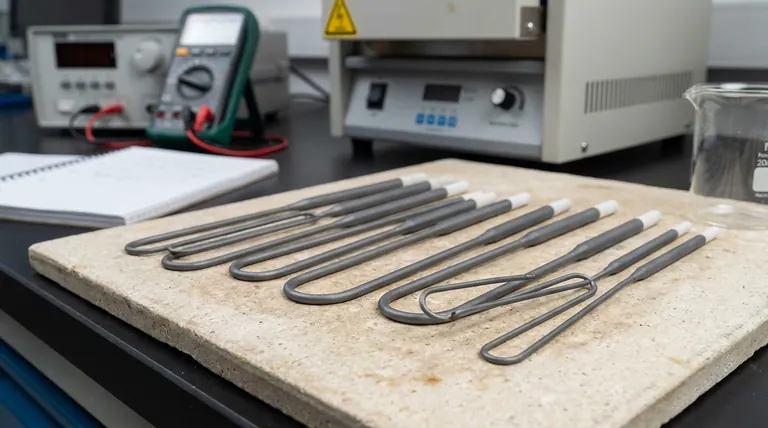
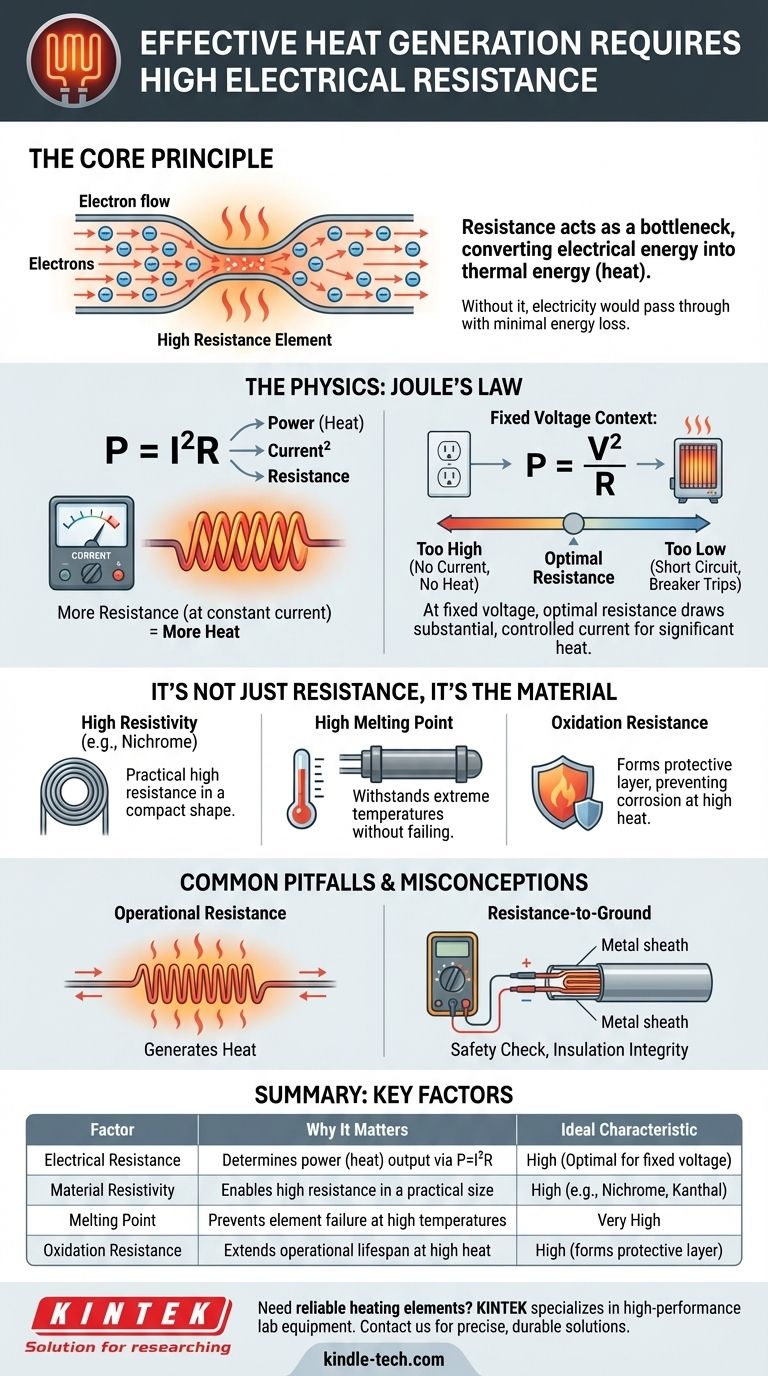
To generate heat effectively, a heating element must have high electrical resistance. This high resistance is the very property that allows the element to act as a bottleneck for electrical current, converting the energy of flowing electrons into thermal energy, which we perceive as heat. Without this resistance, electricity would pass through with minimal energy loss.
