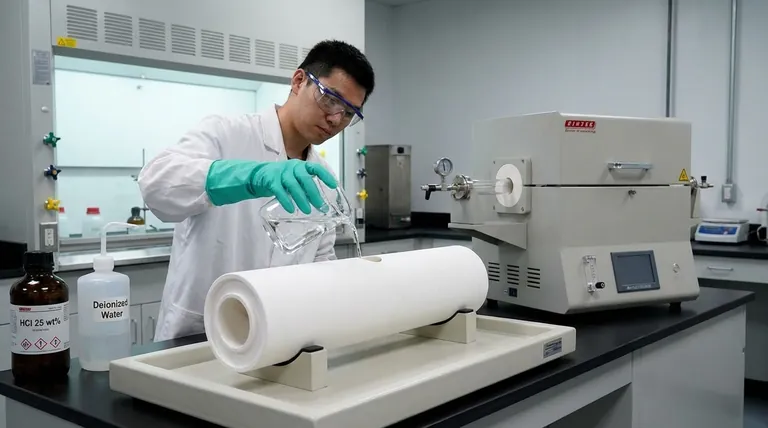
To properly clean an alumina furnace tube, you must first remove it from the furnace and let it cool completely. The standard procedure involves carefully filling the tube with a diluted hydrochloric acid solution (at least 25 wt%), allowing it to soak for approximately 10 minutes to dissolve contaminants, and then thoroughly rinsing it with fresh water until all traces of acid are gone.
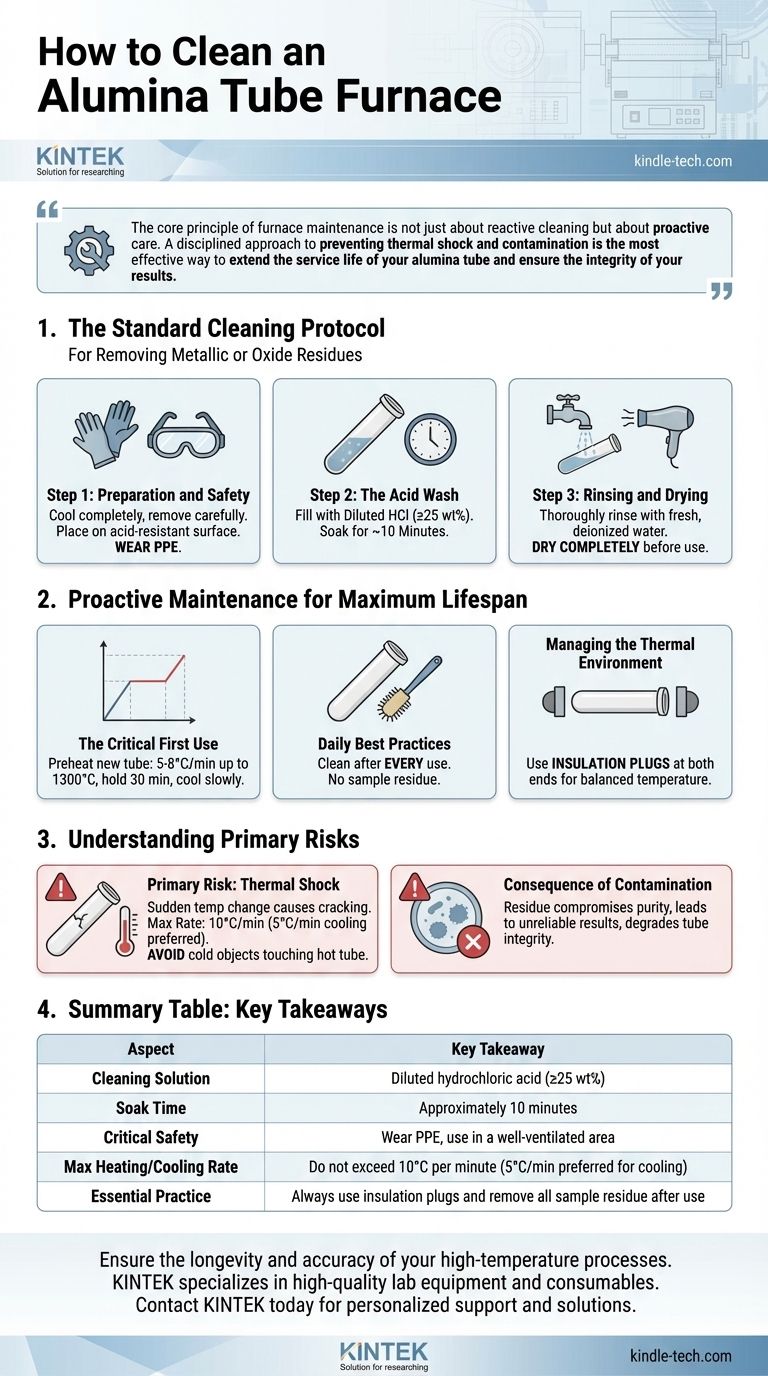
The core principle of furnace maintenance is not just about reactive cleaning but about proactive care. A disciplined approach to preventing thermal shock and contamination is the most effective way to extend the service life of your alumina tube and ensure the integrity of your results.

