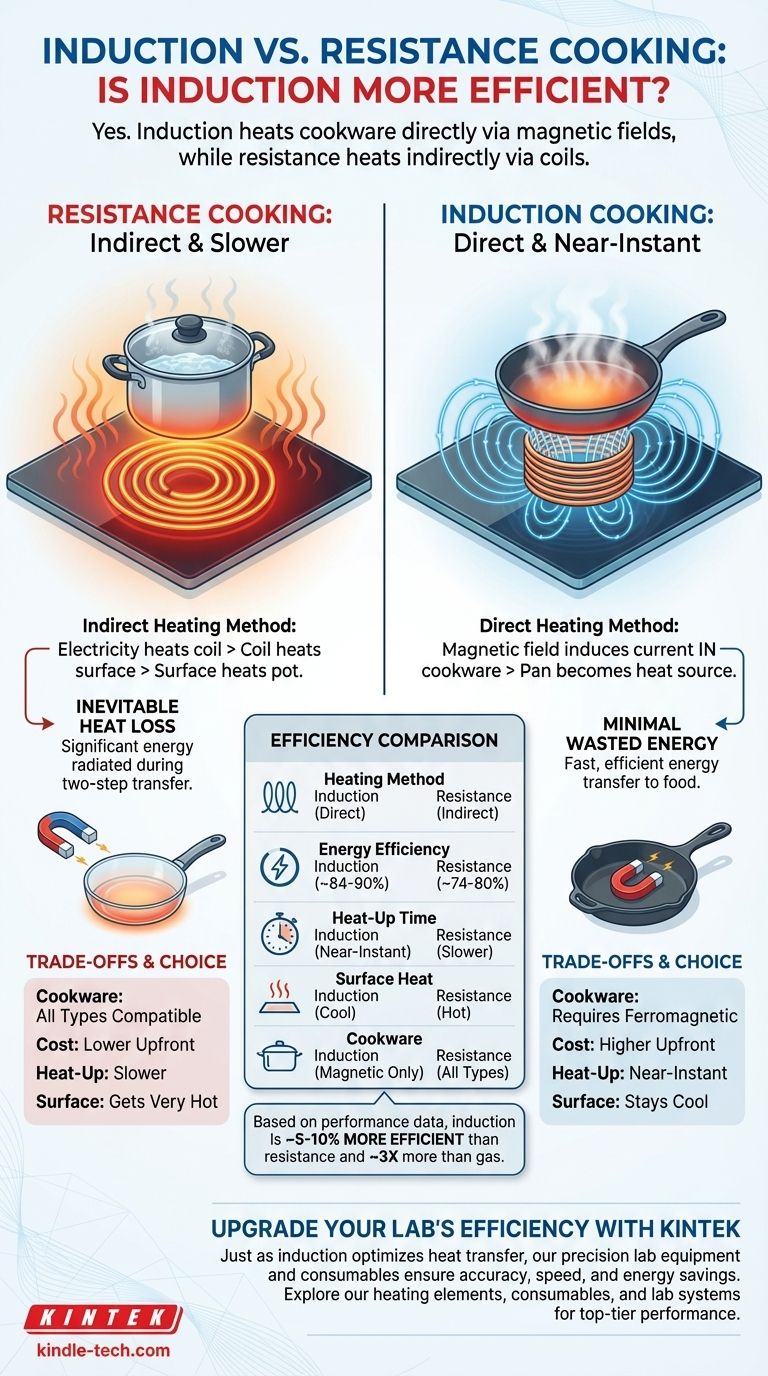
Yes, induction cooking is more efficient than conventional resistance cooking. The core reason is that induction technology heats the cookware directly through an electromagnetic field, whereas a resistance cooktop must first heat a coil or surface, which then transfers that heat to the cookware, resulting in significant energy loss.
The fundamental difference lies in the method of heat transfer. Induction turns the pot itself into the heat source for near-instant, highly efficient cooking, while resistance heating is an indirect, two-step process that wastes energy heating the cooktop and the surrounding air.
How Resistance Cooking Works
The Indirect Heating Method
A conventional electric cooktop uses the principle of electrical resistance. Electricity flows through a metal coil located beneath the cooktop surface.
This coil resists the flow of electricity, causing it to get extremely hot and glow.
Inevitable Heat Loss
This heat must first transfer from the glowing-hot coil to the glass or ceramic cooktop surface, and only then does it transfer to the bottom of your pot or pan.
During this two-step process, a significant amount of heat radiates away from the coil and the cooktop surface into the surrounding air, representing wasted energy.
How Induction Cooking Works
The Principle of Electromagnetism
An induction cooktop uses a powerful, high-frequency electromagnet instead of a simple heating coil.
When you turn the cooktop on, this creates a rapidly oscillating magnetic field.
Direct Heating of Cookware
When you place a pan made of a magnetic material (like iron or some stainless steel) onto the surface, this magnetic field induces an electric current directly within the metal of the pan.
This internal current flow is what generates the heat. The cookware becomes its own heat source, while the cooktop surface itself remains cool to the touch.
The Result: Minimal Wasted Energy
Because the pan is heated directly, very little energy is lost to the cooktop surface or the surrounding environment. This makes the transfer of energy to your food incredibly fast and efficient.
Based on performance data, induction cooktops are approximately 5-10% more efficient than conventional electric resistance units. For context, they are about three times more efficient than gas cooktops.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Cookware Requirement
The primary consideration for induction is that it only works with ferromagnetic cookware. Your pots and pans must contain iron to react to the magnetic field.
Cast iron and most stainless steel pans work well. Cookware made of glass, pure aluminum, or copper will not heat up on an induction surface. A simple test is to see if a magnet sticks firmly to the bottom of the pan.
Upfront Cost
Induction cooktops and ranges typically have a higher initial purchase price compared to their traditional electric resistance counterparts.
The Learning Curve
The speed and responsiveness of induction can be surprising. Water boils much faster, and temperature changes are nearly instantaneous, which may require a slight adjustment in cooking style.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Choosing between these technologies depends entirely on your priorities for performance, budget, and convenience.
- If your primary focus is maximum energy efficiency and speed: Induction is the clear technological winner, delivering faster cooking times and lower energy consumption.
- If your primary focus is a lower initial cost and compatibility with all cookware: A conventional electric resistance cooktop is a reliable and more budget-friendly choice.
Ultimately, understanding how each technology generates heat empowers you to select the tool that best fits your needs in the kitchen.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Induction Cooking | Resistance Cooking |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Directly heats cookware via magnetic field | Heats a coil, which then transfers heat to cookware |
| Energy Efficiency | ~84-90% | ~74-80% |
| Heat-Up Time | Near-instantaneous | Slower, requires surface to heat first |
| Cooktop Stays Cool | Yes (only the pan gets hot) | No (surface gets very hot) |
| Cookware Compatibility | Requires magnetic cookware (e.g., cast iron, magnetic stainless steel) | Works with all types of cookware |
Upgrade your kitchen's efficiency with KINTEK's precision lab equipment and consumables. Just as induction technology optimizes heat transfer for cooking, our solutions ensure accuracy, speed, and energy savings for your laboratory processes. Whether you need reliable heating elements, durable consumables, or advanced lab systems, KINTEK serves your laboratory needs with top-tier performance. Contact us today to explore how our products can enhance your lab's productivity and reduce operational costs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM





