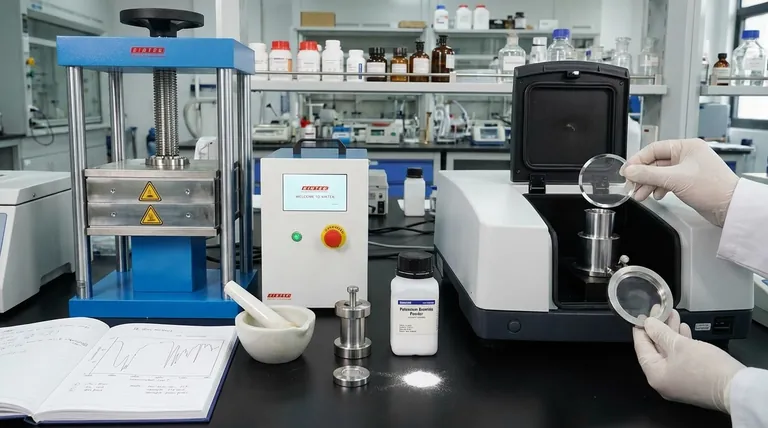
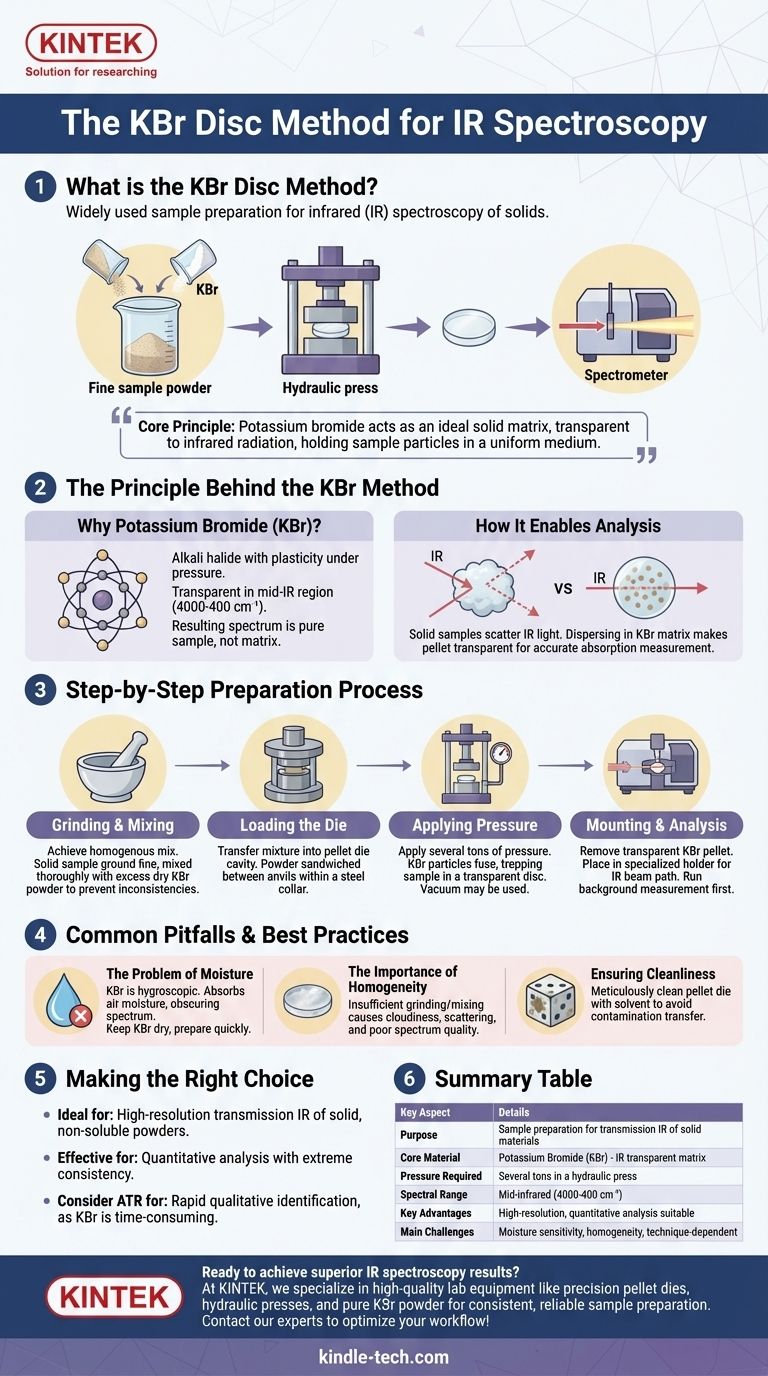
The KBr disc method is a widely used sample preparation technique in infrared (IR) spectroscopy for analyzing solid samples. It involves finely grinding a sample, mixing it with high-purity potassium bromide (KBr) powder, and compressing the mixture under high pressure to form a small, transparent pellet or disc. This disc can then be placed directly in the path of the spectrometer's infrared beam.
