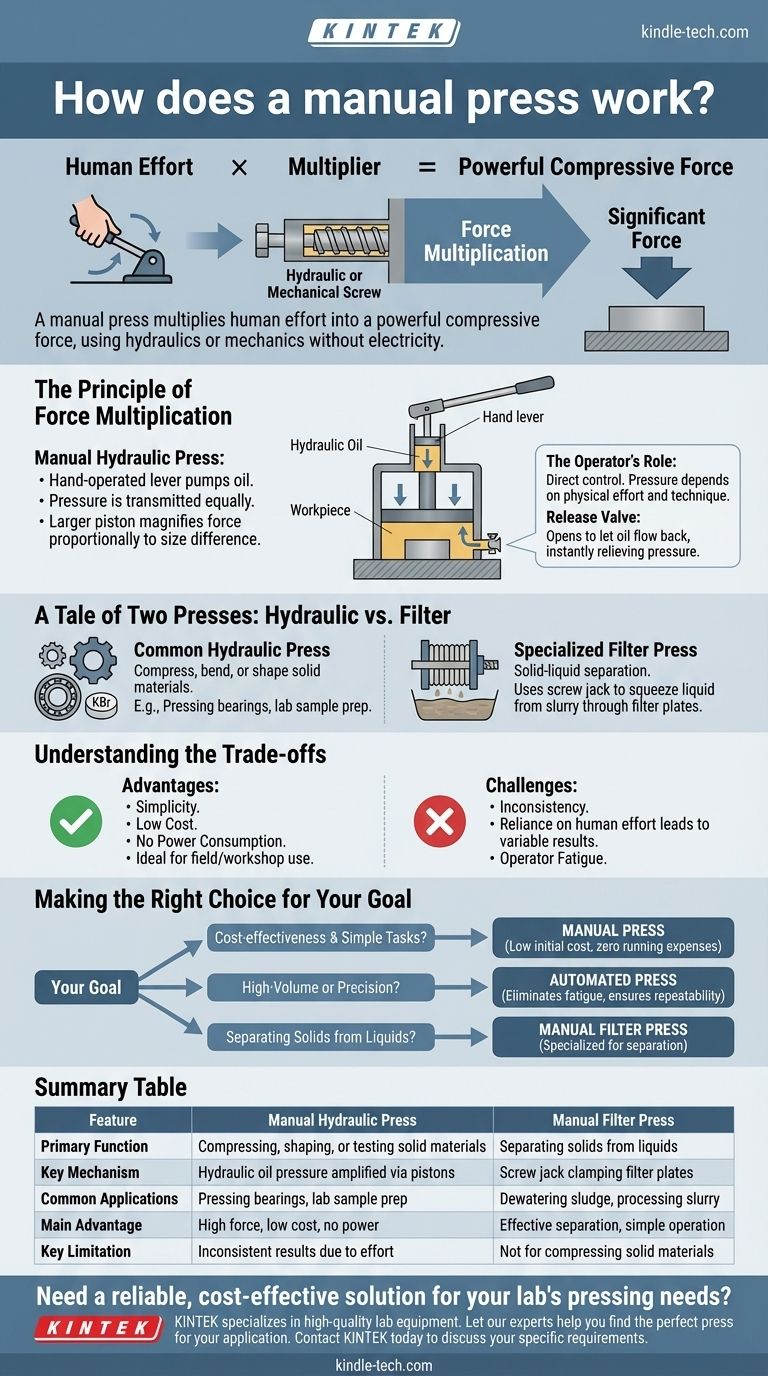
At its core, a manual press is a device that multiplies human effort into a powerful compressive force. The most common type, a manual hydraulic press, uses a hand-operated lever to pressurize a small amount of oil. This hydraulic pressure then acts on a much larger piston, generating a significant force capable of compressing, shaping, or testing materials without any need for electricity.
A manual press translates simple physical action—like pumping a lever or turning a screw—into substantial mechanical force. It trades the precision and ease of automation for radical simplicity, lower cost, and operational independence.

