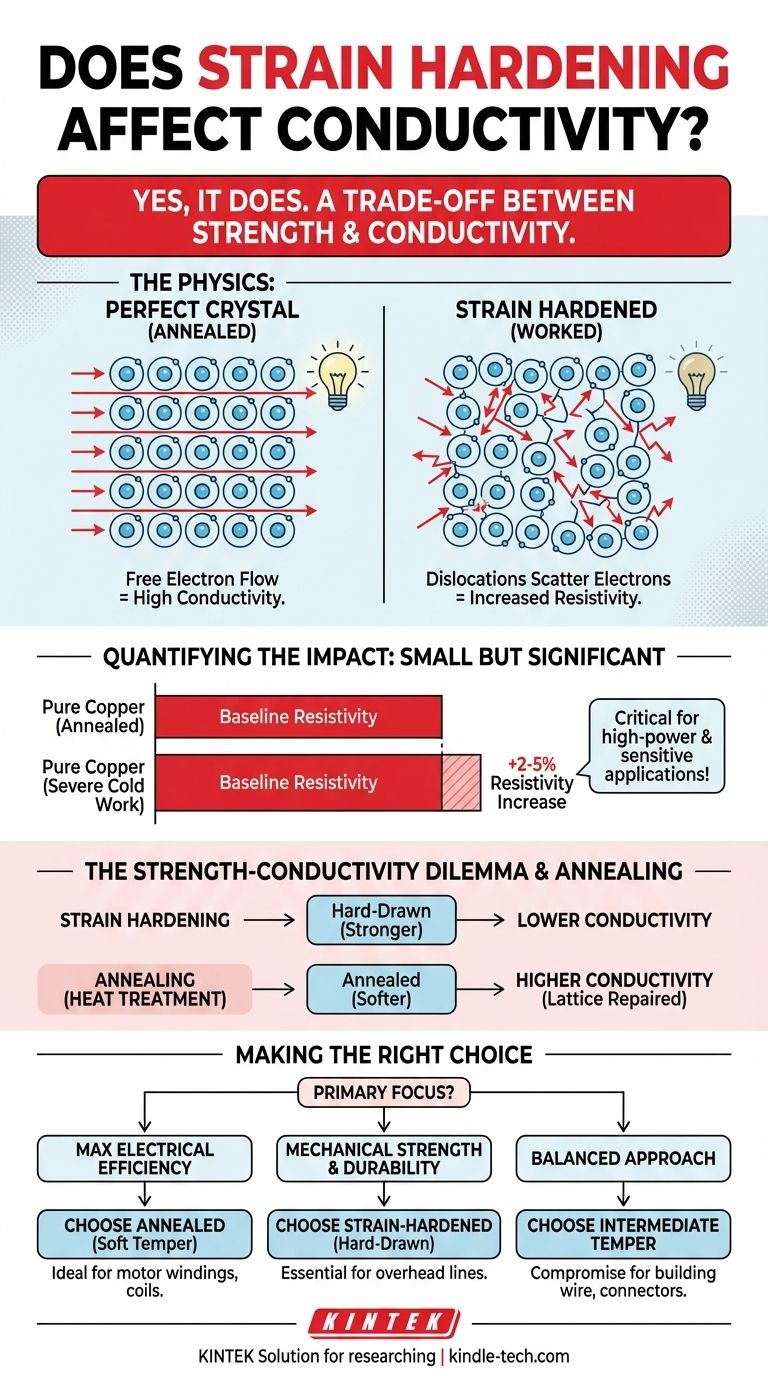
Yes, strain hardening does affect conductivity. The process of strain hardening, also known as work hardening, strengthens a metal by introducing microscopic defects into its crystal structure. While these defects increase mechanical strength, they also disrupt the pathways for electrons, which in turn decreases the material's electrical conductivity (or, viewed another way, increases its electrical resistivity).
Strain hardening creates a fundamental trade-off between a metal's mechanical strength and its electrical performance. The very defects that make a metal harder and stronger also act as obstacles to electron flow, thereby reducing its conductivity.
The Physics Behind the Effect
To understand this relationship, we need to look at how electrons move through a metal and how strain hardening changes the material's internal structure.
How Electrons Move in a Conductor
In a metallic conductor like copper or aluminum, electrons are not tightly bound to individual atoms. Instead, they form a "sea" of free electrons that can move easily throughout the material's crystal lattice.
Electrical conductivity is a measure of how freely these electrons can travel when a voltage is applied. In a theoretically perfect crystal, electron flow would be nearly unimpeded.
