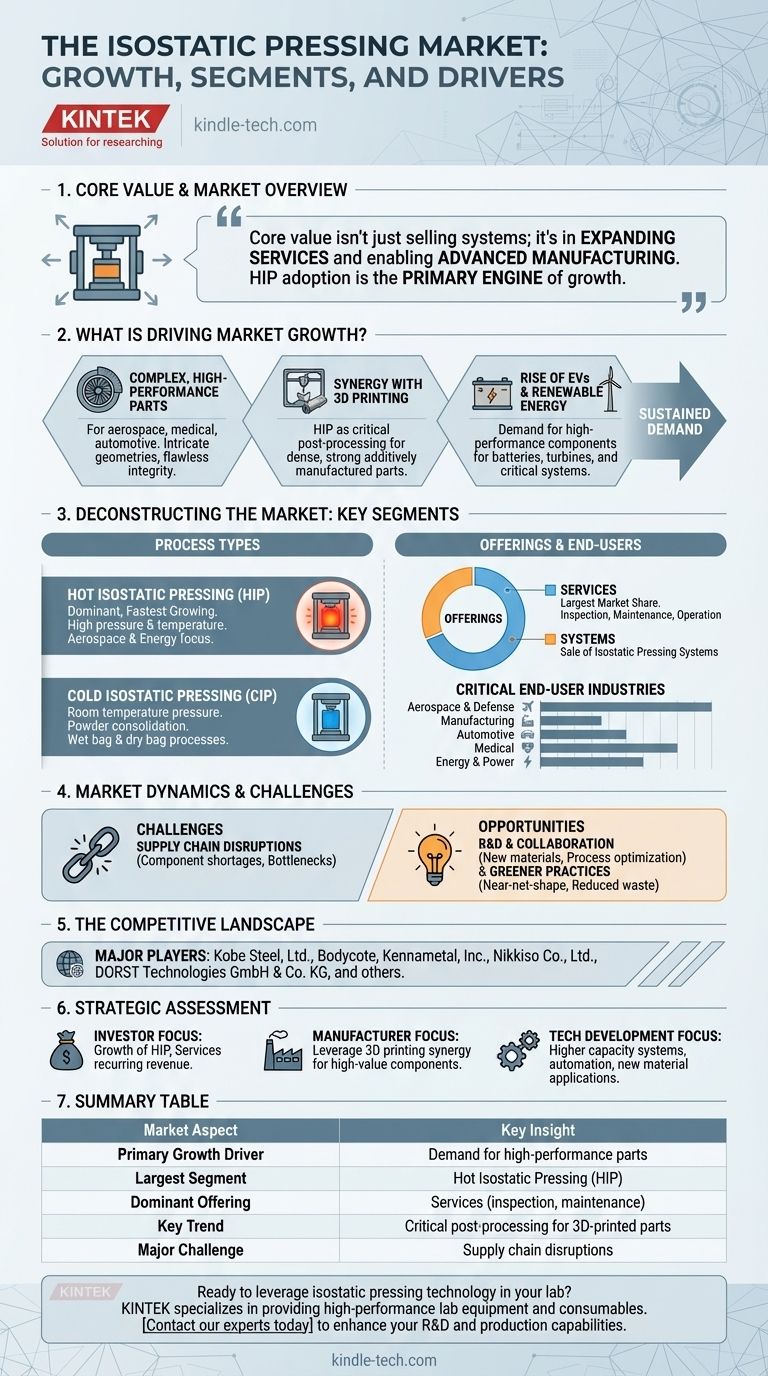
To understand the isostatic pressing market, you must look beyond a single number and analyze its core components and driving forces. The market is primarily segmented into Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) and Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) and is fueled by a growing demand for high-performance, complex parts across critical sectors like aerospace, automotive, medical, and energy. While supply chain disruptions have presented challenges, the market's growth is propelled by technological advancements, particularly in 3D printing, and a significant shift towards services.
The core value of the isostatic pressing market isn't just in selling systems; it's in the expanding services sector and the enabling role it plays in advanced manufacturing. The increasing adoption of Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) to improve the mechanical properties of critical components is the primary engine of growth.

What is Driving Market Growth?
The expansion of the isostatic pressing market is not based on a single factor but on a convergence of industrial needs and technological advancements. These drivers create a sustained demand for both the equipment and the specialized services associated with it.
The Need for Complex, High-Performance Parts
Industries like aerospace, medical, and automotive require components with intricate geometries and flawless structural integrity. Isostatic pressing is a key technology for producing these dense, high-strength parts, which cannot be easily manufactured using traditional methods.
Synergy with 3D Printing
Isostatic pressing, particularly HIP, is increasingly used as a post-processing step for 3D-printed metal parts. This process eliminates internal voids and improves the density and mechanical strength of additively manufactured components, making them suitable for critical, high-stress applications.
