The fundamental difference is how heat is generated and transferred. Conventional heating methods create heat at a source and then transfer it to an object through an intermediary like air or a hot surface. Induction heating, in contrast, uses an electromagnetic field to generate heat directly inside the object itself, with no intermediary transfer.
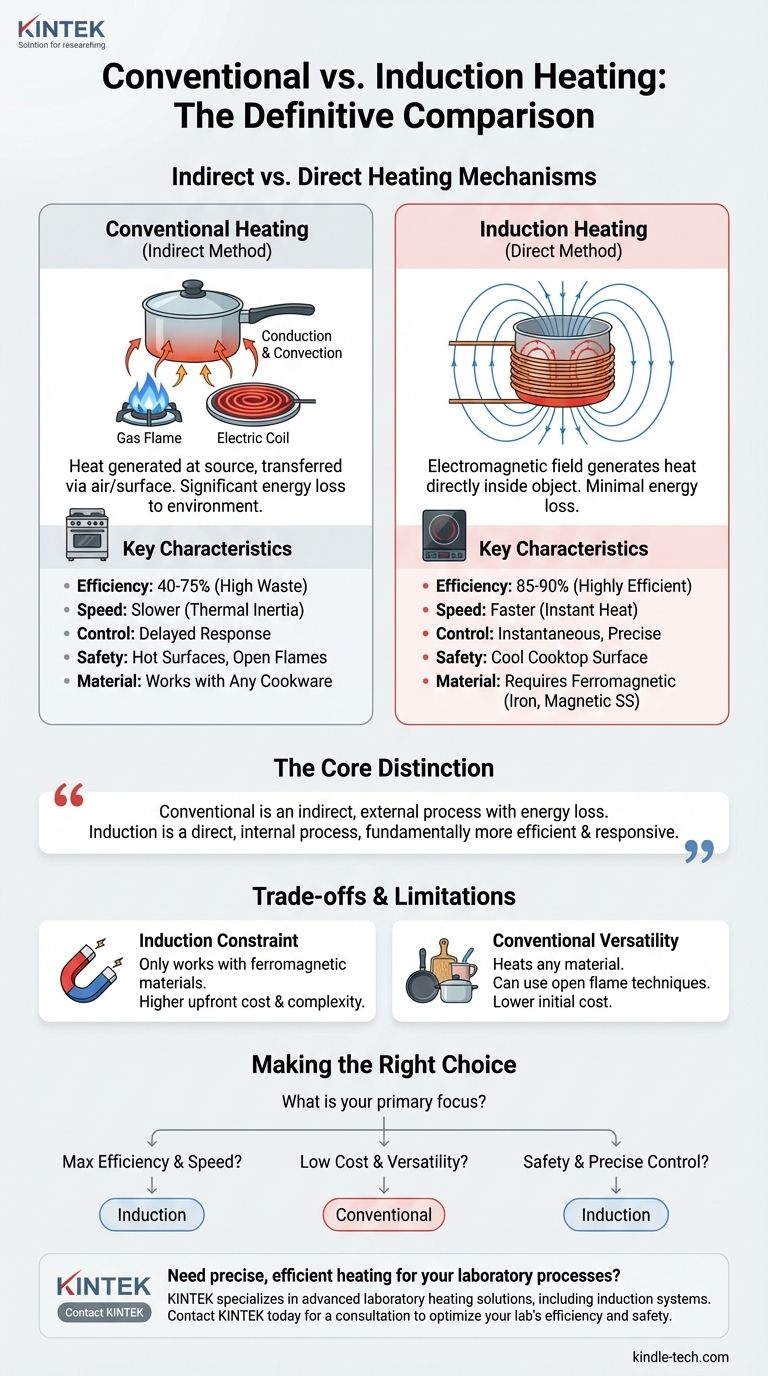
The core distinction is not just the energy source, but the mechanism of heating. Conventional heating is an indirect, external process subject to significant energy loss, while induction is a direct, internal process, making it fundamentally more efficient and responsive.
How Conventional Heating Works: The Indirect Method
Conventional heating relies on one of two primary principles to move energy from a hot source to a cooler target.
The Principles: Conduction and Convection
A heat source, such as a gas flame or an electric resistance coil, gets hot first. This thermal energy is then transferred to the target object—like a pot on a stove—through direct contact (conduction) or through a fluid like air or water (convection).
Inherent Energy Loss
Because the heat must travel from its source, through the air, and into the target, a significant amount of energy is wasted heating the surrounding environment. The heating element itself also radiates heat away from the target, contributing to inefficiency.
