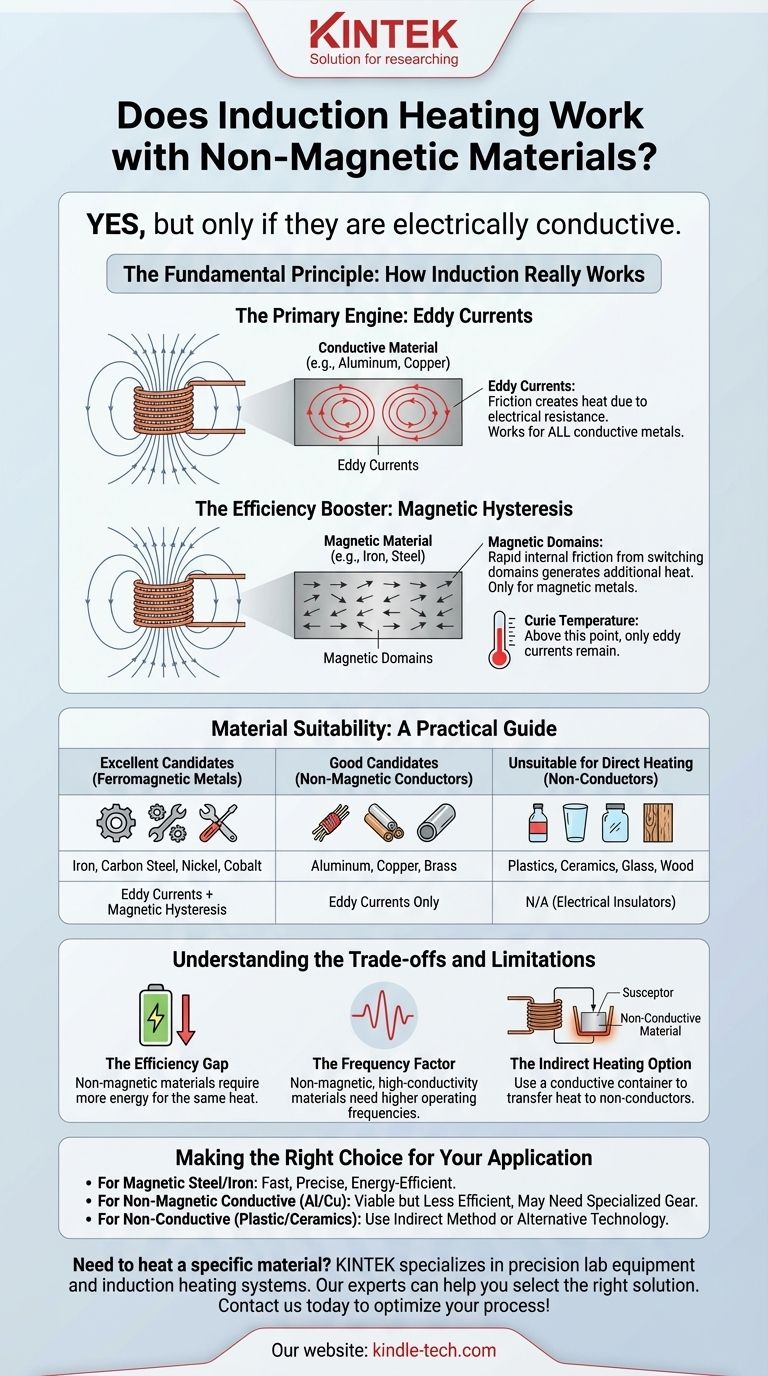
Yes, induction heating works with non-magnetic materials, but only if they are electrically conductive. The core requirement for direct induction heating is not magnetism, but the ability to conduct electricity. Materials like aluminum, copper, and brass can all be heated effectively, though the process is slightly different and often less efficient than with magnetic metals like iron and steel.
The critical factor for induction heating is electrical conductivity, which allows for the generation of internal heat through eddy currents. While magnetism dramatically increases heating efficiency through a secondary effect, it is not a prerequisite for the process to work.
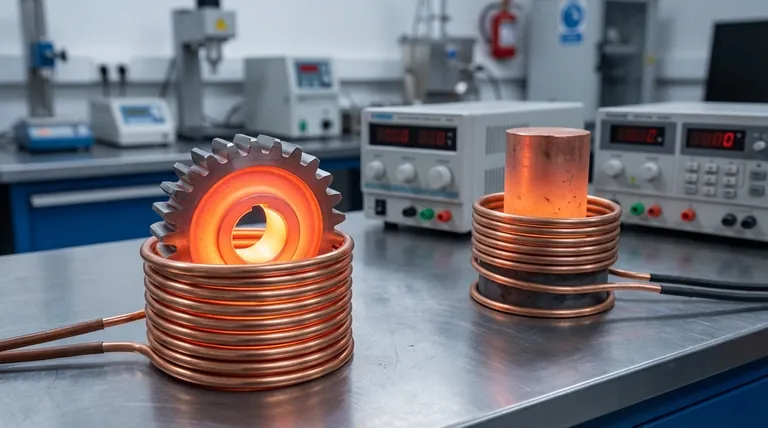

The Fundamental Principle: How Induction Really Works
To understand which materials are suitable, you must first understand the two distinct heating effects generated by an induction coil: eddy currents and magnetic hysteresis.
