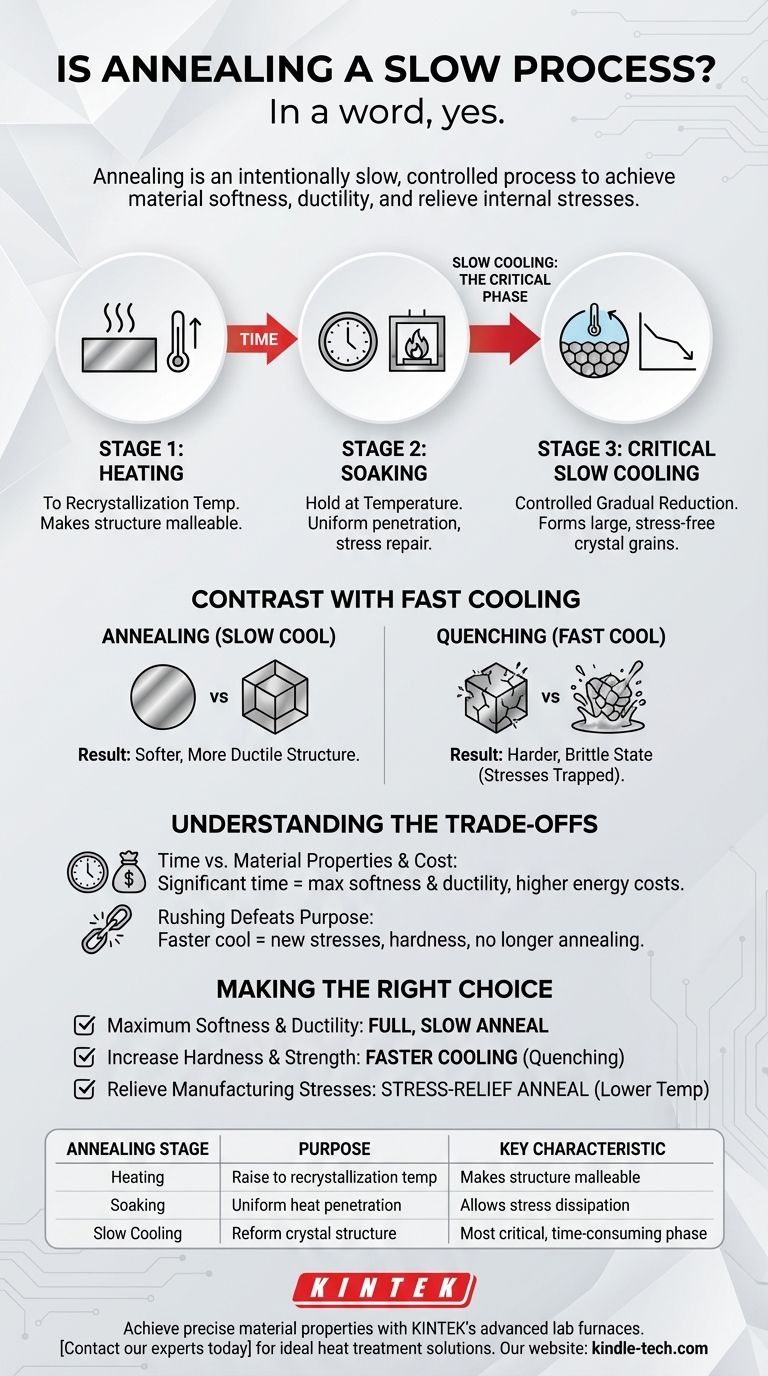
In a word, yes. Annealing is an intentionally slow and highly controlled process. This deliberate pace, particularly during the cooling stage, is not a byproduct but a fundamental requirement for achieving the desired changes in the material's internal structure. The goal is to soften the metal, increase its ductility, and relieve internal stresses.
The slowness of annealing is its most critical feature. The controlled, gradual cooling phase is what allows the material's crystal structure to reform in a uniform, low-stress state, which is the entire purpose of the procedure.
