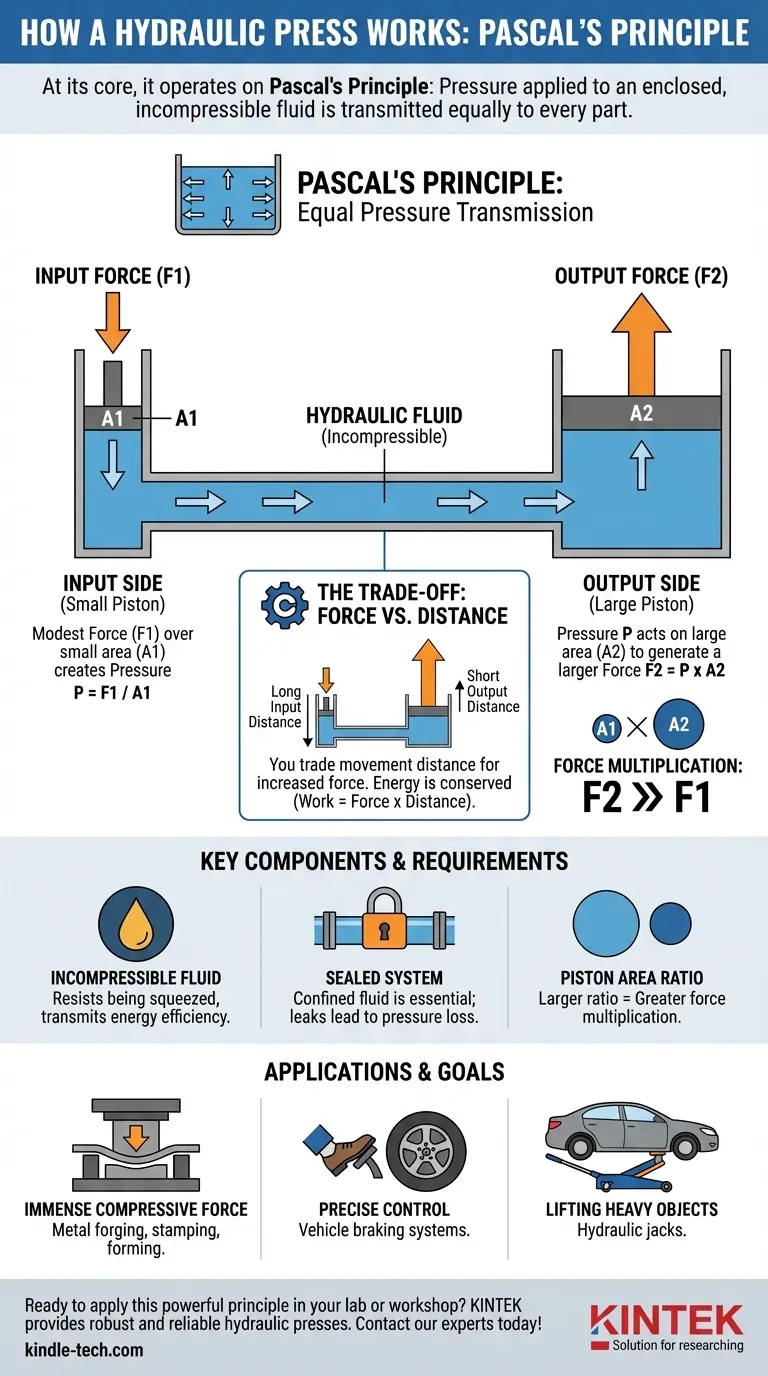
At its core, a hydraulic press operates on a fundamental law of fluid mechanics known as Pascal's Principle. This principle states that pressure applied to an enclosed, incompressible fluid is transmitted equally and without loss to every part of the fluid and the walls of its container. This allows the press to take a small input force and multiply it into a significantly larger output force.
The central concept is not just that pressure is transmitted, but that it is transmitted equally to areas of different sizes. By applying a force to a small piston, you create a pressure that, when acting on a much larger piston, generates a proportionally massive output force.

Deconstructing Pascal's Principle
To understand how a hydraulic press achieves force multiplication, we must first break down the components of the principle itself. It relies on the relationship between force, pressure, and area.
