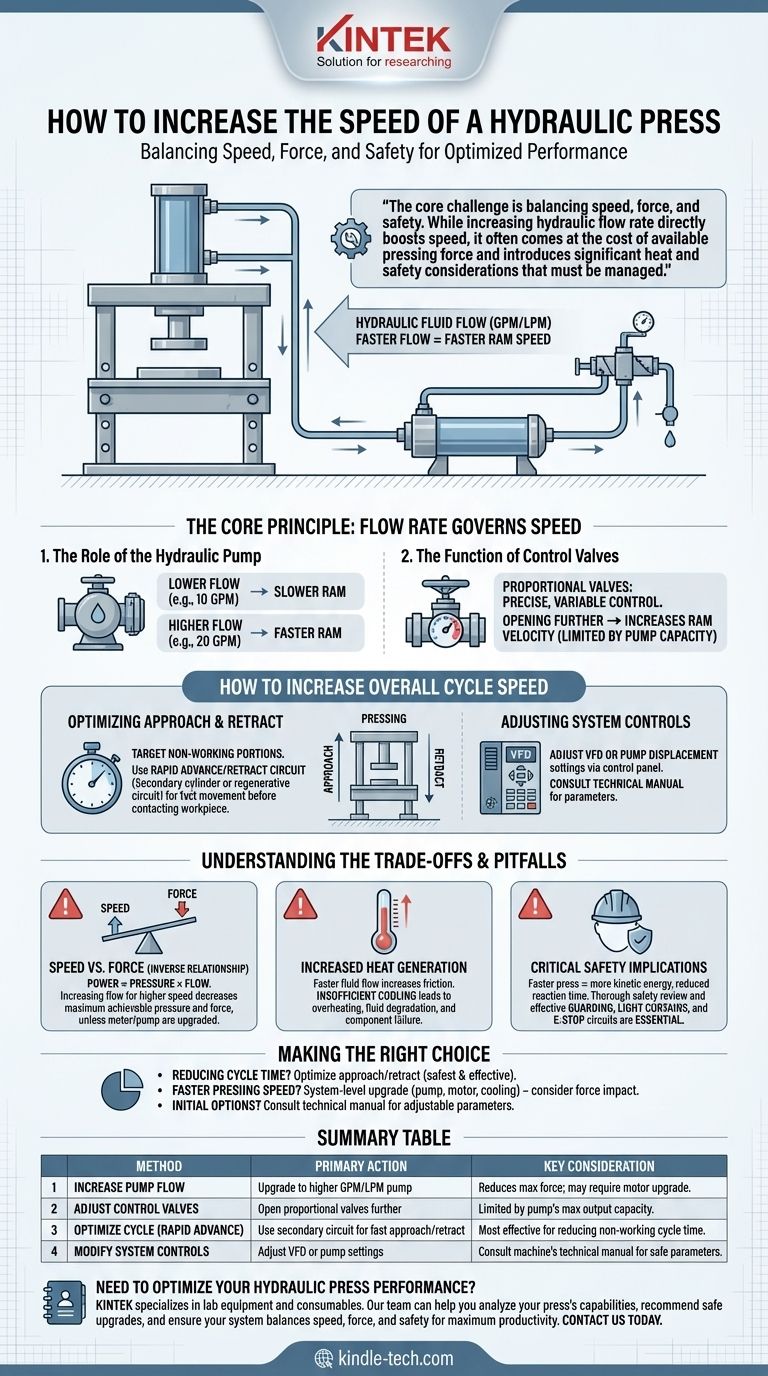
To increase the speed of a hydraulic press, you must increase the hydraulic fluid flow rate to the cylinder, measured in gallons or liters per minute (GPM/LPM). This is primarily achieved by adjusting the output of the hydraulic pump or by modifying the settings on the system's control valves. The faster the cylinder can be filled with fluid, the faster the ram will move.
The core challenge is balancing speed, force, and safety. While increasing hydraulic flow rate directly boosts speed, it often comes at the cost of available pressing force and introduces significant heat and safety considerations that must be managed.
The Core Principle: Flow Rate Governs Speed
A hydraulic press operates based on a simple relationship: the speed of the ram is determined by the volume of fluid pushed into the cylinder over a period of time.
The Role of the Hydraulic Pump
The pump is the heart of the system, creating the flow of hydraulic fluid. The pump's capacity is the ultimate limiting factor for the press's speed.
A pump with a higher flow rating (e.g., 20 GPM) will move the ram faster than a pump with a lower rating (e.g., 10 GPM), assuming the cylinder size is the same.
The Function of Control Valves
Control valves act as gates, directing the flow of fluid from the pump to the cylinder. Modern presses use proportional valves that allow for precise, variable control over the flow rate.
