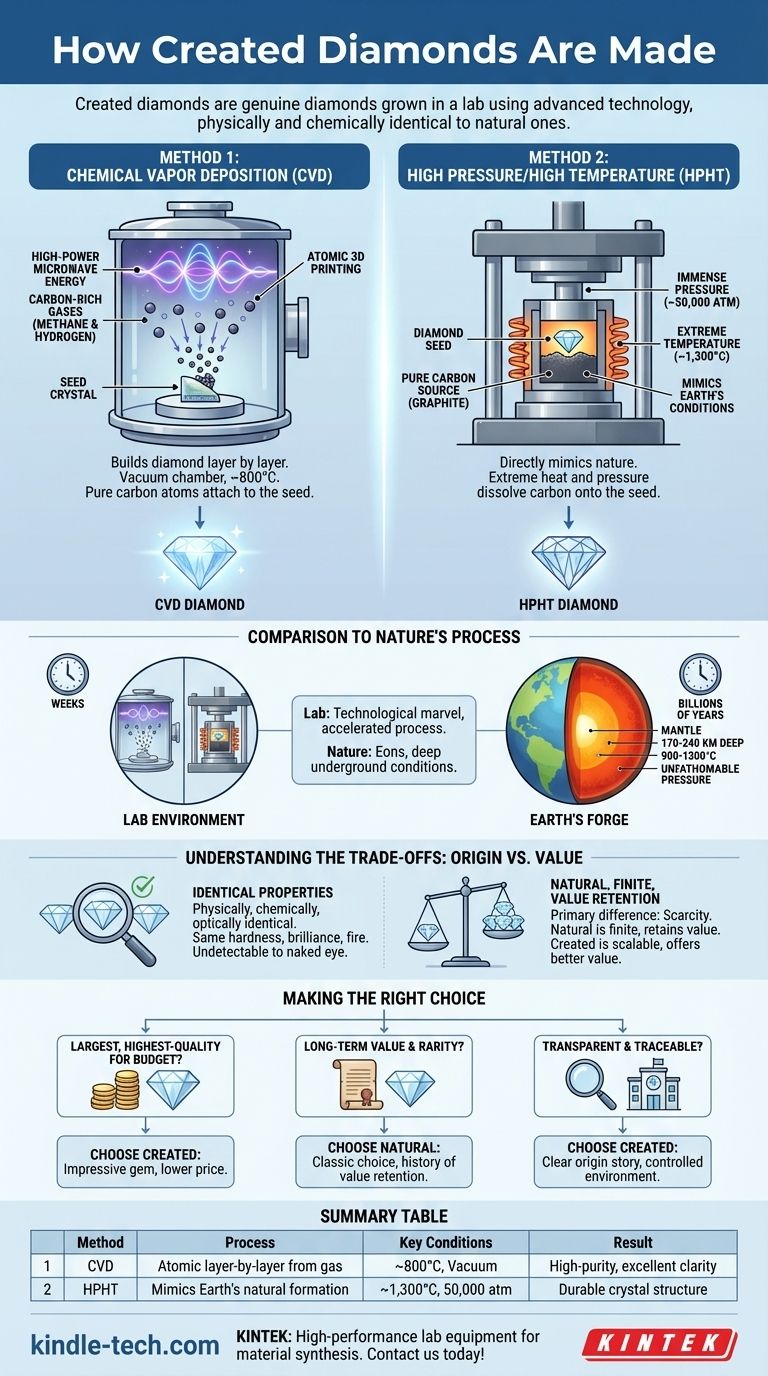
Created diamonds are not imitations; they are genuine diamonds grown in a laboratory environment using advanced technology that replicates the natural diamond-forming process. The two primary methods are Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and High Pressure/High Temperature (HPHT), both of which start with a tiny "seed" diamond and build upon it to form a larger, chemically identical stone.
The core takeaway is that created diamonds are physically and chemically identical to mined diamonds. The only distinction lies in their origin: a controlled lab environment versus the immense, chaotic pressure deep within the Earth's mantle.