The Impact of Strain Hardening
Strain hardening occurs when a metal is permanently deformed (plastically deformed) by processes like bending, rolling, or drawing. This deformation forces atoms out of their ideal positions in the crystal lattice.
This process creates a high density of line defects known as dislocations. These dislocations are essentially microscopic disruptions in the otherwise orderly arrangement of atoms.
Electron Scattering: The Source of Resistance
The free-flowing electrons that carry an electrical current can be thought of as waves traveling through the crystal lattice. Anything that disrupts the perfect, periodic structure of that lattice can cause these electron waves to scatter.
These dislocations act as scattering centers. When an electron encounters a dislocation, its path is deflected, which impedes its overall forward motion. This is the microscopic origin of electrical resistance. Therefore, the more dislocations you introduce through strain hardening, the more scattering events occur, and the higher the material's resistivity becomes.
Quantifying the Impact
While the effect is direct and predictable, its magnitude depends on the material and the extent of the work hardening.
A Small but Significant Change
For most common conductors, the impact is relatively small but can be critical in demanding applications. For example, severe cold working of high-purity copper can increase its resistivity by 2-5%.
While this may seem minor, in applications like high-power transmission lines or sensitive electronics, a few percent increase in resistance can lead to significant energy loss as heat and a meaningful drop in efficiency.
Material Purity is a Factor
The effect of strain hardening on conductivity is more pronounced in high-purity metals. This is because in a pure metal, there are very few other defects (like impurity atoms) to scatter electrons. The primary source of resistance becomes the dislocations themselves.
In a less pure alloy, the baseline resistivity is already higher due to scattering from the alloyed elements, so the additional resistance from dislocations has a smaller relative impact.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The relationship between strain and conductivity is a classic engineering compromise. You often cannot maximize both mechanical strength and electrical conductivity simultaneously in the same material.
The Strength-Conductivity Dilemma
A strain-hardened wire (often called "hard-drawn") is significantly stronger and more resistant to mechanical fatigue. However, it will have a slightly lower conductivity than its softer counterpart.
An annealed wire—one that has been heat-treated after being formed—has a much lower dislocation density. This process softens the metal but restores its conductivity to a maximum level by repairing the crystal lattice.
The Reversibility of Annealing
This trade-off is managed through annealing. By heating a work-hardened metal, you give the atoms enough thermal energy to rearrange themselves back into a more orderly, low-energy state.
This process drastically reduces the number of dislocations, which simultaneously softens the material and increases its conductivity. This is why different "tempers" (e.g., hard, half-hard, soft/annealed) of metals are available.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The choice between a hardened or annealed material depends entirely on the primary requirements of your design.
- If your primary focus is maximum electrical efficiency: Choose a fully annealed material (e.g., "soft temper") to minimize resistive losses, accepting its lower tensile strength and durability. This is common for motor windings and transformer coils.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and durability: Use a strain-hardened material (e.g., "hard-drawn"), accepting the slight penalty in conductivity. This is essential for overhead power lines that must support their own weight over long spans.
- If your primary focus is a balanced approach: Select an intermediate temper (e.g., half-hard) that provides a calibrated compromise between necessary mechanical properties and acceptable electrical performance. This is often used for building wire and connectors.
Understanding this fundamental relationship between a material's mechanical history and its electrical properties is key to making robust engineering decisions.
Summary Table:
| Material Condition | Mechanical Strength | Electrical Conductivity | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annealed (Soft) | Lower | Higher (Maximum) | Ideal for maximum electrical efficiency |
| Strain-Hardened (Hard) | Higher | Lower | Increased strength, slight conductivity penalty |
| Intermediate Temper | Balanced | Balanced | Compromise between strength and conductivity |
Need help selecting the right material for your lab application?
Strain hardening creates a critical trade-off between mechanical strength and electrical performance that can impact your experiments and equipment efficiency. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific needs—whether you require materials with maximum conductivity for sensitive electronics or enhanced durability for demanding mechanical applications.
Let our experts help you optimize your material selection! Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's unique requirements with precision equipment and informed solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Twin Screw Extruder Plastic Granulation Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press contribute to MIC testing? Ensure Precision in Stainless Steel Specimens
- What are the advantages of an electrolytic polishing device for EK-181 steel TEM samples? Ensure Peak Sample Integrity
- What is the process of mounting in metallurgy? A Guide to Perfect Specimen Preparation
- What is the general procedure and what precautions should be taken during the polishing process? Achieve a Flawless Electrode Finish
- How should an RVC sheet be handled and set up during an experiment? Ensure Precision and Data Integrity



















