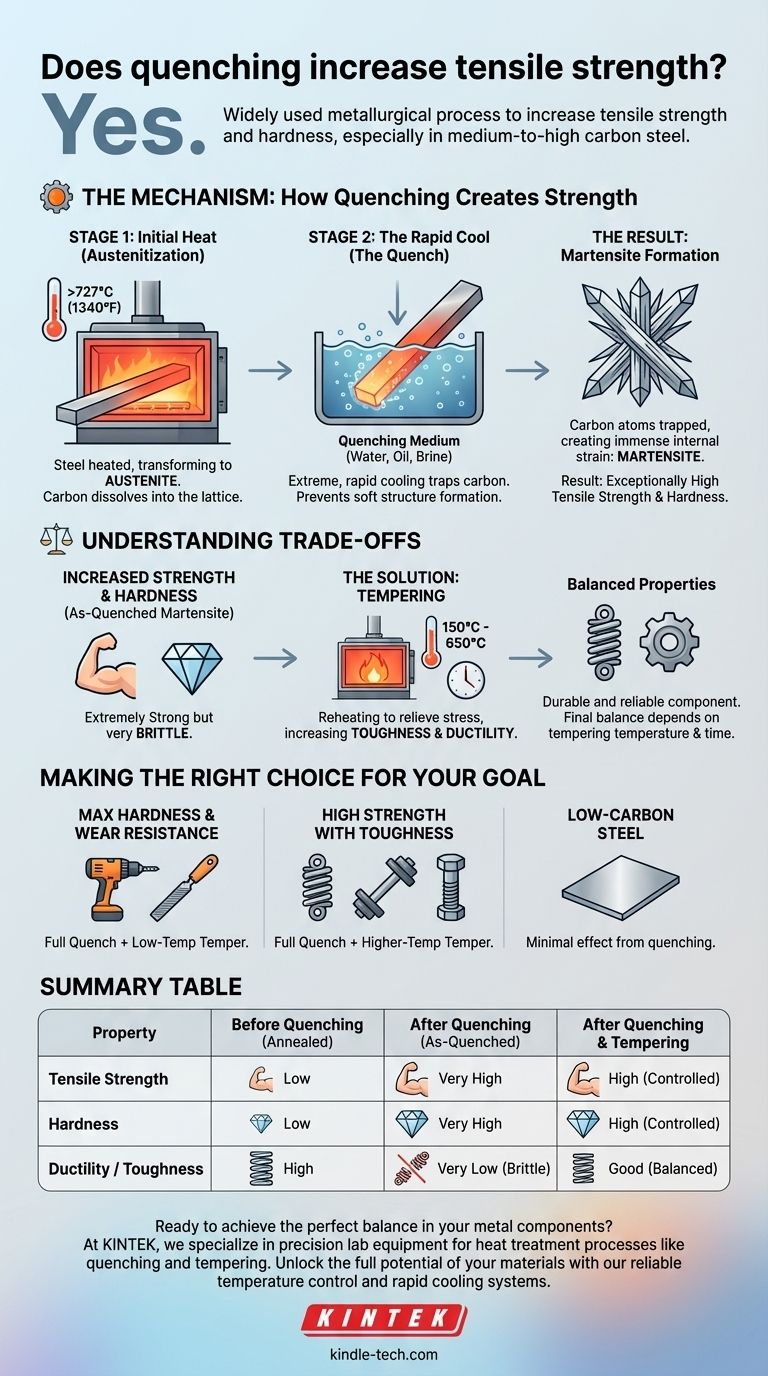
Yes, quenching is a widely used metallurgical process specifically designed to increase the tensile strength and hardness of certain metals, most notably medium-to-high carbon steel. The rapid cooling forces the material's internal crystal structure into a highly strained state called martensite, which is exceptionally hard and strong.
The core principle is that quenching sacrifices ductility to achieve a dramatic increase in strength. This is accomplished by rapidly cooling a metal from a high temperature, trapping its atomic structure in a hard but brittle configuration known as martensite.