Opening these valves further allows more fluid to reach the cylinder per second, increasing the ram's velocity. However, the valves cannot supply a higher flow rate than the pump can produce.
How to Increase Overall Cycle Speed
Simply increasing the pressing speed isn't always the most efficient or safest solution. The goal is typically to reduce the overall cycle time, which includes the approach, pressing, and retract phases.
Optimizing the Approach and Retract
For most applications, the work is only done during a small portion of the ram's travel. The most significant time savings often come from speeding up the non-working portions of the cycle.
Many modern presses use a rapid advance/retract circuit. This uses a smaller, secondary cylinder or a regenerative circuit to move the ram quickly until it is just about to contact the workpiece. The system then switches to the large, high-force cylinder for the slower, controlled pressing action.
Adjusting System Controls
If your press has a variable displacement pump or a motor with a variable frequency drive (VFD), you may be able to increase its output directly through the machine's control panel. Consult your machine's technical manual for available parameters.
Similarly, the settings for proportional control valves can often be adjusted to allow for faster movement during specific parts of the cycle.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Increasing speed is not a simple tweak; it has system-wide consequences that require careful consideration.
The Inverse Relationship: Speed vs. Force
For any given motor power, there is a direct trade-off between pressure (force) and flow (speed). This is a fundamental law of hydraulics: Power = Pressure × Flow.
If you adjust the system to increase flow for higher speed, the maximum achievable pressure (and thus force) will decrease unless you also upgrade the motor and pump.
Increased Heat Generation
Pushing fluid through the system faster increases friction within pipes, valves, and the pump itself. This friction generates excess heat.
If the system's cooling capacity (e.g., heat exchanger, reservoir size) is insufficient, the hydraulic fluid can overheat. This degrades the fluid, damages seals, and can lead to premature component failure and costly downtime.
Critical Safety Implications
A faster-moving press has more kinetic energy and reduces the reaction time for an operator. Any modifications to speed must be accompanied by a thorough safety review.
Guarding, light curtains, and emergency stop circuits must be verified to be effective for the new, higher speeds. Never compromise safety for the sake of production speed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Before making any changes, clearly define what you want to achieve.
- If your primary focus is reducing overall cycle time: Investigate optimizing the approach and retract strokes. This is often the safest and most effective method for increasing throughput without altering the critical pressing phase.
- If your primary focus is a faster pressing speed: This is a significant modification that requires a system-level approach. You will likely need to evaluate upgrading the pump, motor, and cooling system, all while considering the impact on available force.
- If you are exploring initial options: Start by consulting the press's technical manual. Understanding the built-in adjustable parameters for the pump and valves is the first, most logical step before considering any hardware changes.
Ultimately, a holistic view of your production process will yield the most effective and sustainable improvements in efficiency.

Summary Table:
| Method | Primary Action | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Increase Pump Flow | Upgrade to a higher GPM/LPM pump. | Reduces maximum available force; may require motor upgrade. |
| Adjust Control Valves | Open proportional valves further for more flow. | Limited by the pump's maximum output capacity. |
| Optimize Cycle (Rapid Advance) | Use a secondary circuit for fast approach/retract. | Most effective for reducing non-working cycle time. |
| Modify System Controls | Adjust VFD or pump displacement settings via control panel. | Consult the machine's technical manual for safe parameters. |
Need to optimize your hydraulic press performance? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with precision and expertise. Our team can help you analyze your press's capabilities, recommend safe upgrades, and ensure your system balances speed, force, and safety for maximum productivity. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and let us provide a solution tailored to your laboratory's workflow.
Visual Guide
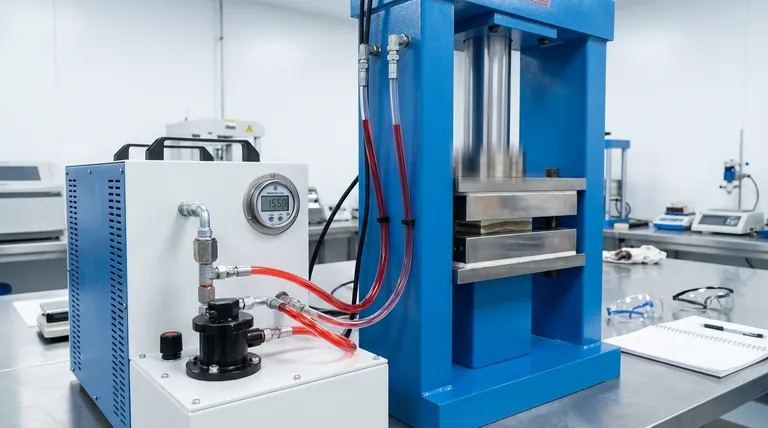
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates Split Manual Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy



