The Two Paths to a Perfect Crystal
While a natural diamond takes billions of years to form, a created diamond can be grown in a matter of weeks. This is accomplished through two distinct but equally effective technological processes.
Method 1: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Think of the CVD process as atomic 3D printing. It builds a diamond layer by layer.
A thin slice of a diamond, known as a seed crystal, is placed inside a sealed vacuum chamber.
The chamber is then heated to around 800°C and filled with a mixture of carbon-rich gases, typically methane and hydrogen.
High-power microwave energy ionizes these gases, breaking their molecular bonds. This causes pure carbon atoms to "rain" down and attach themselves to the diamond seed, replicating its crystal structure and growing a new, larger diamond.
Method 2: High Pressure/High Temperature (HPHT)
The HPHT method more directly mimics the conditions deep within the Earth.
A small diamond seed is placed into a chamber with a source of pure carbon, like graphite.
This chamber is then subjected to the same conditions that form diamonds in nature: extreme temperatures (around 1,300°C) and immense pressure (nearly 50,000 atmospheres).
Under these conditions, the carbon source melts and dissolves, crystallizing onto the diamond seed and forming a new, complete diamond crystal.
How This Compares to Nature's Process
The lab's controlled environment is a technological marvel that accelerates a process nature takes eons to complete.
The Earth's Diamond Forge
Natural diamonds form in a specific zone of the Earth's mantle, roughly 170 to 240 kilometers below the surface.
There, carbon is subjected to the same brutal conditions replicated by the HPHT process—unfathomable pressure and temperatures between 900°C and 1,300°C.
This intense environment forces carbon atoms into their most compact arrangement, creating the incredibly hard crystal structure of a diamond.
The Journey to the Surface
These diamonds are then brought to the surface in a geological instant through deep-source volcanic eruptions.
The magma travels rapidly, carrying the diamonds within rocks known as kimberlite, which then cool and form the pipes where diamonds are mined today.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Origin vs. Value
While they are identical in substance, the difference in origin creates important distinctions in perception and long-term value.
Identical Properties, Different Story
A lab-created diamond is physically, chemically, and optically identical to a natural diamond. They are both pure carbon crystals with the same hardness, brilliance, and fire.
Even a trained gemologist cannot tell the difference with the naked eye and requires specialized equipment to detect the subtle markers of a diamond's growth environment.
The Question of Rarity and Value
The primary difference is scarcity. Natural diamonds are a finite resource created by a geological process that cannot be replicated on a massive scale.
This rarity is why natural diamonds historically hold or increase their value over time. While created diamonds offer better value retention than simulants (like cubic zirconia), their ability to be produced on demand means they do not appreciate in the same way as their mined counterparts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision between a created and a natural diamond ultimately depends on your personal priorities and what you value most in a gemstone.
- If your primary focus is obtaining the largest, highest-quality stone for your budget: Created diamonds offer a significant value proposition, allowing for a more impressive gem at a lower price point.
- If your primary focus is long-term financial value and the tradition of rarity: Natural diamonds remain the classic choice, backed by a history of value retention and the allure of a finite natural resource.
- If your primary focus is a transparent and traceable supply chain: Created diamonds provide a clear origin story from a controlled laboratory, avoiding the complexities of traditional mining.
Ultimately, both paths lead to a genuine diamond; the only difference is the story of its creation.
Summary Table:
| Method | Process | Key Conditions | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVD | Atomic layer-by-layer growth from carbon-rich gas | ~800°C, vacuum chamber | High-purity diamond with excellent clarity |
| HPHT | Mimics Earth's natural diamond formation | ~1,300°C, 50,000 atm pressure | Durable diamond crystal structure |
Need precise lab equipment for advanced material synthesis? KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory equipment and consumables, including systems for controlled environments like those used in diamond growth. Whether you're in research, manufacturing, or quality control, our solutions ensure accuracy and reliability. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- How do CVD diamonds grow? A Step-by-Step Guide to Lab-Grown Diamond Creation
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- What is the process of coating deposition? A Step-by-Step Guide to Thin Film Engineering
- What is direct current DC magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















