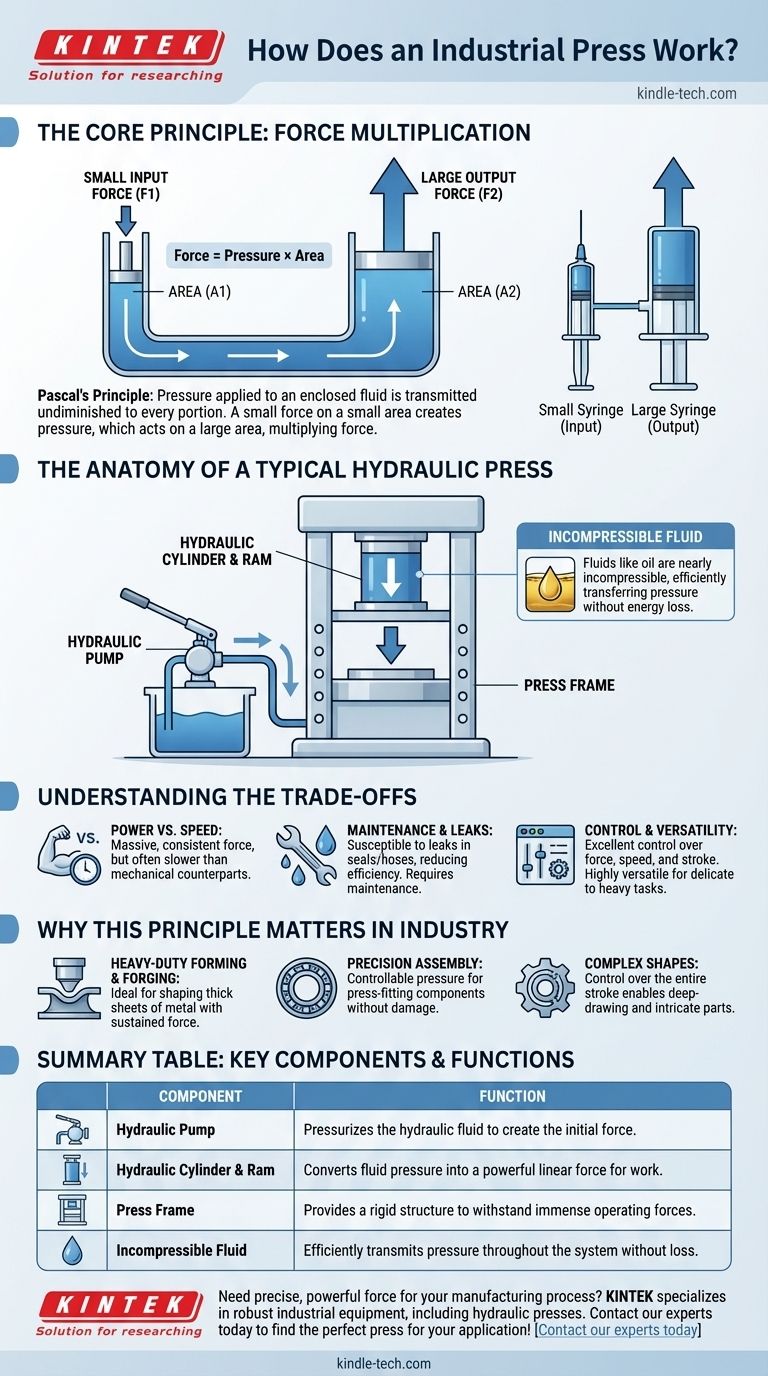
At its core, an industrial press multiplies force. The most common type, a hydraulic press, uses a pump to pressurize an incompressible fluid (like oil). This pressurized fluid then acts on a large piston, generating an immense compressive force capable of shaping, cutting, or assembling materials.
The fundamental principle is force multiplication. A small force applied over a small area creates pressure in a fluid, which then exerts a much larger force over a larger area, turning a modest input into a powerful industrial output.

The Core Principle: How Force is Multiplied
The operation of a hydraulic press is governed by a fundamental law of physics. Understanding this single concept explains its immense power.
Pascal's Principle Explained
A hydraulic press works on Pascal's Principle, which states that pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted undiminished to every portion of the fluid and the walls of the containing vessel.
The key formula is Force = Pressure × Area.
Because the pressure is constant throughout the system, if you apply force to a small piston (small area), the resulting pressure acts on a much larger piston (large area), multiplying the output force significantly.
The Role of Incompressible Fluid
Hydraulic systems use fluids like oil because they are nearly incompressible.
When force is applied, the fluid doesn't lose energy by being squeezed. Instead, it efficiently transfers the pressure from the small piston to the large one.
The Two-Piston System in Action
Imagine two syringes filled with water and connected by a tube. One syringe is small, and the other is very large.
Pushing the plunger of the small syringe (the input piston) with a small amount of force is relatively easy. This action creates pressure in the water, which travels through the tube and pushes on the plunger of the large syringe (the output piston), moving it with much greater force.
The Anatomy of a Typical Hydraulic Press
While the principle is simple, a functional press relies on several key components working together.
The Hydraulic Pump
This is the engine of the system. The pump draws hydraulic fluid from a reservoir and pressurizes it, creating the initial force that will be multiplied.
The Hydraulic Cylinder and Ram
The cylinder houses the main piston, often called the ram. This is the large-area component where the pressurized fluid acts, creating the powerful downward stroke that performs the work.
The Press Frame
The frame is the robust structure that contains and withstands the enormous forces generated by the press. It must be incredibly strong and rigid to ensure accuracy and safety during operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, hydraulic presses are not the only solution, and their design comes with specific characteristics.
Power vs. Speed
Hydraulic presses can generate massive amounts of force that is consistent throughout the entire stroke. However, they are often slower than their mechanical counterparts, which operate using a crankshaft.
Maintenance and Leaks
Any system relying on high-pressure fluid is susceptible to leaks. Seals and hoses are critical maintenance points, as a leak not only creates a mess but also reduces the press's efficiency and power.
Control and Versatility
A major advantage of hydraulic systems is their excellent control. The force, speed, and stroke length can often be precisely adjusted, making them highly versatile for a wide range of applications from delicate assembly to heavy forging.
Why This Principle Matters in Industry
Understanding how a press works reveals why it is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing. The choice of a press is directly tied to the task at hand.
- If your primary focus is heavy-duty forming or forging: The immense and sustained force of a hydraulic press is ideal for shaping thick sheets of metal.
- If your primary focus is precision assembly: The controllable pressure allows for press-fitting bearings or other components with exact force, preventing damage.
- If your primary focus is working with complex shapes: The ability to control the entire stroke gives operators the flexibility needed for deep-drawing or creating intricate parts.
Ultimately, the simple principle of fluid pressure allows us to shape the modern world with controlled and monumental force.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Hydraulic Pump | Pressurizes the hydraulic fluid to create the initial force. |
| Hydraulic Cylinder & Ram | Converts fluid pressure into a powerful linear force for work. |
| Press Frame | Provides a rigid structure to withstand immense operating forces. |
| Incompressible Fluid | Efficiently transmits pressure throughout the system without loss. |
Need precise, powerful force for your manufacturing process? KINTEK specializes in robust industrial equipment, including hydraulic presses designed for heavy-duty forming, precision assembly, and complex shaping tasks. Our solutions deliver the controlled, monumental force you need to shape your world efficiently and reliably. Contact our experts today to find the perfect press for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability



















