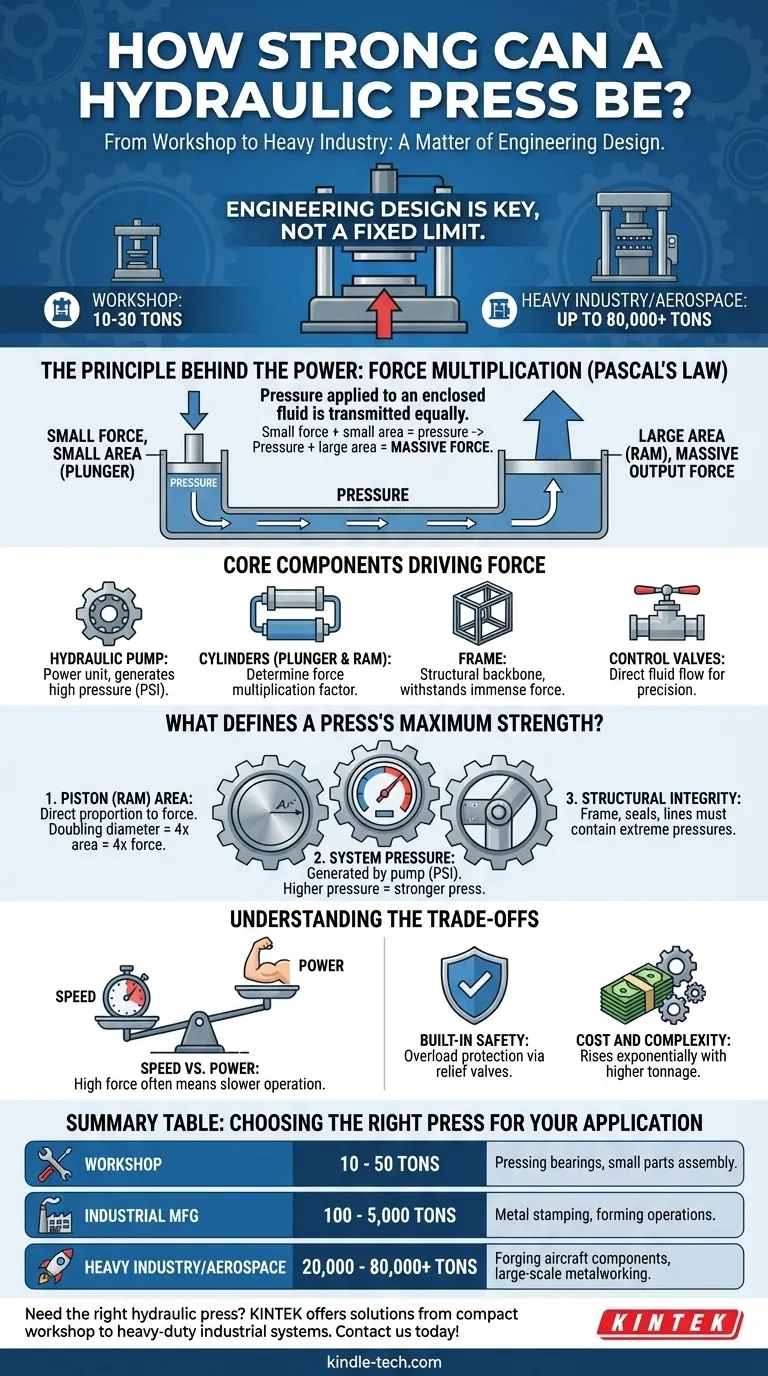
The strength of a hydraulic press is a matter of engineering design, not a fixed limit. While small workshop presses generate 10 to 30 tons of force, the largest industrial presses used in aerospace and heavy forging can exceed 50,000 and even approach 80,000 tons of force. Their power is determined by the hydraulic system's pressure and the size of the piston applying that pressure.
A hydraulic press doesn't create energy; it multiplies force. Its immense strength comes from a core principle of fluid dynamics: applying a small force over a small area generates pressure that, when exerted on a much larger area, results in a massive output force.

