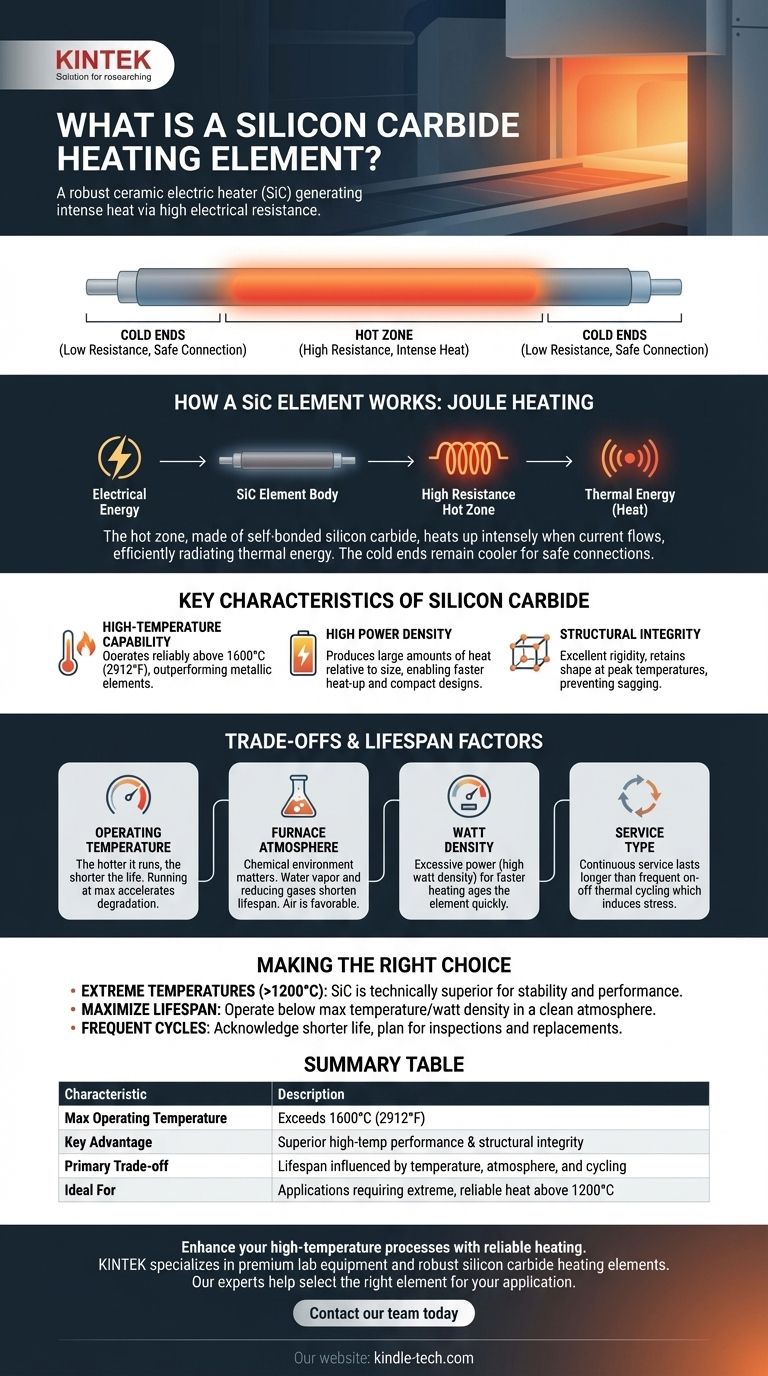
At its core, a silicon carbide (SiC) heating element is a high-performance electric heater made from a robust ceramic compound. It functions by passing an electric current through its body, which has high electrical resistance, thereby generating intense heat. Its unique construction features a central high-resistance "hot zone" for heat generation and two lower-resistance "cold ends" that allow for safe connection to a power supply outside the heated chamber.
While renowned for their ability to reach extremely high temperatures, the true value of a silicon carbide heating element lies in its durability and predictable performance, which are directly tied to how well its operating environment is managed.