The core principle is straightforward: potassium bromide is transparent to infrared radiation and becomes plastic under pressure. This allows it to act as an ideal solid matrix, holding the sample particles in a uniform, transparent medium that does not interfere with the spectral measurement.

The Principle Behind the KBr Method
Why Potassium Bromide?
The choice of KBr is deliberate. Alkali halides, like KBr, possess the unique physical property of flowing under extreme pressure. This plasticity allows the fine powder to fuse into a solid, glass-like disc.
Critically, KBr has no significant absorbance in the mid-infrared region (4000-400 cm⁻¹), which is the area of interest for most analyses. This IR transparency ensures that the resulting spectrum is purely that of the sample, not the matrix holding it.
How It Enables Analysis
Solid samples cannot typically be analyzed directly by transmission IR spectroscopy because they scatter most of the infrared light. By dispersing the sample powder within the KBr matrix, the resulting pellet becomes transparent enough for the IR beam to pass through, allowing for an accurate absorption measurement.
The Step-by-Step Preparation Process
Step 1: Grinding and Mixing
The first and most critical step is to achieve a homogenous mix. The solid sample is ground into an extremely fine powder, typically with an agate mortar and pestle.
This fine sample powder is then mixed with a much larger amount of dry KBr powder. Thorough mixing is essential to ensure the sample is evenly distributed throughout the final disc, preventing inconsistencies in the spectrum.
Step 2: Loading the Die
The KBr/sample mixture is carefully transferred into the cavity of a pellet die. This apparatus consists of a stainless steel collar and two anvils (or bolts) that fit snugly inside.
The powder is poured into the collar, which rests on one anvil. The second anvil is then inserted on top, sandwiching the powder.
Step 3: Applying Pressure
The entire die assembly is placed into a hydraulic press. Pressure is applied, often in the range of several tons, which compacts the powder.
Under this pressure, the KBr particles deform and fuse together, trapping the sample particles within the newly formed transparent disc. Some procedures require a vacuum to be applied to the die during pressing to remove trapped air and moisture.
Step 4: Mounting and Analysis
Once the pressure is released, the transparent KBr pellet is carefully removed from the die. It is often retained within the steel collar for support.
This collar is then placed into a specialized sample holder that fits into the spectrometer's sample compartment. A background measurement, using a pure KBr disc, is typically run first to correct for any minor absorbance from the KBr itself or atmospheric moisture.
Common Pitfalls and Best Practices
The Problem of Moisture
Potassium bromide is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the air. Water has very strong absorption bands in the IR spectrum and can easily obscure important features of the sample.
To avoid this, KBr must be kept perfectly dry (often stored in an oven) and the pellet should be prepared and analyzed quickly.
The Importance of Homogeneity
If the sample is not ground finely enough or mixed thoroughly, the final pellet will be cloudy. This cloudiness causes the IR light to scatter, resulting in a poor-quality spectrum with a sloping baseline and reduced signal intensity.
Ensuring Cleanliness
The pellet die must be meticulously cleaned before use, often with a solvent like chloroform. Any residual contamination on the die surfaces can be transferred to the KBr pellet and will appear in the final spectrum, leading to incorrect analysis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
A properly prepared KBr disc yields a high-quality spectrum, but the process is technique-dependent.
- If your primary focus is analyzing a solid, non-soluble powder: The KBr disc method is the gold standard for high-resolution transmission IR spectroscopy.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis: This method can be effective, but requires extreme consistency in sample weight, grinding, and pressing to ensure reproducibility.
- If your primary focus is a rapid qualitative identification: While effective, the KBr method is more time-consuming than modern techniques like Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR), which may be preferable for quick scans.
Ultimately, mastering the KBr disc technique provides a powerful and reliable tool for the detailed infrared analysis of solid materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Sample preparation for transmission IR spectroscopy of solid materials |
| Core Material | Potassium Bromide (KBr) - IR transparent matrix |
| Pressure Required | Several tons in a hydraulic press |
| Spectral Range | Mid-infrared region (4000-400 cm⁻¹) |
| Key Advantages | High-resolution spectra, suitable for quantitative analysis |
| Main Challenges | Moisture sensitivity, requires homogeneous mixing, technique-dependent |
Ready to achieve superior IR spectroscopy results?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need to master techniques like the KBr disc method. Our precision pellet dies, hydraulic presses, and pure KBr powder ensure consistent, reliable sample preparation for accurate spectral analysis.
Whether you're setting up a new lab or optimizing your current IR workflow, our experts can help you select the right equipment for your specific application.
Contact our team today to discuss your laboratory needs and discover how KINTEK solutions can enhance your analytical capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- kbr pellet press 2t
- Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press for XRF KBR FTIR Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy



