The Principle Behind the Power: Force Multiplication
The remarkable strength of a hydraulic press is based on a concept known as Pascal's Law. This principle states that pressure applied to an enclosed, incompressible fluid is transmitted equally throughout the fluid.
How it Works
A basic press consists of two interconnected cylinders of different sizes, a smaller one called the plunger and a larger one called the ram. Both are filled with hydraulic fluid.
When a small force is applied to the plunger, it creates pressure in the fluid. This pressure is transmitted undiminished to the larger ram.
Because the ram has a much larger surface area, the same pressure results in a much larger output force. This is the essence of force multiplication.
The Core Components Driving Force
Several key components work together to generate and contain this force:
- Hydraulic Pump: This is the power unit that pressurizes the hydraulic fluid (typically oil). The pump's ability to generate high pressure is a primary factor in the press's strength.
- Hydraulic Cylinders (Plunger and Ram): The ratio of the ram's area to the plunger's area determines the force multiplication factor.
- Frame: This is the structural backbone of the press. Its role is critical, as it must be strong enough to withstand the immense forces it generates without deforming or failing.
- Control Valves: These direct the flow of high-pressure fluid, allowing the operator to extend or retract the ram with precision.
What Defines a Press's Maximum Strength?
The "tonnage" of a press is not an arbitrary number. It is the direct result of three primary engineering factors.
1. Piston (Ram) Area
This is the most significant factor in force multiplication. The force generated is directly proportional to the surface area of the ram's face.
Doubling the diameter of the ram quadruples its surface area, and therefore quadruples the potential output force for a given system pressure.
2. System Pressure
The hydraulic pump creates the pressure, measured in pounds per square inch (PSI). A more powerful pump that can generate higher PSI will result in a stronger press, assuming all other components can handle it.
Industrial systems often operate at pressures of 3,000 PSI or more.
3. Structural Integrity
A press can only be as strong as its weakest point. The frame, seals, and hydraulic lines must be engineered to contain the extreme pressures and forces involved.
The structural design is often the ultimate limiting factor in a press's maximum tonnage, as building a frame to resist 50,000 tons of force is a monumental engineering challenge.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Immense power does not come without compromises. The design of any hydraulic press involves balancing competing factors.
Speed vs. Power
There is a direct trade-off between force and speed. To move a large ram a short distance, the small plunger must travel a much greater distance.
This means that presses with very high force multiplication ratios are often very slow in operation.
Built-in Safety
A key advantage of hydraulic systems is their inherent overload protection. A pressure relief valve can be set to a maximum, preventing the press from exceeding its structural limits.
This makes them much safer and more durable than mechanical presses, which can catastrophically fail if overloaded.
Cost and Complexity
As the required tonnage increases, the cost and complexity rise exponentially. A 1,000-ton press requires a significantly more robust frame, a more powerful pump, and larger components than a 100-ton press.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The required strength of a hydraulic press is entirely dependent on the task it needs to perform.
- If your primary focus is workshop tasks like pressing bearings or small parts: A press in the 10 to 50-ton range is typically more than sufficient.
- If your primary focus is industrial manufacturing like metal stamping or forming: Presses commonly range from 100 to 5,000 tons.
- If your primary focus is extreme heavy industry like forging aircraft components: These applications require the world's largest presses, often exceeding 20,000 tons.
Ultimately, the strength of a hydraulic press is a direct and calculated outcome of its design, engineered to solve a specific problem.
Summary Table:
| Application | Typical Force Range | Key Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Workshop | 10 - 50 tons | Pressing bearings, small parts assembly |
| Industrial Manufacturing | 100 - 5,000 tons | Metal stamping, forming operations |
| Heavy Industry/Aerospace | 20,000 - 80,000+ tons | Forging aircraft components, large-scale metalworking |
Need the right hydraulic press for your specific application? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and industrial machinery, offering solutions from compact workshop presses to heavy-duty industrial systems. Our experts can help you select the perfect press based on your force requirements, space constraints, and operational needs. Contact us today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK's hydraulic solutions can enhance your productivity and precision!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What is the use of KBr? Master Sample Prep for Accurate IR Spectroscopy
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy



