The Principle of Force Multiplication
The genius of a manual press lies in its ability to amplify a small input force into a large output force. This is typically achieved through one of two common mechanisms: hydraulics or a mechanical screw.
How a Manual Hydraulic Press Works
A manual hydraulic press is built on a fundamental principle of fluid dynamics. It consists of a cylinder filled with an incompressible fluid, usually hydraulic oil.
A hand-operated lever or pump is used to apply pressure to a small piston. This pressure is transmitted equally throughout the oil.
Because the oil also pushes against a much larger piston, the resulting force is magnified proportionally to the difference in piston size. A small effort on the handle creates immense force on the workpiece.
The Operator's Role
The operator directly controls the entire process. Each pump of the handle incrementally increases the pressure and the force applied to the material being pressed.
This direct control allows for a tactile feel of the operation but also means the consistency and repeatability of the pressure depend heavily on the operator's physical effort and technique.
Releasing the Pressure
Once the desired compression is achieved, a simple release valve is opened. This allows the hydraulic oil to flow back into its reservoir, instantly relieving the pressure and allowing the main piston to retract.
A Tale of Two Presses: Hydraulic vs. Filter
While "manual press" often implies a hydraulic shop press, another common type serves a completely different purpose. Understanding the distinction is crucial.
The Common Hydraulic Press
This is the tool most people envision. Its purpose is to compress, bend, or shape solid materials.
Applications range from pressing bearings and gears in a machine shop to preparing laboratory samples for analysis, such as creating KBr pellets for FTIR spectroscopy.
The Specialized Filter Press
A manual filter press is designed for solid-liquid separation. Instead of a piston, it uses a screw jack to clamp together a series of filter plates.
A slurry is pumped into the chambers between the plates, and the pressure from the screw squeezes the liquid out through a filter cloth, leaving the solid material behind.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The manual press is a simple tool, and its primary strengths are also the source of its limitations.
The Advantage of Simplicity
Because they lack complex electronic components, manual presses are significantly cheaper than their automatic counterparts.
They require no power consumption, making them ideal for field use or workshops with limited infrastructure. Maintenance is also straightforward and less costly.
The Challenge of Consistency
The greatest drawback is the reliance on human effort. Applying a precise, repeatable amount of force from one task to the next is difficult.
This can lead to inconsistent results, especially in processes that require exact pressure specifications. Operator fatigue can also become a factor in repetitive tasks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right type of press depends entirely on your specific requirements for precision, volume, and budget.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and simple tasks: A manual press is an excellent choice due to its low initial investment and zero running expenses.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production or precision: An automated press is superior because it eliminates operator fatigue and ensures repeatable, consistent pressure.
- If your primary focus is separating solids from liquids: You need a specialized manual filter press, not a standard hydraulic press used for compression.
Ultimately, understanding the direct relationship between physical input and mechanical output is the key to mastering the manual press.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Manual Hydraulic Press | Manual Filter Press |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Compressing, shaping, or testing solid materials | Separating solids from liquids |
| Key Mechanism | Hydraulic oil pressure amplified via pistons | Screw jack clamping filter plates |
| Common Applications | Pressing bearings, lab sample preparation (e.g., KBr pellets) | Dewatering sludge, processing slurry |
| Main Advantage | High force generation, low cost, no power needed | Effective solid-liquid separation, simple operation |
| Key Limitation | Inconsistent results due to operator effort | Not suitable for compressing solid materials |
Need a reliable, cost-effective solution for your lab's pressing needs?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including manual presses ideal for sample preparation, material testing, and more. Our manual hydraulic presses offer the simplicity and power you need without the complexity or cost of automated systems.
Let our experts help you find the perfect press for your application. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific laboratory requirements and discover how our durable, purpose-built equipment can enhance your workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the use of KBr? Master Sample Prep for Accurate IR Spectroscopy
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.



















