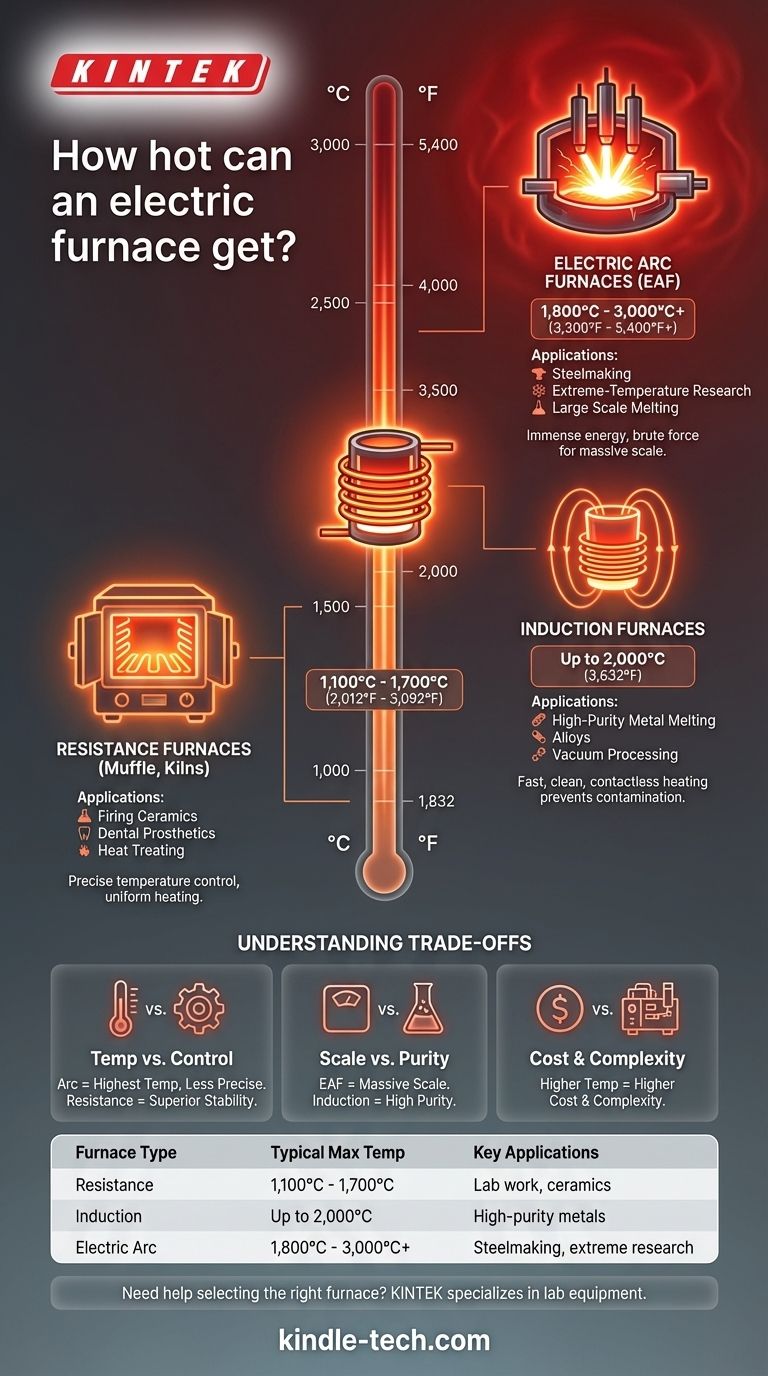
The maximum temperature of an electric furnace varies enormously based on its design and purpose, ranging from around 1,100°C (2,000°F) for common models to well over 3,000°C (5,400°F) for specialized laboratory equipment. Industrial electric arc furnaces, used for steelmaking, routinely reach temperatures of 1,800°C (3,300°F).