The Primary Engine: Eddy Currents
An induction heater generates a powerful, rapidly alternating magnetic field. When an electrically conductive material is placed within this field, small, circular electrical currents—known as eddy currents—are induced within the material.
Because every material has some electrical resistance, the flow of these eddy currents generates friction and thus, heat. This is the primary mechanism that heats all conductive metals, whether they are magnetic or not.
The Efficiency Booster: Magnetic Hysteresis
This second effect occurs only in magnetic materials like iron and steel. These materials are composed of small magnetic regions called domains.
The rapidly switching magnetic field forces these domains to flip their alignment back and forth millions of times per second. This rapid internal friction generates a significant amount of additional heat, making the induction process much faster and more energy-efficient for magnetic metals.
This effect ceases once the material reaches its Curie temperature, the point at which it loses its magnetic properties. Above this temperature, all further heating is done only by eddy currents.
Material Suitability: A Practical Guide
The performance of induction heating is directly tied to a material's electrical conductivity and its magnetic properties.
Excellent Candidates (Ferromagnetic Metals)
Materials like iron, carbon steel, nickel, and cobalt are ideal for induction heating. They benefit from the powerful combination of both eddy currents and magnetic hysteresis, resulting in rapid and highly efficient heating.
Good Candidates (Non-Magnetic Conductors)
This category includes materials like aluminum, copper, and brass. They are not magnetic, so they are heated solely by the eddy current effect.
While the process is effective, it is generally less energy-efficient than with ferromagnetic materials. It often requires higher frequencies or more power to achieve the same heating rate.
Unsuitable for Direct Heating (Non-Conductors)
Materials such as plastics, ceramics, glass, and wood cannot be heated directly with induction. They are electrical insulators, meaning eddy currents cannot be induced within them.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Choosing to use induction heating, especially for non-magnetic materials, involves clear trade-offs.
The Efficiency Gap
Heating a non-magnetic material like aluminum will always require more energy to reach the same temperature as an identically shaped piece of steel. The absence of the hysteresis effect is a significant factor in overall wall-plug efficiency.
The Frequency Factor
A material's resistance and skin effect determine how effectively eddy currents are generated. Non-magnetic materials with high conductivity (like copper) often require much higher operating frequencies to heat efficiently, which can impact the cost and complexity of the required induction equipment.
The Indirect Heating Option
For non-conductive materials like plastics, an indirect method is possible. A conductive container or element (called a susceptor) is heated by the induction coil, and this heat is then transferred to the non-conductive material via conduction or radiation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if induction is the right technology, evaluate your specific material and goals.
- If your primary focus is heating magnetic steel or iron: Induction is an exceptionally fast, precise, and energy-efficient choice for your application.
- If your primary focus is heating non-magnetic but conductive materials like aluminum or copper: Induction is a perfectly viable method, but you must account for lower energy efficiency and potentially specialized higher-frequency equipment.
- If your primary focus is heating non-conductive materials like plastic or ceramics: Direct induction will not work; you must either use an indirect heating method with a susceptor or choose an alternative technology like resistance or infrared heating.
Ultimately, understanding the distinction between conductivity and magnetism is the key to successfully applying induction technology to your specific challenge.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Induction Heating Suitability | Key Heating Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic & Conductive (e.g., Steel) | Excellent | Eddy Currents + Magnetic Hysteresis |
| Non-Magnetic & Conductive (e.g., Aluminum, Copper) | Good | Eddy Currents Only |
| Non-Conductive (e.g., Plastics, Ceramics) | Not Suitable (Directly) | N/A |
Need to heat a specific material? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment, including induction heating systems tailored for both magnetic and non-magnetic conductive materials. Our experts can help you select the right solution for efficient and controlled heating in your laboratory. Contact us today to discuss your application and optimize your process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Aluminum Oxide Al2O3 Heat Sink for Insulation
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
People Also Ask
- What is silicon carbide rod heated to high temperature used as? A Premier Heating Element for Extreme Environments
- What is the maximum temperature for a SiC heating element? Unlock the Key to Longevity and Performance
- What is a silicon carbide heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat for Industrial Processes
- What kind of metal is used in heating elements? A Guide to Materials for Every Temperature & Atmosphere
- What is SiC elements? The Ultimate High-Temperature Heating Solution



















