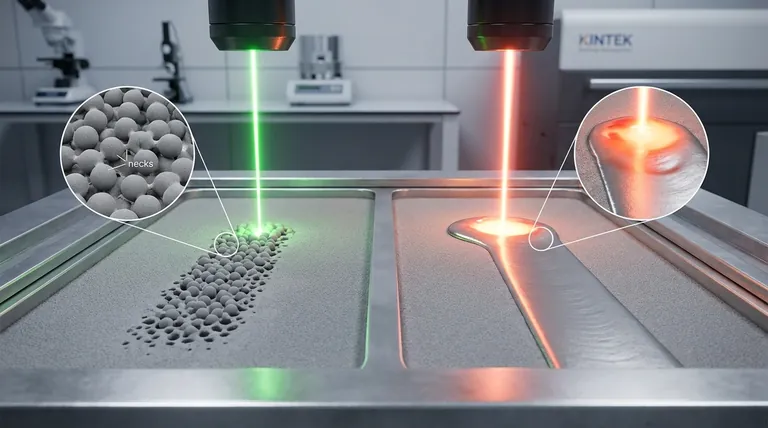
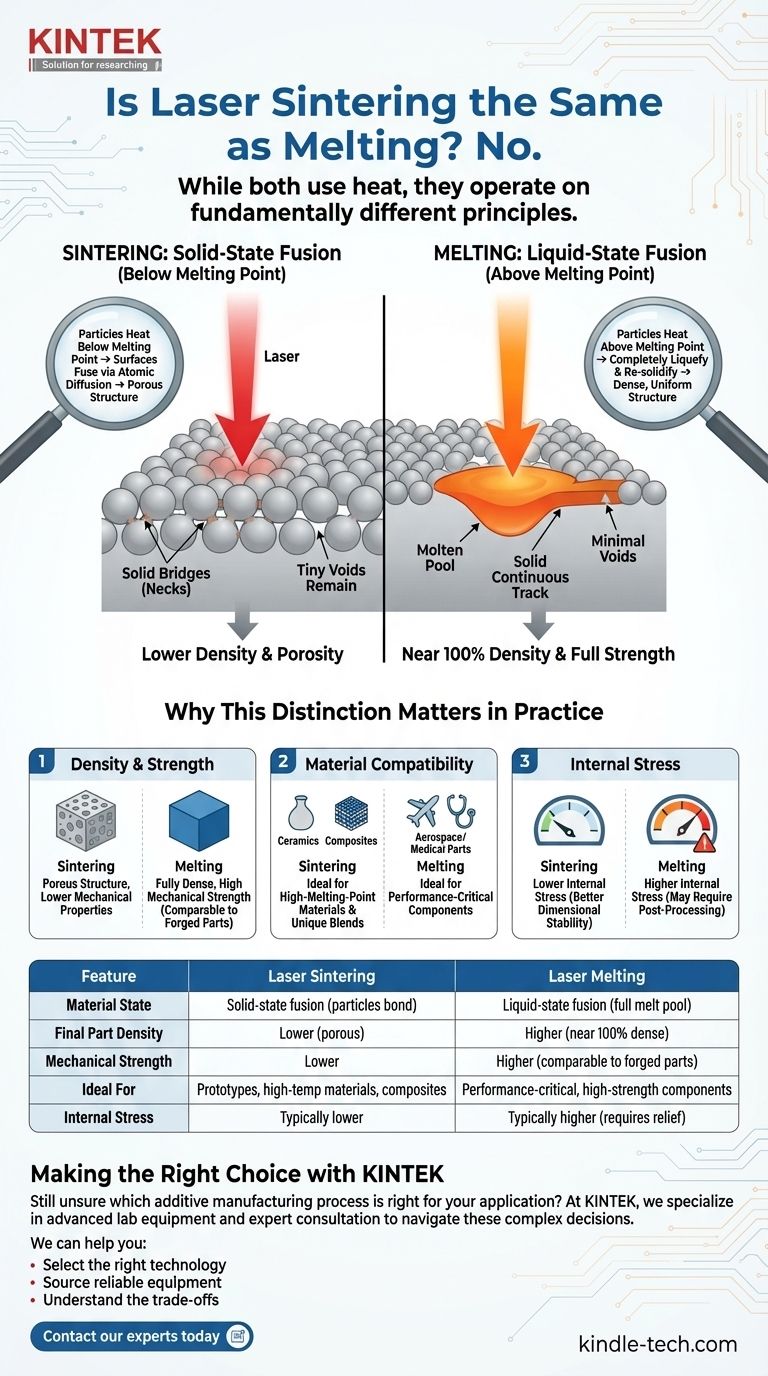
No, laser sintering is not the same as melting. While both processes use heat to form a solid object from powder, they operate on fundamentally different principles. Laser sintering heats particles just enough for their surfaces to fuse together without the material ever becoming a complete liquid. Melting, by contrast, uses enough energy to turn the powder into a molten pool that solidifies into a dense part.