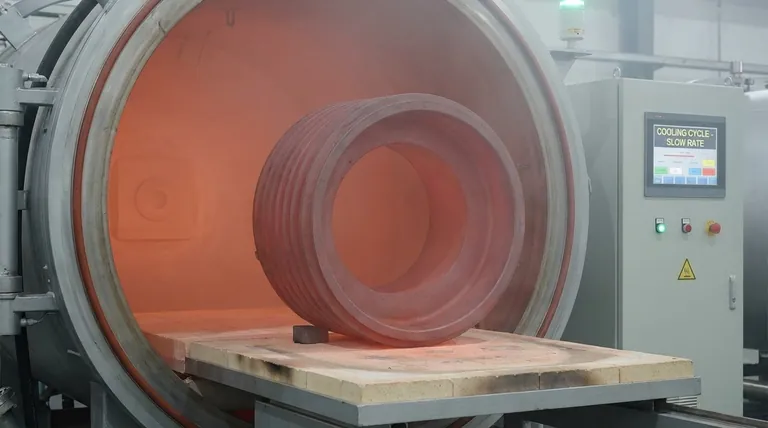

Why Annealing Relies on a Slow, Controlled Pace
Annealing is a three-stage process, and while heating and holding the material take time, the cooling stage is the most defining and time-consuming part. Understanding each stage reveals why speed is the enemy of a successful anneal.
Stage 1: Heating to a Specific Temperature
The first step is to heat the metal to its recrystallization temperature. At this point, the material's crystalline structure becomes malleable enough for new, defect-free grains to begin forming, though the metal itself remains solid.
Stage 2: Soaking at Temperature
The material is then held, or "soaked," at this elevated temperature for a set period. This allows the heat to penetrate the material uniformly and provides the necessary time for the internal structure to fully repair itself and for internal stresses to dissipate.
Stage 3: The Critical Slow Cooling Phase
This is the heart of the annealing process. The material must be cooled at a very slow, controlled rate. This gradual reduction in temperature allows the new, stress-free crystal grains to form and grow in a large, orderly fashion, resulting in a softer, more ductile structure.
Contrast with Fast Cooling
To understand the importance of slow cooling, consider its opposite: quenching. Rapidly cooling a hot metal in water or oil traps its crystal structure in a hard, brittle state. Annealing's slow cooling achieves the exact opposite outcome.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heat treatment process always involves balancing time, cost, and the desired final properties of the material. Annealing is no exception.
Time vs. Material Properties
The primary trade-off is time versus outcome. The significant time required for a furnace to heat, soak, and then cool very slowly is the "cost" you pay for achieving maximum softness, ductility, and machinability.
Why Rushing Defeats the Purpose
Attempting to speed up the cooling phase of an anneal negates its benefits. A faster cool would introduce new internal stresses and result in a harder, less ductile material. You would no longer be annealing; you would be performing a different heat treatment, such as normalizing, which yields different properties.
Energy and Operational Costs
The long cycle times directly translate to higher energy consumption and operational costs. The furnace is occupied for an extended period, which must be factored into any production schedule or budget.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "slowness" of annealing is a tool, not a drawback. Your specific goal determines whether it's the right tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is maximum softness and ductility: A full, slow anneal is the correct and necessary process to achieve these properties.
- If your primary focus is to increase hardness and strength: A faster cooling process like quenching, often followed by tempering, is the appropriate choice.
- If you only need to relieve internal stresses from manufacturing: A lower-temperature, often faster, stress-relief anneal might be a more efficient alternative.
Ultimately, the speed of any heat treatment is a deliberate variable used to precisely engineer the final properties of the material.
Summary Table:
| Annealing Stage | Purpose | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Heating | Raise metal to recrystallization temperature | Makes the crystalline structure malleable |
| Soaking | Hold at temperature for uniform heat penetration | Allows internal stresses to dissipate |
| Slow Cooling | Reform crystal structure in a low-stress state | Most critical, time-consuming phase for achieving desired properties |
Achieve precise material properties with KINTEK's advanced lab furnaces. Whether you need to perform a full anneal for maximum softness or a stress-relief cycle for efficiency, KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables that deliver consistent, controlled results. Contact our experts today to discuss the ideal heat treatment solution for your laboratory's specific materials and goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can graphite withstand heat? Unlocking its extreme 3,600°C potential in inert environments
- What temperature can graphite withstand? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Potential
- Why is graphite used in furnaces? For Extreme Heat, Purity, and Efficiency
- What are the applications of graphite material? Leveraging Extreme Heat and Precision for Industrial Processes
- Does graphite have a melting point? Unlocking the Extreme Heat Resistance of Graphite



















