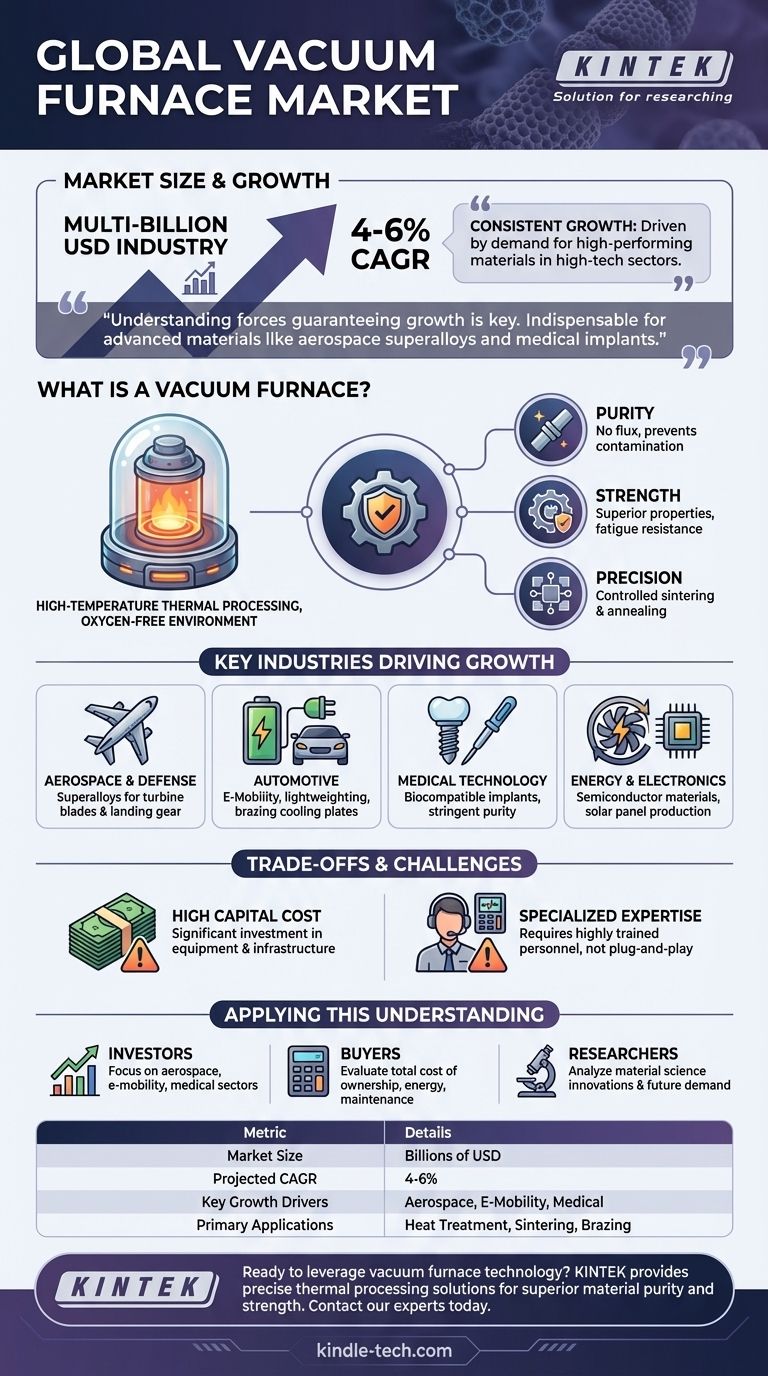
The global vacuum furnace market is a substantial, multi-billion dollar industry characterized by consistent growth. While specific market size figures from research firms can vary, they all point to a market valued in the billions of US dollars with a strong projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR), often cited in the range of 4-6%. This expansion is not driven by a single factor, but by the relentless demand for higher-performing materials across a range of critical, high-tech sectors.
The specific dollar value of the vacuum furnace market is less important than understanding the forces that guarantee its growth. The market's strength comes from its indispensable role in creating the advanced materials that define modern technology, from aerospace superalloys to medical implants.

What is a Vacuum Furnace and Why is it Critical?
To understand the market's value, you must first understand the core problem a vacuum furnace solves. It is a specialized piece of industrial equipment designed for high-temperature thermal processing of materials in a controlled, oxygen-free environment.
The Core Function: Heat Treatment Without Contamination
At high temperatures, most metals react with oxygen and other atmospheric gases. This reaction, called oxidation, can create a layer of scale, compromise the material's surface finish, and alter its chemical properties.
A vacuum furnace removes the atmosphere before heating. This prevents unwanted chemical reactions, ensuring the material being processed remains pure and its properties are precisely controlled.