The term "electric furnace" describes several distinct technologies. The key is to understand that the heating method—whether resistance, induction, or electric arc—is what dictates the furnace's temperature capabilities and its ideal application.

The Spectrum of Electric Furnace Technology
Not all electric furnaces are created equal. The technology used to generate heat fundamentally defines the furnace's performance, cost, and purpose. The three primary methods each occupy a different segment of the temperature spectrum.
Resistance Furnaces (Muffle Furnaces & Kilns)
A resistance furnace is the most common type for laboratory and small-scale industrial work. It operates by passing a high electrical current through heating elements, which glow hot and radiate heat into an insulated chamber.
These furnaces are valued for their precise temperature control and uniform heating.
Their maximum temperature is typically limited by the materials used for the heating elements, generally falling between 1,100°C and 1,700°C (2,012°F - 3,092°F). This makes them ideal for applications like firing ceramics, dental prosthetics, and metallurgical heat treating.
Induction Furnaces
Induction furnaces use a completely different principle. They generate a powerful, high-frequency magnetic field that directly heats the conductive material (like metal) inside the furnace, without direct contact.
This method is extremely fast and clean, as the heat is generated within the material itself, minimizing contamination.
Small melting furnaces of this type can reach 1,600°C (2,900°F), while specialized vacuum induction furnaces can achieve temperatures up to 2,000°C (3,632°F) for processing high-purity alloys.
Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF)
At the highest end of the temperature and power scale is the electric arc furnace. This device creates a massive electric arc—essentially a continuous bolt of lightning—between graphite electrodes and the material to be melted.
The energy released by this arc is immense, allowing these furnaces to melt enormous quantities of material very quickly.
Industrial EAFs used for steel recycling operate at around 1,800°C (3,300°F). Highly specialized laboratory arc furnaces can push this limit significantly, exceeding 3,000°C (5,400°F) for advanced materials research.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace isn't just about finding the highest temperature. Each technology comes with a distinct set of compromises that makes it suitable for different tasks.
Temperature vs. Control
While an electric arc furnace achieves the highest temperatures, it is a violent and less precise process. A resistance furnace offers far superior temperature stability and uniformity, which is critical for sensitive processes like annealing or crystal growth.
Scale vs. Purity
EAFs are built for brute force on a massive scale, capable of melting tons of scrap steel at once. In contrast, an induction furnace is favored for smaller, high-value batches where purity is paramount, as the contactless heating prevents contamination from heating elements.
Cost and Complexity
Unsurprisingly, the equipment required to safely generate and contain a 3,000°C electric arc is vastly more complex and expensive than the components of a 1,200°C resistance kiln. The operational and infrastructure costs scale directly with the temperature and power requirements.
Matching the Furnace to the Application
To select the right technology, you must first define your goal. The required temperature is only one piece of the puzzle.
- If your primary focus is general lab work, heat treating, or firing ceramics: A resistance or muffle furnace operating up to 1,700°C provides the necessary heat and control.
- If your primary focus is melting high-purity metals or alloys: An induction furnace, capable of reaching 2,000°C, offers the required clean and efficient heating.
- If your primary focus is large-scale steel production or extreme-temperature research: An electric arc furnace, with temperatures from 1,800°C to over 3,000°C, is the only technology that provides the necessary power.
Ultimately, understanding the underlying heating mechanism is the key to selecting the right tool for your specific thermal processing goal.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical Max Temperature | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance Furnace | 1,100°C - 1,700°C | Lab work, ceramics, heat treating |
| Induction Furnace | Up to 2,000°C | High-purity metal melting, alloys |
| Electric Arc Furnace | 1,800°C - 3,000°C+ | Steelmaking, extreme-temperature research |
Need help selecting the right furnace for your lab's thermal processing needs? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering a range of electric furnaces for applications from precise heat treatment to high-temperature melting. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What is the primary advantage of using a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature and Atmosphere Control
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing



















