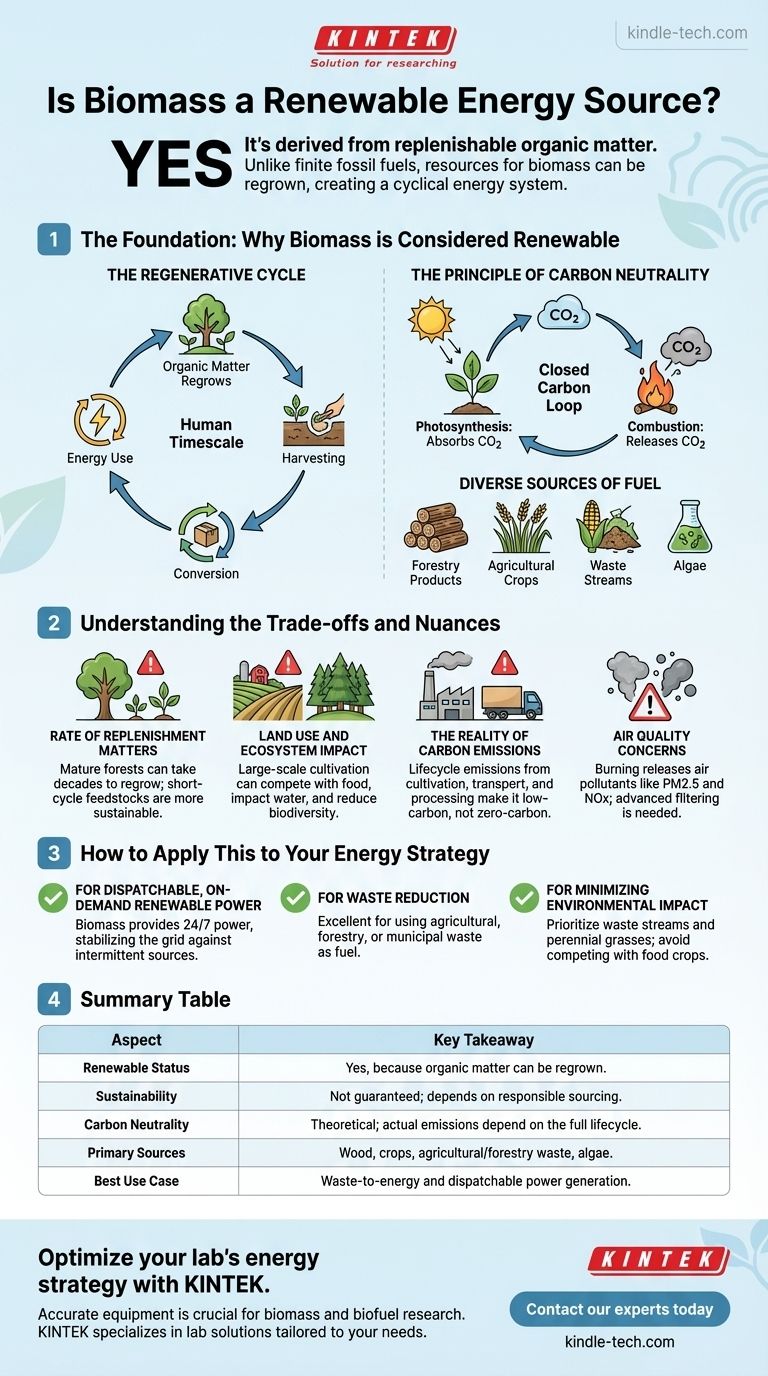
Yes, biomass is classified as a renewable energy source. This is because it is derived from organic matter—such as plants, wood, and waste—that can be replenished on a human timescale. Unlike finite fossil fuels that take millions of years to form, the resources for biomass can be regrown, creating a cyclical energy system.
While biomass is technically renewable, its true sustainability is not guaranteed. The environmental benefit of biomass depends entirely on responsible sourcing and management, making the distinction between "renewable" and "sustainable" critically important.
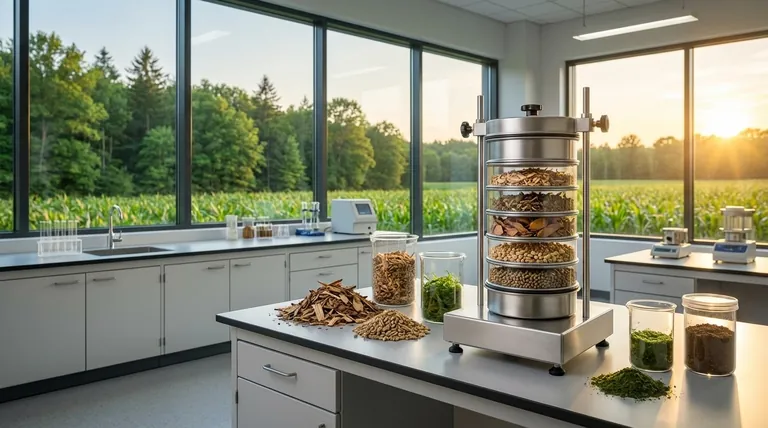

The Foundation: Why Biomass is Considered Renewable
Biomass energy is built on the principle of using organic materials as fuel. This classification as renewable hinges on two core concepts: a regenerative cycle and a balanced carbon loop.