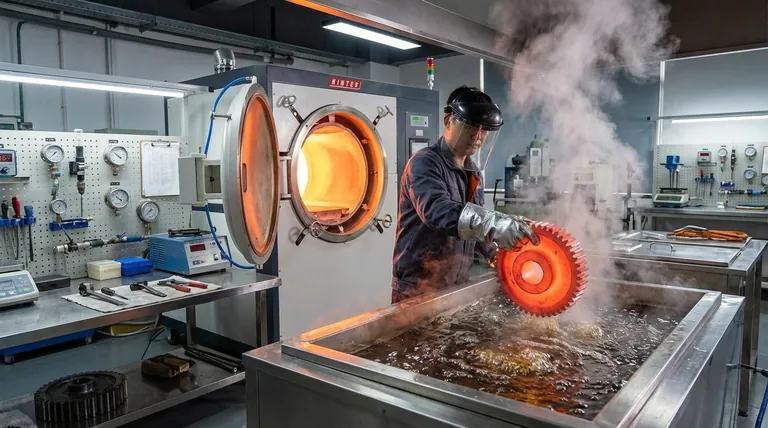

The Mechanism: How Quenching Creates Strength
To understand why quenching works, you must first understand the journey of the metal's internal structure during the process. It's a two-stage transformation.
Stage 1: The Initial Heat (Austenitization)
Before quenching, steel is first heated to a specific high temperature, typically above 727°C (1340°F).
At this temperature, the steel's crystal structure transforms into a phase called austenite. Austenite has a unique ability to dissolve carbon atoms within its lattice.
Properly heating the material is critical. A higher temperature ensures all the carbon is fully dissolved, setting the stage for the maximum possible increase in strength during the quench.
Stage 2: The Rapid Cool (The Quench)
Once the steel is properly heated, it is submerged rapidly into a quenching medium like water, oil, or brine.
This extreme cooling happens so fast that the dissolved carbon atoms do not have time to move out and form the softer structures they normally would during slow cooling.
The Result: Martensite Formation
The carbon atoms become trapped within the iron crystal lattice, which is trying to change back to its room-temperature form.
This trapping of atoms creates immense internal strain, distorting the crystal lattice into a new, body-centered tetragonal structure. This highly strained, hard structure is martensite. It is this internal strain that makes the material so resistant to deformation, directly resulting in higher tensile strength and hardness.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Increasing one mechanical property often comes at the expense of another. Quenching is a classic example of this balancing act.
The Critical Flaw: Brittleness
While as-quenched martensite is extremely strong, it is also very brittle. It has very low toughness, meaning it cannot absorb much energy before fracturing.
For most practical applications, a part made of purely quenched steel would be useless, as it would likely shatter under impact or sharp loads rather than bending or deforming.
The Solution: Tempering
To make the quenched steel useful, it almost always undergoes a second heat treatment process called tempering.
Tempering involves reheating the quenched part to a much lower temperature and holding it for a specific time. This process relieves some of the internal stress and allows for a controlled, slight rearrangement of the microstructure.
This reduces the hardness and tensile strength slightly but dramatically increases the material's toughness and ductility, making it a durable and reliable component. The final balance of properties is controlled by the tempering temperature and time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Quenching and tempering is a combined process used to precisely engineer a material's final properties. The right approach depends entirely on the intended application.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance (e.g., for cutting tools or files): Use a full quench followed by a very low-temperature temper to relieve stress without significantly softening the material.
- If your primary focus is high strength with significant toughness (e.g., for springs, axles, or structural bolts): Use a full quench followed by a higher-temperature temper to achieve a robust balance of strength and ductility.
- If you are working with low-carbon steel: Quenching will have a minimal effect, as there is not enough carbon present to form a significant amount of martensite.
Quenching is the step that creates the potential for high strength, but tempering is the critical process that refines it for practical use.
Summary Table:
| Property | Before Quenching (Annealed) | After Quenching (As-Quenched Martensite) | After Quenching & Tempering |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Low | Very High | High (Controlled) |
| Hardness | Low | Very High | High (Controlled) |
| Ductility / Toughness | High | Very Low (Brittle) | Good (Balanced) |
| Primary Use Case | Forming/Machining | Not typically used alone | Springs, tools, structural parts |
Ready to achieve the perfect balance of strength and toughness in your metal components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision lab equipment for heat treatment processes like quenching and tempering. Whether you're developing new alloys, performing quality control, or optimizing production parameters, our furnaces and quenching systems deliver the reliable temperature control and rapid cooling rates you need.
Let us help you unlock the full potential of your materials. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can I vacuum the inside of my furnace? A Guide to Safe DIY Cleaning vs. Professional Service
- How to vacuum out a furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe DIY Maintenance
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? Selecting the Right Hot Zone for Your Process
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What does a vacuum furnace do? Achieve High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Components



