The critical distinction lies in the state of the material during fusion. Sintering is a solid-state process where particles are "welded" together, while melting is a liquid-state process where particles are completely liquefied and reformed. This difference has profound implications for a finished part's density, strength, and material properties.
The Fundamental Difference: Solid-State vs. Liquid-State Fusion
To truly grasp the concept, you must understand what happens at the microscopic level. The terms "sintering" and "melting" describe two distinct physical transformations.
What Happens During Sintering?
In a sintering process, a laser provides thermal energy to a bed of powder. This heat is carefully controlled to remain below the material's melting point.
The energy excites the atoms on the surface of the powder granules, causing them to diffuse across the boundary and bond with neighboring particles. This process, known as atomic diffusion, creates solid bridges or "necks" between the particles.
The core material of each particle never liquefies. Think of it like pressing two very sticky balls of dough together—they fuse where they touch, but they don't melt into a single puddle. The result is a solid mass that is inherently porous, as tiny voids remain between the fused particles.
What Happens During Melting?
In a process that uses melting, such as Selective Laser Melting (SLM), the laser's energy is high enough to raise the material's temperature above its melting point.
This completely breaks down the crystalline structure of the powder, turning a localized area into a tiny, molten pool.
This liquid metal then cools and solidifies into a fully dense, uniform structure. As the laser moves, it creates a continuous track of solid material with minimal to no voids, much like a welder laying a bead.
Why This Distinction Matters in Practice
The difference between a solid-state and liquid-state process is not just academic; it directly determines the characteristics and applications of the final part.
Impact on Density and Strength
Sintered parts are naturally porous. The voids left between the bonded particles result in a lower density compared to a solid block of the same material. This porosity generally leads to reduced mechanical properties, such as tensile strength and fatigue resistance.
Melted parts are almost fully dense. Because the material fully liquefies and re-solidifies, parts made via melting can achieve densities over 99%, giving them mechanical properties that are often comparable to traditionally forged or cast parts.
Impact on Material Compatibility
Sintering is highly effective for materials with extremely high melting points, such as certain ceramics or refractory metals. Reaching the energy level required to melt these materials is often impractical or can damage the material, making sintering the superior choice.
It also allows for the creation of unique material blends by sintering powders of different materials that might not be suitable for melting together.
Impact on Internal Stress
The intense and rapid heating and cooling cycles involved in melting can introduce significant residual stress into a part. This stress can cause warping or cracking and often requires post-processing heat treatments to relieve.
Because sintering occurs at lower temperatures, it typically induces less internal stress, potentially leading to better dimensional stability straight out of the machine.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither process is universally "better." Each comes with a distinct set of advantages and disadvantages that make it suitable for different goals.
Sintering: Speed and Material Flexibility
The primary advantage of sintering is its ability to process materials that are difficult to melt. It can also be a faster process as less energy is required per volume of material.
The Drawback of Sintering: Porosity
The unavoidable trade-off for this flexibility is porosity. For any application where maximum strength, density, or fluid-tightness is critical, a purely sintered part is often unsuitable without secondary processing steps like infiltration (filling the pores with another material).
Melting: Superior Mechanical Performance
The clear benefit of melting-based processes is performance. The resulting dense, homogenous parts are strong, durable, and suitable for high-stress, performance-critical applications in aerospace, medical, and automotive industries.
The Drawback of Melting: Stress and Complexity
The high energy involved in melting creates challenges. The process requires more careful control to manage residual stress, and it may be limited in the types of materials it can effectively process without introducing defects.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's requirements should dictate the process you choose. Understanding this core difference empowers you to select the right tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and mechanical strength: You should choose a process based on full melting, like SLM or Electron Beam Melting (EBM), for performance-critical components.
- If your primary focus is working with high-temperature ceramics or creating novel material composites: Sintering (like Selective Laser Sintering - SLS) offers a distinct advantage where full melting is impractical.
- If your primary focus is creating prototypes or parts where structural integrity is not the top priority: Sintering can be a faster and more versatile option.
By understanding the physics of fusion, you can look past marketing terms and select the additive manufacturing process that truly aligns with your engineering requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Laser Sintering | Laser Melting |
|---|---|---|
| Material State | Solid-state fusion (particles bond) | Liquid-state fusion (full melt pool) |
| Final Part Density | Lower (porous) | Higher (near 100% dense) |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower | Higher (comparable to forged parts) |
| Ideal For | Prototypes, high-melting-point materials, composites | Performance-critical, high-strength components |
| Internal Stress | Typically lower | Typically higher (may require stress relief) |
Still unsure which additive manufacturing process is right for your application?
The choice between sintering and melting is critical for achieving the desired material properties, density, and performance in your final parts. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and expert consultation needed to navigate these complex decisions.
We can help you:
- Select the right technology for your specific material and performance goals.
- Source reliable equipment for materials research and process development.
- Understand the trade-offs to optimize your manufacturing workflow.
Let's discuss your project requirements. Contact our experts today to ensure you choose the best process for success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What factors influence the general design of a tube furnace? Match Your Process with the Perfect System
- What are the benefits of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature & Atmosphere Control
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab



