The Standard Cleaning Protocol
For removing metallic or oxide residues, an acid wash is the accepted method. This should be performed in a well-ventilated area with appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
Step 1: Preparation and Safety
First, ensure the alumina tube is completely cool and has been carefully removed from the furnace assembly. Place it on a stable, clean surface that is resistant to acid. Always wear gloves and eye protection when handling chemicals.
Step 2: The Acid Wash
Carefully fill the tube with a hydrochloric acid (HCl) solution with a concentration of at least 25 wt%. Be mindful of the chemical's reactivity with the specific contaminants you are trying to remove.
Let the tube soak for about 10 minutes. This duration is typically sufficient to dissolve common residues without damaging the alumina surface.
Step 3: Rinsing and Drying
After soaking, carefully drain the acid into an appropriate waste container. Thoroughly rinse the inside of the tube with fresh, deionized water multiple times to neutralize and remove any remaining acid.
Allow the tube to dry completely before placing it back into service. Introducing moisture into a high-temperature environment can cause thermal shock and damage the tube.
Proactive Maintenance for Maximum Lifespan
Cleaning is a necessary task, but the best strategy is to minimize the need for it. Proper operational procedures are critical for protecting your investment.
The Critical First Use
When using a new alumina tube, it must be preheated to eliminate manufacturing stresses and burn off any surface pollutants. A typical program involves heating at a rate of 5-8°C per minute up to 1300°C, holding for 30 minutes, and then cooling slowly.
Daily Best Practices
After every use, ensure the inside of the tube is clean and that no sample material remains. Residue left at high temperatures can fuse to the tube wall, making it difficult to remove and potentially contaminating future experiments.
Managing the Thermal Environment
Insulation plugs are essential for proper operation. Place ceramic plugs at both ends of the tube to help create a balanced temperature field. This prevents the ends of the tube from overheating, which can damage the O-ring seals and compromise the system's air tightness.
Understanding the Primary Risks
Mishandling an alumina tube can lead to premature failure. Understanding the two main risks—thermal shock and contamination—is key to avoiding them.
The Primary Risk: Thermal Shock
Alumina is a ceramic and is brittle. A sudden, drastic change in temperature will cause it to crack. This is known as thermal shock.
Never allow a low-temperature object to touch the furnace tube while it is hot. Most critically, adhere to strict heating and cooling rates. A rate not exceeding 10°C per minute is a safe guideline, with a slower cooling rate of 5°C per minute being preferable.
The Consequence of Contamination
Any sample residue left inside the tube can become a source of contamination for subsequent runs. This compromises the purity of your work and can lead to inaccurate or unreliable results. Over time, fused residue can also chemically attack the alumina, degrading the tube's structural integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your maintenance approach should align with your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is routine cleaning after a run: Follow the acid wash protocol carefully, ensuring thorough rinsing and complete drying.
- If your primary focus is maximizing tube lifespan: Prioritize slow, controlled heating and cooling rates and always avoid introducing cold items into a hot furnace.
- If your primary focus is ensuring experimental purity: Pre-bake every new tube and maintain a strict cleaning discipline, never leaving sample residue behind after a cycle.
Ultimately, consistent and careful handling is the definitive factor in the long-term performance and reliability of your furnace tube.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Cleaning Solution | Diluted hydrochloric acid (≥25 wt%) |
| Soak Time | Approximately 10 minutes |
| Critical Safety | Wear PPE, use in a well-ventilated area |
| Max Heating/Cooling Rate | Do not exceed 10°C per minute (5°C/min preferred for cooling) |
| Essential Practice | Always use insulation plugs and remove all sample residue after use |
Ensure the longevity and accuracy of your high-temperature processes. Properly maintaining your alumina furnace tubes is critical for reliable results and protecting your lab equipment investment. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including furnace tubes and accessories, to serve all your laboratory needs. Let our experts help you optimize your furnace maintenance protocol. Contact KINTEK today for personalized support and solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control



