How a SiC Element Works: The Principle of Resistance
A SiC element operates on the simple principle of Joule heating, where electrical energy is converted into thermal energy. However, its sophisticated design optimizes this process for industrial high-temperature applications.
The Hot Zone: The Engine of Heat
The central section of the element, the hot zone, is made of self-bonded silicon carbide. This material is engineered to have high electrical resistance.
When current flows through this section, the resistance causes it to heat up intensely, efficiently radiating thermal energy into the furnace or kiln.
The Cold Ends: The Critical Connection
The terminal sections, or cold ends, are infused with silicon metal or other materials to dramatically lower their electrical resistance compared to the hot zone.
This design ensures that the ends remain significantly cooler, allowing for safe and reliable electrical connections without overheating the terminals or the furnace walls they pass through.
Key Characteristics of Silicon Carbide
SiC elements are chosen over other types, like standard metallic elements, for a specific set of demanding characteristics.
High-Temperature Capability
The primary advantage of SiC is its ability to operate reliably at very high temperatures, often exceeding 1600°C (2912°F), where most metallic elements would fail.
High Power Density
SiC elements can be "watt loaded" to a high degree, meaning they can produce a large amount of heat relative to their size. This enables faster furnace heat-up times and more compact designs.
Structural Integrity
As a ceramic material, silicon carbide possesses excellent rigidity and retains its shape even at peak temperatures, preventing the sagging that can occur with metallic elements over time.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Lifespan Factors
The longevity of a SiC heating element is not infinite. It is a consumable component whose life is determined by a clear set of trade-offs and operating conditions.
The Impact of Operating Temperature
The relationship is simple: the hotter you run the element, the shorter its life will be. Operating an element consistently at its maximum rated temperature will accelerate its degradation.
The Influence of Furnace Atmosphere
The chemical environment inside the furnace is critical. Certain atmospheres, particularly those with water vapor or specific reducing gases, can react with the silicon carbide and shorten its lifespan. Air is generally a favorable atmosphere.
The Effect of Watt Density
Pushing excessive power through an element (high watt density) to achieve faster heating will cause it to age and fail more quickly. Proper engineering involves balancing heat-up requirements with element longevity.
Continuous vs. Intermittent Service
Thermal cycling—the process of repeatedly heating up and cooling down—induces stress on the element. An element in continuous service at a stable temperature will typically last much longer than one used intermittently.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting and operating a SiC element requires balancing performance goals with operational realities.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures (above 1200°C): A SiC element is the technically superior choice over conventional metallic elements for its stability and performance.
- If your primary focus is maximizing element lifespan: Operate the elements below their maximum rated temperature and watt density while ensuring a clean, compatible furnace atmosphere.
- If your application involves frequent on-off cycles: Acknowledge that this constitutes intermittent service and plan for a shorter element life and more frequent inspections or replacements.
Ultimately, understanding these core principles is the key to harnessing the power of silicon carbide elements effectively and economically.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Max Operating Temperature | Exceeds 1600°C (2912°F) |
| Key Advantage | Superior high-temperature performance & structural integrity |
| Primary Trade-off | Lifespan is influenced by temperature, atmosphere, and cycling |
| Ideal For | Applications requiring extreme, reliable heat above 1200°C |
Ready to enhance your high-temperature processes with reliable, durable heating?
KINTEK specializes in premium lab equipment and consumables, including robust silicon carbide heating elements designed for demanding laboratory and industrial environments. Our experts can help you select the right element to maximize performance and longevity for your specific application, whether it's continuous high-temperature operation or complex thermal cycling.
Contact our team today to discuss your heating needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can bring efficiency and reliability to your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are silicon carbide heating elements used for? Reliable High-Temp Heating for Industrial Processes
- What is silicon carbide rod heated to high temperature used as? A Premier Heating Element for Extreme Environments
- What is SiC elements? The Ultimate High-Temperature Heating Solution
- What is SiC melting point? Discover the Extreme Thermal Stability of Silicon Carbide
- What are the uses of silicon carbide rod? The Ultimate Heating Solution for Extreme Temperatures



