Common Examples
This method is the basis for most traditional heating technologies, including gas stoves, standard electric cooktops, ovens, and industrial furnaces.
How Induction Heating Works: The Direct Method
Induction heating bypasses the slow, inefficient transfer of external heat by turning the target object into its own heat source.
The Principle: Electromagnetism
An induction system uses a copper coil to generate a high-frequency alternating magnetic field. This field itself is not hot.
Generating "Eddy Currents"
When a material that is electrically conductive and magnetic (ferromagnetic), such as an iron skillet, is placed within this field, the field induces tiny, circulating electrical currents within the metal. These are known as eddy currents.
Resistance Creates Heat
The metal's natural resistance to the flow of these eddy currents creates immense friction on a molecular level, which generates heat instantly and precisely. In essence, the pan becomes the heater, not the cooktop surface.
Understanding the Key Differences
The shift from an indirect to a direct heating method creates profound differences in performance, safety, and control.
Efficiency and Speed
Induction is vastly more efficient (85-90%) because nearly all the energy is converted to heat directly where it's needed. Conventional gas (40-55%) and electric (65-75%) methods lose much of their energy to the surrounding air. This efficiency also makes induction significantly faster.
Precision and Control
Induction offers near-instantaneous control. Adjusting the power immediately changes the strength of the magnetic field and, therefore, the rate of heating. Conventional methods suffer from thermal inertia—they take time to heat up and, more importantly, to cool down.
Safety
With induction, the cooktop surface remains cool to the touch, only getting warm from residual heat transferred back from the hot pan. This dramatically reduces the risk of burns compared to a red-hot electric coil or gas grate.
The Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, induction is not universally applicable and comes with specific constraints.
The Material Constraint
The single biggest limitation of induction is that it only works with ferromagnetic materials like cast iron and many types of stainless steel. Cookware made of glass, copper, or aluminum will not heat up on an induction cooktop.
Upfront Cost and Complexity
Induction systems typically have a higher initial purchase price than their conventional counterparts. They also rely on sophisticated electronics to generate the magnetic field, which can be more complex to repair.
The Versatility of Flame
Conventional heating, particularly a gas flame, can heat any material regardless of its magnetic properties. It can also be used for techniques like charring or roasting over an open flame, something induction cannot replicate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's priorities should dictate which technology is the better fit.
- If your primary focus is maximum energy efficiency and speed: Induction is the undisputed choice due to its direct, internal heating mechanism that minimizes waste.
- If your primary focus is low initial cost and material versatility: Conventional heating offers a lower barrier to entry and works with virtually any type of cookware or material.
- If your primary focus is safety and precise temperature control: Induction provides a cooler work surface and instantaneous responsiveness that is unmatched by conventional methods.
Ultimately, understanding the core difference between indirect and direct heating empowers you to select the technology that best aligns with your true priorities.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Conventional Heating | Induction Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Indirect (external source) | Direct (internal to object) |
| Typical Efficiency | 40-75% | 85-90% |
| Speed | Slower (heats source first) | Faster (instant heat in object) |
| Control | Slower response (thermal inertia) | Instantaneous, precise control |
| Safety | Hot surfaces, open flames | Cool cooktop surface (heat is in pan) |
| Material Compatibility | Works with any material | Requires ferromagnetic materials (e.g., iron, magnetic stainless steel) |
Need precise, efficient heating for your laboratory processes?
Understanding the fundamental differences between conventional and induction heating is the first step toward optimizing your lab's efficiency and safety. The right heating technology can drastically improve your results, reduce energy costs, and enhance operator safety.
KINTEK specializes in providing advanced laboratory heating solutions, including induction systems, tailored to the unique demands of research and development. Our expertise ensures you get the precise control and efficiency your work requires.
Let us help you select the ideal heating system for your specific application.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and discover how our lab equipment can power your innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates Split Manual Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory plate hot press play in the vulcanization and molding of fluorosilicone rubber (F-LSR)?
- Why is a laboratory hot press required for Oxygen Depolarized Cathodes? Ensure Precision Molding and Conductivity.
- What are the advantages of hot pressing for PEO electrolytes? Achieve superior density and solvent-free performance.
- Why is a laboratory precision hot press necessary for processing high-performance composite solid-state electrolyte membranes?
- How is pressure generated and applied in a hot press? Master High-Intensity Hydraulic & Pneumatic Systems



