The Regenerative Cycle
Unlike coal, oil, or natural gas, which are finite resources, biomass comes from living or recently living organisms. The primary sources—including dedicated energy crops, agricultural waste, forestry residues, and even algae—can be grown and harvested. This ability to regrow the fuel source is the fundamental reason it is categorized as renewable.
The Principle of Carbon Neutrality
In theory, biomass is a carbon-neutral energy source. As plants grow, they absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere through photosynthesis. When this biomass is later burned or converted into energy, it releases that same amount of CO2 back into the atmosphere. This creates a closed loop, where the carbon released is offset by the carbon absorbed during the plant's growth, preventing a net increase in atmospheric CO2.
Diverse Sources of Fuel
The term "biomass" covers a wide range of organic materials. This diversity allows for flexibility in sourcing fuel, which can include:
- Forestry Products: Wood pellets, chips, and logging residues.
- Agricultural Crops: Dedicated energy crops like switchgrass and miscanthus.
- Waste Streams: Agricultural waste (corn stover), food processing waste, and municipal solid waste.
- Algae: A developing source that can be cultivated for biofuel production.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
Viewing biomass as unconditionally "green" is a common oversimplification. Its environmental impact is highly dependent on how the biomass is sourced, processed, and used.
The Rate of Replenishment Matters
A resource being renewable does not mean it is instantly available. Harvesting a mature forest for energy and replacing it with saplings creates a "carbon debt" that can take decades, or even centuries, to repay. Truly sustainable biomass relies on feedstocks with short regrowth cycles, such as agricultural waste or fast-growing grasses.
Land Use and Ecosystem Impact
Growing dedicated energy crops at a large scale can have significant environmental consequences. It may compete with food production for arable land and water, drive up food prices, and lead to deforestation or the conversion of natural habitats to monoculture farms, reducing biodiversity.
The Reality of Carbon Emissions
The concept of carbon neutrality is an ideal. In practice, the entire lifecycle of biomass energy is not emission-free. Energy is consumed in cultivating, harvesting, drying, and transporting the biomass, all of which typically relies on fossil fuels. These "upstream" emissions mean that most biomass energy systems are low-carbon, not zero-carbon.
Air Quality Concerns
Burning solid biomass, particularly wood, releases air pollutants like particulate matter (PM2.5), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Without advanced filtering and combustion technology, biomass power plants can negatively impact local air quality and public health.
How to Apply This to Your Energy Strategy
Your evaluation of biomass should be guided by your specific goals. It is not a universally perfect solution, but a tool with specific strengths and weaknesses.
- If your primary focus is dispatchable, on-demand renewable power: Biomass is a strong contender because, unlike intermittent solar and wind, it can generate power 24/7 to stabilize the grid.
- If your primary focus is waste reduction: Using agricultural, forestry, or municipal waste as a fuel source is an excellent application of biomass, as it solves a disposal problem while generating energy.
- If your primary focus is minimizing environmental impact: Prioritize biomass sourced from waste streams or from perennial grasses grown on marginal land, and be wary of systems that rely on clear-cutting forests or competing with food crops.
Ultimately, judging biomass requires looking beyond its renewable label to understand the origin and lifecycle of its fuel.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Renewable Status | Yes, because organic matter can be regrown. |
| Sustainability | Not guaranteed; depends on responsible sourcing. |
| Carbon Neutrality | Theoretical; actual emissions depend on the full lifecycle. |
| Primary Sources | Wood, crops, agricultural/forestry waste, algae. |
| Best Use Case | Waste-to-energy and dispatchable power generation. |
Optimize your lab's energy strategy with KINTEK.
Whether you're processing biomass samples, analyzing biofuels, or researching sustainable energy solutions, having the right laboratory equipment is crucial for accurate and efficient results. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your research needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can support your biomass and renewable energy projects. Let us help you achieve your sustainability goals with reliable, precision-engineered equipment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- What are the factors affecting sieving performance and efficiency? Optimize Your Particle Separation Process
- What is the function of sieving equipment in CuAlMn alloys? Master Pore Size Precision
- How are vibratory sieve shakers and standard sieves utilized to analyze the effects of biomass torrefaction? Optimize Grindability
- What is the primary function of a mechanical sieve shaker for biomass analysis? Optimize Particle Size Distribution
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification



















