Yes, induction heating is powered entirely by electricity. While it uses electromagnetic principles like radio frequency (RF) energy to generate heat, the entire process begins with and is sustained by an electrical current from a standard power source. The technology simply converts electrical energy into heat in a fundamentally different and more direct way than a traditional electric stove.
Induction heating does not "burn" electricity to create warmth. Instead, it uses electricity to generate a magnetic field that turns your cookware into its own heat source, resulting in a highly efficient and precise method of heating.

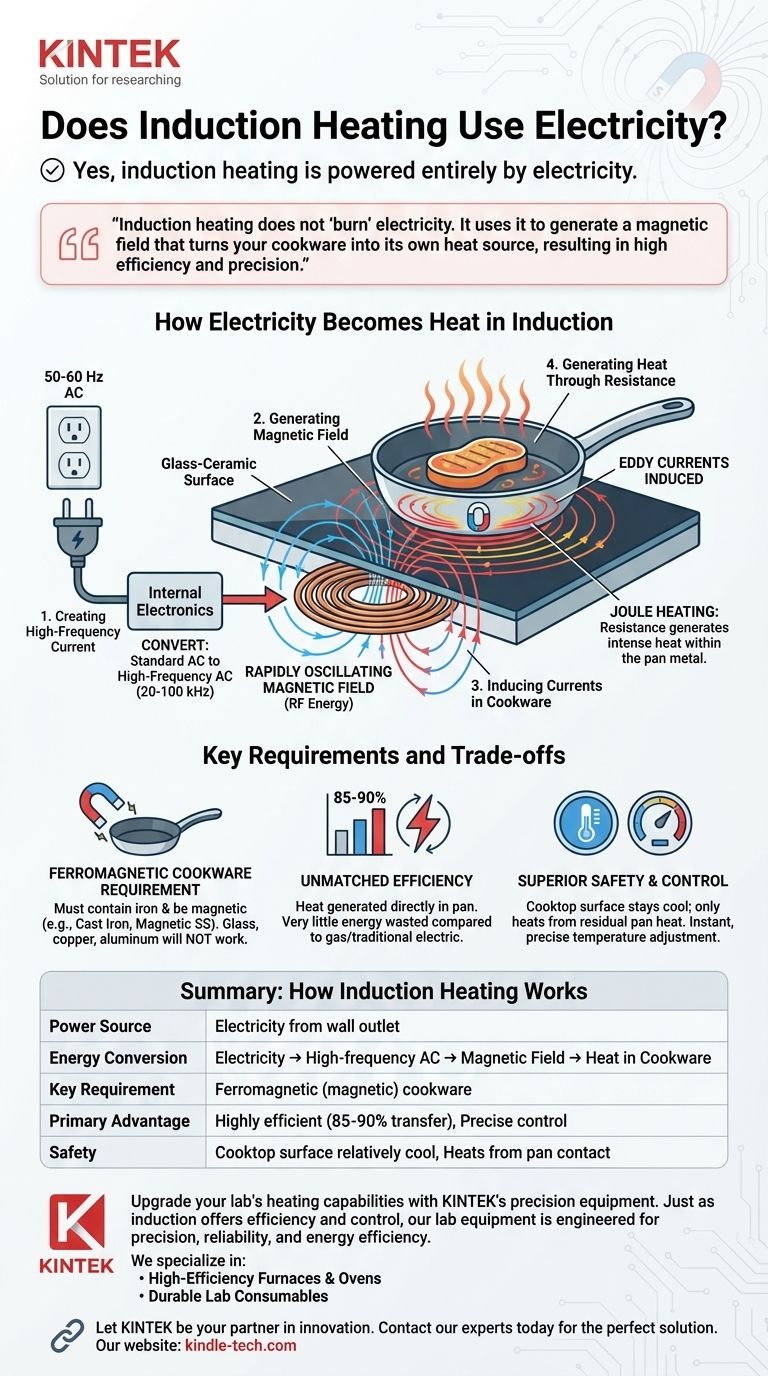
How Electricity Becomes Heat in Induction
Induction cooking is a fascinating process of energy conversion. The electricity from your wall outlet doesn't heat a resistive element; it powers a system that creates a magnetic field.
Step 1: Creating a High-Frequency Current
An induction cooktop contains a coil of copper wire beneath its ceramic or glass surface. When you turn the unit on, electricity flows into this coil.