Key Benefits: Purity, Strength, and Precision
The vacuum environment enables several critical industrial processes that are impossible in a standard furnace. These processes deliver three key benefits:
- Purity: Processes like brazing and diffusion bonding create clean, strong joints without the need for flux, which can be a source of contamination and corrosion.
- Strength: Vacuum heat-treating, hardening, and tempering of specialty steels and alloys produce components with superior mechanical properties, like hardness and fatigue resistance.
- Precision: Processes like sintering (fusing metal powders) and annealing (softening metal) can be controlled with extreme accuracy, resulting in parts with uniform density and structure.
Key Industries Driving Market Growth
The market isn't growing in a vacuum; it is being pulled forward by the needs of the world's most demanding industries. Understanding these applications reveals the "why" behind the market's robust health.
Aerospace and Defense: Forging with Superalloys
This is a primary driver. Jet engine turbine blades, landing gear, and structural components are made from nickel-based superalloys and titanium. These materials only achieve their required strength and heat resistance through precise vacuum heat treatment.
Automotive: The Rise of E-Mobility and Lightweighting
The shift to electric vehicles (EVs) and the constant push for fuel efficiency create huge demand. Vacuum furnaces are used for brazing EV battery cooling plates, sintering high-strength gears for transmissions, and heat-treating lightweight structural components.
Medical Technology: Biocompatible Implants and Tools
The medical device industry relies on vacuum processing for its stringent purity requirements. Titanium hip implants, stainless steel surgical instruments, and dental prosthetics are all heat-treated in a vacuum to ensure biocompatibility and prevent contamination.
Energy and Electronics: Powering the Future
Vacuum furnaces are essential for manufacturing components for the energy and electronics sectors. This includes brazing parts for power generation turbines and processing materials used in semiconductor manufacturing and solar panel production.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While the technology is critical, the market has inherent complexities and barriers that shape its landscape. A clear-eyed view of these challenges is essential.
The High Cost of Entry: Capital Investment
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital expenditure. The cost of the equipment, combined with the required infrastructure for power, cooling water, and process gases, makes the initial investment substantial for any organization.
The Need for Specialized Expertise: Operational Complexity
This is not "plug-and-play" equipment. Operating and maintaining a vacuum furnace requires highly trained personnel who understand metallurgy, vacuum technology, and process control. This need for expertise can be a significant operational cost and barrier.
The Competitive Landscape: Consolidation vs. Niche Players
The market consists of a few large, established global players and many smaller, specialized manufacturers. These smaller firms often thrive by focusing on custom solutions or specific processes, such as furnaces for R&D labs or unique material applications.
How to Apply This Understanding to Your Goal
Your interest in the market size likely stems from a specific goal. Use this deeper context to inform your strategy.
- If you are an investor: Focus on the growth drivers in aerospace, e-mobility, and medical devices. Companies supplying furnaces and services to these booming sectors are best positioned for growth.
- If you are a potential buyer: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, not just the initial price. Factor in energy consumption, maintenance requirements, and the cost of training operators.
- If you are an engineer or researcher: Look beyond the furnace itself and analyze the material science innovations that necessitate advanced vacuum processing, as this is where future demand will originate.
Ultimately, the vacuum furnace market is a direct reflection of our global demand for stronger, purer, and more reliable materials.
Summary Table:
| Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size | Valued in the Billions of USD |
| Projected CAGR | 4-6% |
| Key Growth Drivers | Aerospace, E-Mobility, Medical Technology |
| Primary Applications | Heat Treatment, Sintering, Brazing |
Ready to leverage the power of vacuum furnace technology for your lab or production line? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, providing the precise thermal processing solutions your projects demand. Our expertise helps laboratories and manufacturers in aerospace, medical, and automotive sectors achieve superior material purity and strength. Contact our experts today to discuss how our vacuum furnaces can meet your specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are common heat treatment methods? Master Annealing, Hardening, and Quenching for Optimal Material Performance
- What is a low temperature form of brazing? Discover Solid-State Joining for Heat-Sensitive Materials
- What are the different types of industrial furnaces? Find the Right Heating Solution for Your Process
- What kind of energy does pyrolysis generate? Converting Waste into Valuable Fuels
- What impact do high-temperature drying and calcination equipment have on apatite-nepheline waste properties?
- What is the use of a batch furnace? Achieve Precision Heat Treatment for Your Lab or Workshop
- What is the arc melting method for alloy preparation? A Guide to High-Volume Metal Melting
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum oven for Ni@TiN-NTs catalysts? Preserve Morphology & Catalytic Activity



















