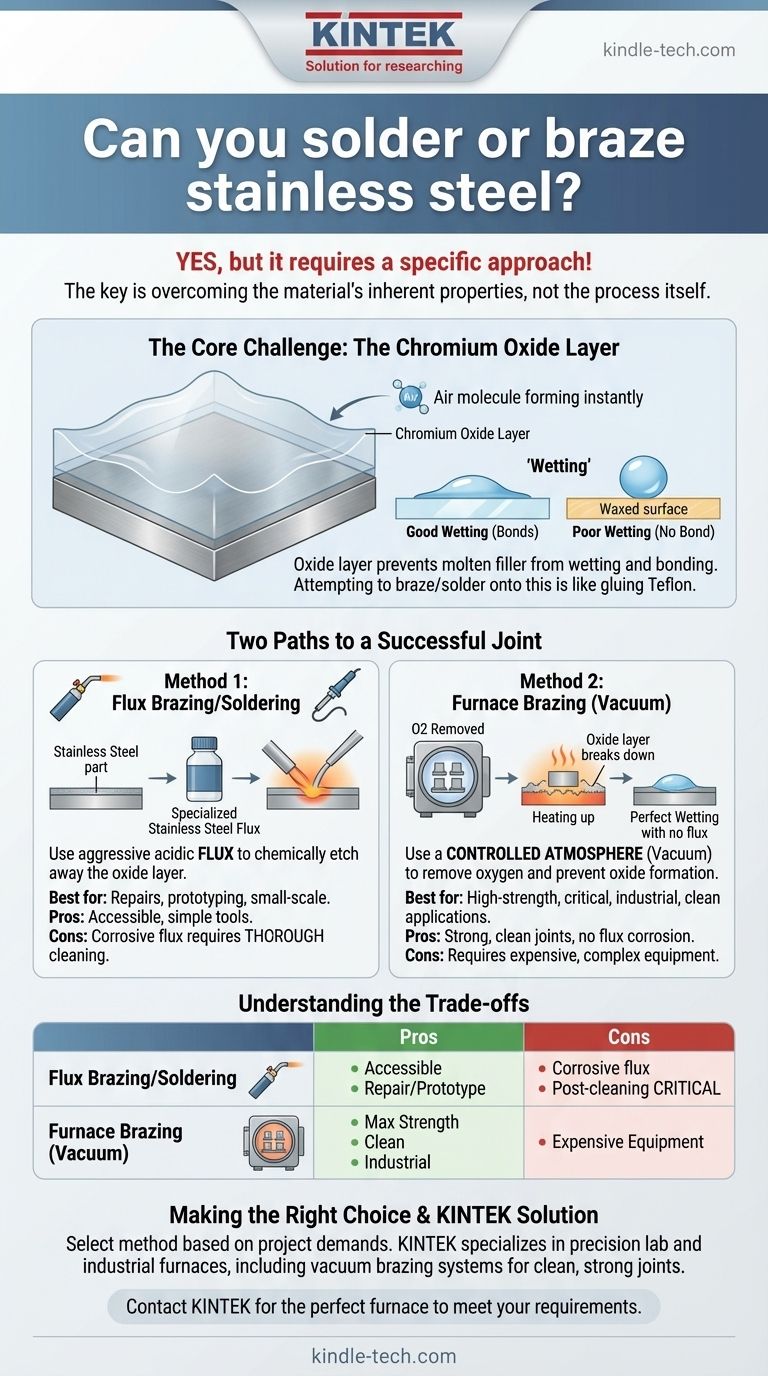
The core challenge in joining stainless steel is its protective chromium oxide layer. This invisible, self-healing skin grants the metal its corrosion resistance but also acts as a barrier that prevents solder or brazing filler from bonding to the base metal. A successful joint is only possible if this oxide layer is either chemically removed or prevented from forming during the heating process.