Internal electronics then convert the standard alternating current (AC) from your outlet (typically 50-60 Hz) into a much higher-frequency AC, often in the range of 20-100 kHz.
Step 2: Generating a Magnetic Field
This high-frequency alternating current running through the copper coil generates a powerful, rapidly oscillating magnetic field. This field is a form of radio frequency (RF) energy, a part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
This magnetic field extends a few millimeters above the cooktop surface, right where your pot or pan sits.
Step 3: Inducing Currents in the Cookware
When you place a pan made of a magnetic material (like cast iron or magnetic stainless steel) onto the cooktop, the magnetic field passes through its base.
This rapidly changing field induces small, swirling electrical currents directly within the metal of the pan. These are known as eddy currents.
Step 4: Generating Heat Through Resistance
The metal in your pan has natural electrical resistance. As the induced eddy currents flow against this resistance, they generate significant friction and, consequently, immense heat.
This effect, known as Joule heating, is what cooks your food. The pan itself becomes the source of the heat, not the cooktop surface.
Understanding the Key Requirements and Trade-offs
The physics ऑब्जेक्टिव induction dictates its primary advantages and limitations. Understanding these is key to using the technology effectively.
The Ferromagnetic Cookware Requirement
Induction only works with cookware that is ferromagnetic (i.e., contains iron and is magnetic).
Materials like glass, copper, or aluminum are not magnetic and will not heat up on an induction cooktop because the magnetic field cannot induce sufficient eddy currents within them. You can test your cookware with a simple refrigerator magnet; if it sticks firmly to the bottom, the pan will work.
Unmatched Efficiency
Because heat is generated directly in the pan, very little energy is wasted. Around 85-90% of the electrical energy is converted directly into heat in the pan.
In contrast, traditional electric cooktops lose significant heat to the surrounding air and the cooktop itself, and gas ranges lose even more heat around the sides of the pot.
Superior Safety and Control
The cooktop surface does not get hot on its own; it only warms up from residual heat transferred back from the pan. This makes it much safer than a glowing-hot electric or gas burner.
The magnetic field can be adjusted or shut off instantly, giving you incredibly precise and rapid control over the cooking temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding if induction is right for you depends on what you value most in a cooking experience.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and lower utility bills: Induction is the most efficient cooking technology available, transferring more energy directly to your food than gas or traditional electric.
- If your primary focus is speed and precise control: Induction offers the fastest heating and the most responsive temperature adjustments, allowing for rapid boils and immediate simmers.
- If your primary focus is compatibility with all cookware: You must be prepared to invest in new, induction-ready pots and pans if your current set is made of glass, copper, or non-magnetic aluminum.
Ultimately, understanding induction heating is about recognizing it as a clever transformation of electrical energy, not the absence of it.
Summary Table:
| Feature | How Induction Heating Works |
|---|---|
| Power Source | Electricity from a standard wall outlet |
| Energy Conversion | Electricity → High-frequency AC → Magnetic Field → Heat in Cookware |
| Key Requirement | Cookware must be ferromagnetic (magnetic) |
| Primary Advantage | Highly efficient (85-90% energy transfer) and precise temperature control |
| Safety | Cooktop surface stays relatively cool; only heats from contact with the pan |
Upgrade your lab's heating capabilities with KINTEK's precision equipment.
Just as induction heating offers superior control and efficiency in the kitchen, KINTEK's advanced lab equipment is engineered for precision, reliability, and energy efficiency in your laboratory workflows. Whether you need precise temperature control for reactions or efficient sample preparation, our products are designed to meet the rigorous demands of modern research.
We specialize in serving laboratories with:
- High-Efficiency Furnaces & Ovens: For precise thermal processing.
- Durable Lab Consumables: Ensuring consistent and reliable results.
Let KINTEK be your partner in innovation. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your specific application and experience the KINTEK difference in quality and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace over HIP? Optimize Fiber-Foil Composite Production
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace play in the fabrication of CuCrFeMnNi alloys? Achieve High Purity
- What is the core role of a vacuum hot press furnace in composites? Master Precision Bonding and Densification
- How does the mechanical pressure from a vacuum hot-pressing furnace facilitate the densification of B4C/Al composites?
- Why is the vacuum system of a Vacuum Hot Pressing furnace critical for ODS ferritic stainless steel performance?



















