In short, a PVD coating is exceptionally thin. The typical thickness of a Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) coating ranges from 0.25 to 5 microns (micrometers). For context, a human hair is about 70 microns thick. In certain precision applications, such as optical coatings, the layer can be as thin as 0.02 microns.
The core takeaway is that the thinness of a PVD coating is not a limitation but a deliberate feature. This precision allows for the enhancement of a part's surface properties—like hardness and corrosion resistance—without altering its fundamental dimensions, which is critical for high-performance components.
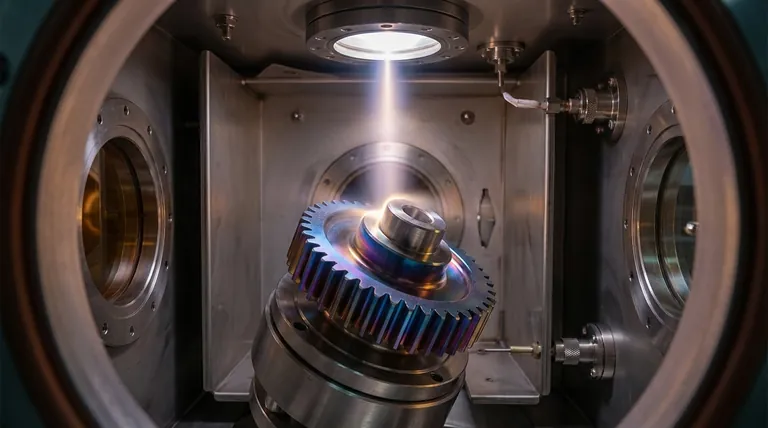
Why PVD Coatings Are Intentionally Thin
The value of PVD lies in its ability to add significant performance benefits with a minimal physical footprint. This is a direct result of the application process and the goals it's designed to achieve.
Preserving Critical Dimensions and Geometry
For many components, even a tiny change in dimension can lead to failure. The ultra-thin nature of PVD coatings makes them ideal for these applications.
A coating of just a few microns adds extreme surface hardness without changing a part's size enough to affect its tolerance. This is essential for components like plastic injection molds, fine blanking tools, and HSS or carbide cutting tools, where precision is paramount. A thinner coating (typically 3-5μm) also preserves the sharpness of a cutting blade, which reduces cutting force and heat generation during use.
Molecular-Level Application
PVD is a vacuum deposition process where a solid material is vaporized in a vacuum chamber and deposited, atom by atom, onto the surface of a part.
This molecular-level application is inherently precise. It allows for the creation of a very dense, well-adhered, and extremely uniform thin film. The process grants engineers fine control over the coating's final thickness and properties.
Function Over Bulk
The primary goal of a PVD coating is to impart new properties to the surface of an object, not to add bulk.
Whether the goal is increasing hardness, reducing friction, preventing corrosion, or providing a decorative color, these properties can be achieved with a very thin layer. The underlying substrate material still provides the structural integrity, while the coating provides the enhanced surface performance.
How Thickness Impacts Performance
The specified thickness of a PVD coating is directly tied to its intended function. A thicker coating is not always better and is chosen based on the desired outcome.
Hardness and Wear Resistance
PVD coatings form ceramic and composite layers that are significantly harder than the base metal. For example, a Titanium Nitride (TiN) coating can dramatically increase the fatigue limit and endurance of a titanium alloy part.
Thicker coatings (approaching 5 microns) are generally used for applications demanding maximum wear and abrasion resistance, as there is more material to withstand erosion over time.
Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
The PVD process creates a dense, non-porous layer that acts as an effective barrier against oxidation and corrosion. Even a thin layer of 1-2 microns can provide substantial protection for materials like stainless steel.
Decorative Finishes
For decorative applications on items like jewelry, watches, or architectural fixtures, a very thin coating is often all that is needed. A layer of 0.25 to 1.5 microns is typically sufficient to provide a durable, vibrant color without obscuring the texture and fine details of the underlying material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the PVD process has inherent characteristics that are important to understand.
Dependence on Substrate Quality
A PVD coating is so thin that it will perfectly replicate the texture of the underlying surface. It will not hide or fill in scratches, tool marks, or other imperfections. A flawless, mirror-polish PVD finish can only be achieved if the part is polished to a mirror finish before coating.
Not a Structural Repair Method
PVD is a surface enhancement process, not a repair technology. It cannot be used to rebuild worn-down parts or add significant material thickness. Its purpose is to improve the performance of a part that is already dimensionally correct.
A Line-of-Sight Process
In most PVD processes, the coating material travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate. This means complex internal channels or deeply recessed features can be difficult or impossible to coat uniformly without complex part rotation fixtures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The ideal PVD coating thickness is determined by your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is high-precision tooling (molds, cutting edges): Opt for a thinner coating (1-3 microns) to preserve sharp edges and maintain critical tolerances while gaining hardness and lubricity.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance (for sliding components): Specify a thicker coating in the 3-5 micron range, provided the slight dimensional change is acceptable for the part's function.
- If your primary focus is a decorative finish (jewelry, architectural hardware): A thinner coating (0.25-1.5 microns) will provide the desired color and durability without obscuring surface details.
Ultimately, PVD coating thickness is a precisely controlled variable engineered to deliver specific performance enhancements without compromise.
Summary Table:
| Application Goal | Recommended Thickness | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| High-Precision Tooling (Molds, Cutters) | 1-3 microns | Preserves sharp edges, maintains tolerances, adds hardness |
| Maximum Wear Resistance (Sliding Parts) | 3-5 microns | Enhanced abrasion resistance, longer component life |
| Decorative Finishes (Jewelry, Hardware) | 0.25-1.5 microns | Durable color, retains surface detail, corrosion protection |
Need a precise PVD coating solution for your lab equipment or tools? KINTEK specializes in high-performance PVD coatings that enhance hardness, corrosion resistance, and durability without compromising part dimensions. Whether you're coating lab tools, molds, or precision instruments, our expertise ensures optimal thickness and performance for your specific application. Contact us today to discuss how our PVD coatings can extend the life and performance of your laboratory equipment!
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD silicon deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- What materials are deposited in PECVD? Discover the Versatile Thin-Film Materials for Your Application
- What is meant by vapor deposition? A Guide to Atomic-Level Coating Technology



