The Rise of Electric Vehicles and Renewable Energy
The global shift toward electric vehicles and renewable energy systems has created new demand. These industries rely on high-performance components for batteries, turbines, and other critical systems, driving the need for the advanced material properties achieved through isostatic pressing.
Deconstructing the Market: Key Segments
To accurately assess the market, it's essential to understand its primary segments. The distinctions between process types, offerings, and end-user industries reveal where the value and growth are concentrated.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) vs. Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP)
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is the dominant and fastest-growing segment. It uses high pressure and elevated temperature to produce fully dense materials. Its growth is directly tied to the demand for superior mechanical properties in sectors like aerospace and energy.
Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) involves applying pressure at room temperature. It is often used for consolidating powders before a final sintering step. It is segmented into wet bag and dry bag processes.
Systems vs. Services
The market is divided into two primary offerings: the sale of isostatic pressing systems and the provision of related services.
The services segment is expected to hold the largest market share. This is because the equipment requires regular inspection, maintenance, and expert operation to ensure reliability and prevent failures, creating a steady and growing demand for specialized service providers.
Critical End-User Industries
Several industries are key consumers of this technology. The most significant include aerospace and defense, manufacturing, automotive, medical, and energy and power. The unique requirements of each of these sectors fuel innovation and demand for customized pressing solutions.
Market Dynamics and Challenges
While the growth trends are strong, the market also faces operational challenges and strategic pressures that shape the competitive landscape.
Supply Chain Disruptions
The ecosystem has experienced a decline in production activities among component suppliers. This has led to shortages of essential components for Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs), creating bottlenecks and impacting the delivery of new systems.
The Opportunity in R&D and Collaboration
Leading manufacturers are heavily investing in research and development to explore new materials and optimize processes. Collaborations with other companies are a key strategy to expand product offerings and geographical reach, turning R&D into a competitive advantage.
A Push for Greener Practices
There is a growing trend toward more sustainable manufacturing. Isostatic pressing aligns with this by enabling near-net-shape manufacturing, which reduces material waste and optimizes resource utilization compared to traditional subtractive methods.
The Competitive Landscape
The market includes established global players who are investing heavily to strengthen their positions, particularly in HIP technology.
Who are the Major Players?
The key companies shaping the isostatic pressing market include Kobe Steel, Ltd. (Japan), Bodycote (UK), Kennametal, Inc. (US), Nikkiso Co., Ltd. (Japan), and DORST Technologies GmbH & Co. KG (Germany), among others.
Making a Strategic Assessment
Your approach to this market should be guided by your specific goals, whether you are an investor, manufacturer, or end-user.
- If your primary focus is investment: Concentrate on the growth of the Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) segment and the dominant, recurring revenue of the services market.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing: Leverage the synergy between 3D printing and isostatic pressing to produce high-value, complex components for the aerospace, medical, and automotive sectors.
- If your primary focus is technology development: Explore opportunities in higher capacity systems, advanced process automation, and new material applications to meet evolving industry demands.
Ultimately, the isostatic pressing market is a critical enabler of modern manufacturing, and its health is directly tied to the innovation occurring in the world's most demanding industries.
Summary Table:
| Market Aspect | Key Insight |
|---|---|
| Primary Growth Driver | Demand for high-performance parts in aerospace, medical, and automotive. |
| Largest Segment | Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP). |
| Dominant Offering | Services (inspection, maintenance) hold the largest market share. |
| Key Trend | Critical post-processing for 3D-printed metal components. |
| Major Challenge | Supply chain disruptions for essential components. |
Ready to leverage isostatic pressing technology in your lab? KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables that support advanced manufacturing processes like HIP and CIP. Whether you are developing new materials, optimizing 3D-printed parts, or ensuring quality control, our solutions are designed to meet the rigorous demands of laboratories in aerospace, medical, and energy sectors. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your R&D and production capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Electric Split Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- What role does an industrial-grade omnidirectional press play in the preparation of ultra-fine grained VT6 titanium?
- How does Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) benefit SiC ceramic reactors? Achieve Flawless Material Integrity
- What is cold isostatic pressing of metal powder? Achieve Uniform Density in Complex Metal Parts
- What are the advantages of the isostatic pressing process? Achieve High Density and Complex Geometries
- What is the pressing method in ceramics? A Guide to Shaping Dense, High-Performance Parts
- What is the function of a Cold Isostatic Press (CIP) in the fabrication of pouch-type all-solid-state batteries?
- What is the difference between hot isostatic pressing and cold isostatic pressing? A Guide to Forming vs. Densification
- How does a cold isostatic press (CIP) facilitate LPSCl/LLZO interfaces? Unlock Superior Solid-State Battery Bonds



