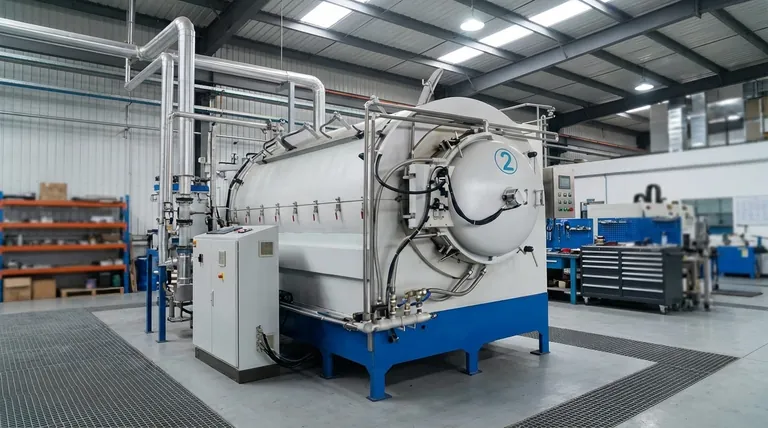

The Core Challenge: The Chromium Oxide Layer
Stainless steel's defining characteristic is its resistance to rust and corrosion. This property comes from a thin, transparent, and incredibly tenacious layer of chromium oxide that forms instantly on its surface when exposed to air.
What is 'Wetting'?
For a strong brazed or soldered joint, the molten filler metal must "wet" the surfaces of the parts being joined. Wetting is the ability of a liquid to flow over and adhere to a solid surface, similar to how water spreads across clean glass instead of beading up on a waxed car.
Why the Oxide Layer Prevents Wetting
This passive oxide layer is non-metallic and acts like a barrier. The molten filler metal cannot wet or bond with the oxide; it can only bond with the pure stainless steel underneath. Attempting to braze or solder onto this layer is like trying to glue two pieces of Teflon together—the adhesive simply won't stick.
Two Paths to a Successful Joint
To achieve a strong bond, you must defeat the chromium oxide layer. There are two primary strategies for this: using an active chemical flux or controlling the atmosphere itself.
Method 1: Chemical Removal with Flux
For soldering and torch brazing, the solution is to use a flux. However, the standard fluxes used for copper or mild steel are not aggressive enough.
You must use a specialized flux designed for stainless steel. This is typically a more active, acidic compound that chemically etches away the oxide layer as the part is heated, exposing the pure metal beneath for the filler to wet.
Method 2: Atmospheric Control with Furnace Brazing
For the highest-strength and cleanest joints, industrial processes use a controlled atmosphere. The most common of these is vacuum brazing.
By heating the parts in a high-vacuum furnace, virtually all oxygen is removed from the environment. This not only prevents the oxide layer from re-forming as the steel heats up but can also cause the existing oxide layer to break down, allowing for perfect wetting without any flux.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right method depends entirely on your application, required joint strength, and available equipment. Neither method is universally superior; they serve different needs.
Flux Brazing/Soldering: Pros and Cons
This is the more accessible method, suitable for repairs, prototyping, and small-scale work. It can be done with a simple torch.
The major drawback is the corrosive nature of the flux. After joining, it is absolutely critical to thoroughly clean all residual flux from the joint. If left behind, it will attack the stainless steel and cause severe corrosion and potential joint failure.
Furnace Brazing (Vacuum): Pros and Cons
This method produces exceptionally strong, clean, and aesthetically perfect joints with no risk of flux corrosion. It is the preferred method for critical applications in aerospace, medical, and high-performance industries.
The obvious limitation is equipment. Vacuum furnaces are complex, expensive industrial machines, placing this method outside the reach of most hobbyists or small shops.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your joining method based on the demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is a small-scale repair or non-structural application: Use a torch with a specialized stainless steel flux for either soldering or brazing, and prioritize meticulous post-braze cleaning.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength, cleanliness, and repeatability for a commercial product: Furnace brazing, particularly vacuum brazing, is the definitive and superior industrial process.
Ultimately, successfully joining stainless steel is a matter of respecting its unique chemistry and choosing the right tool to manage its protective oxide layer.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Requirement | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Flux Brazing/Soldering | Specialized stainless steel flux & thorough cleaning | Repairs, prototyping, small-scale, non-structural work |
| Furnace Brazing (Vacuum) | Controlled, oxygen-free atmosphere (vacuum furnace) | High-strength, critical, clean, industrial applications |
Need a reliable brazing solution for your stainless steel components? The right equipment is critical for success. KINTEK specializes in precision lab and industrial furnaces, including vacuum brazing systems that deliver clean, strong, and flux-free joints. Our experts can help you select the perfect furnace to meet your project's strength and cleanliness requirements. Contact our team today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK can enhance your joining process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is the basic of brazing? A Guide to Strong, Low-Heat Metal Joining
- Can you braze two different metals? Yes, and here’s how to do it successfully.
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- What is the most important factor influencing the strength of the brazed joint? Master Joint Clearance for Maximum Strength
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing



