What is Pressure?
Pressure is simply the amount of force exerted over a specific area. The formula is Pressure = Force / Area. A small force concentrated on a tiny area can create immense pressure.
The Core Tenet of the Law
Pascal's Law is built on this concept. When you apply pressure at any single point in a confined fluid—like the oil in a hydraulic system—that same pressure level is instantly mirrored everywhere else within that fluid.
The Role of the Fluid
This principle only works effectively if the fluid is incompressible. Hydraulic systems use specialized oil because it resists being squeezed, ensuring that the energy from the input force is used to move the output piston, not to compress the fluid itself.
How the Press Achieves Force Multiplication
The genius of the hydraulic press lies in its simple mechanical design, which exploits Pascal's Law to its full potential. The system consists of two pistons of different sizes connected by a chamber of hydraulic fluid.
The Input Side (Small Piston)
An operator or a small motor applies an initial, modest force (let's call it F1) to a small piston with a small surface area (A1). This action generates a specific amount of pressure within the fluid, calculated as P = F1 / A1.
Pressure Transmission
According to Pascal's Principle, this exact pressure (P) is transmitted undiminished throughout the fluid. It pushes in all directions with the same intensity, including against the face of the second, larger piston.
The Output Side (Large Piston)
This second piston has a much larger surface area (A2). Since the pressure (P) is the same, the resulting output force (F2) is calculated as F2 = P x A2.
Because A2 is significantly larger than A1, the output force F2 becomes proportionally larger than the input force F1. This relationship is the key to the entire mechanism: you get a massive force advantage.
Understanding the Trade-offs
This force multiplication does not come from nowhere; it is a conversion. Physical laws are always balanced, and the hydraulic press is no exception. Understanding the trade-offs is crucial for practical application.
The Force vs. Distance Trade-off
To generate that large output force, you must pay a price in distance. In order to move the large piston a small distance, the small piston must be moved a much greater distance. You are trading movement distance for an increase in force. Energy is conserved; the work done on both sides remains the same (Work = Force x Distance).
The Need for a Sealed System
Pascal's Law only applies to a confined fluid. Any leak in the system will cause a loss of pressure, immediately reducing the output force and rendering the press inefficient or inoperable. The integrity of seals and hoses is paramount.
Fluid Properties Matter
The choice of hydraulic oil is not arbitrary. It is chosen for its incompressibility, its ability to lubricate the moving parts of the system, and its stability under high temperatures and pressures. Using the wrong fluid can lead to poor performance and system damage.
Applying the Principle to Your Goal
The hydraulic press is a tool that converts distance into force. How you leverage this conversion depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is immense compressive force: You need a system with the largest possible ratio between the output and input piston areas. This is the design used in heavy industrial applications like metal forging, stamping, and forming.
- If your primary focus is precise, powerful control: You need a system that allows for fine modulation of the input force. This principle is used in vehicle braking systems, where a small push on the brake pedal results in a powerful and evenly applied clamping force on the wheels.
- If your primary focus is lifting heavy objects: You can use a system where a small, repeatable pump action on the input piston incrementally raises the output piston. This is the mechanism behind the common hydraulic jack used to lift a car.
By understanding that a hydraulic press trades a long input travel for a short and powerful output stroke, you can appreciate its application across countless engineering challenges.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Pascal's Principle | Foundation of Operation | Pressure in a confined fluid is transmitted equally in all directions. |
| Small Input Piston | Applies Initial Force | Creates high pressure with a small force over a small area. |
| Hydraulic Fluid | Transmits Pressure | Must be incompressible (e.g., specialized oil). |
| Large Output Piston | Generates Amplified Force | Converts equal pressure into a much larger force due to its larger area. |
| Trade-off | Force vs. Distance | A small input force over a long distance creates a large output force over a short distance. |
Ready to apply this powerful principle in your lab or workshop?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust and reliable lab equipment, including hydraulic presses tailored for your specific needs—whether for material testing, sample preparation, or industrial prototyping. Our expertise ensures you get the precise force multiplication and control your projects demand.
Let's build your solution together. Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK hydraulic press can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy



