The core principle is that a heating element's job is to efficiently convert electrical energy into heat. This requires a material with high resistivity—an intrinsic property that allows it to achieve a high total resistance in a practical shape, get very hot without melting or degrading, and operate safely at a fixed voltage.

The Physics of Electrical Heating: Resistance is Key
To understand why high resistance is necessary, we must look at the fundamental relationship between power, current, and resistance. This relationship is the foundation of how nearly all electric heaters, from toasters to industrial furnaces, operate.
Why High Resistance Creates Heat
The amount of heat generated is directly related to the electrical power dissipated by the element. This is described by Joule's first law, often expressed with the power formula: P = I²R.
Here, Power (P) is the heat generated per second, Current (I) is the flow of electrons, and Resistance (R) is the opposition to that flow. This formula clearly shows that for a given amount of current, power (heat) is directly proportional to the resistance. More resistance means more heat.
The Role of a Fixed Voltage
This can seem confusing when considering another version of the power formula: P = V²/R, where V is Voltage. This version suggests that power is inversely proportional to resistance, implying lower resistance is better.
The key is understanding your source. Most heating appliances plug into a wall outlet, which provides a fixed voltage (e.g., 120V or 240V). In this fixed-voltage scenario, the element's resistance is what determines how much current it draws.
An extremely high resistance would allow almost no current to flow, generating no heat. An extremely low resistance (like a copper wire) would create a short circuit, drawing massive current but failing to dissipate it as controlled heat before a breaker trips or the wire melts.
Therefore, the goal is an optimal resistance: high enough to generate significant heat, but low enough to allow a substantial, controlled current to flow from the fixed voltage source.
It's Not Just Resistance, It's the Material
A simple number in ohms doesn't tell the whole story. The material from which the element is made is just as critical as its final resistance value. The best materials for heating elements have a combination of specific properties.
High Specific Resistance (Resistivity)
Resistivity is an intrinsic property of a material that measures how strongly it resists electric current. Materials like Nichrome (a nickel-chromium alloy) have high resistivity.
This means you can create a component with high resistance using a relatively short and robust piece of wire, which is practical for building compact and durable appliances.
High Melting Point
A heating element is useless if it melts when it does its job. The material must have a very high melting point to withstand the extreme temperatures it is designed to produce. This ensures a long and reliable operational life.
Resistance to Oxidation
At high temperatures, many materials react with oxygen in the air and corrode or burn out quickly. Effective heating element alloys form a protective oxide layer on their surface, which prevents further degradation and dramatically extends their lifespan.
Common Pitfalls and Misconceptions
Understanding the context of a resistance measurement is crucial. The resistance of an element during operation is fundamentally different from a diagnostic measurement meant to check for failures.
Operational Resistance vs. Resistance-to-Ground
The "high resistance" we've discussed is the element's operational resistance—the opposition to current flowing from one end of the element to the other to generate heat.
A completely different measurement is resistance-to-ground. This is a safety and maintenance check to ensure the element is electrically isolated from its metal sheath or furnace housing. An acceptable reading here might be 90-100 ohms, while a low reading (e.g., under 10 ohms) indicates an electrical short and a failure, as insulators have broken down. These are two distinct concepts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting or evaluating a heating element requires looking beyond a single number and focusing on the overall objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum heat from a wall outlet: You need an element with the optimal resistance for its fixed voltage, allowing it to draw significant current safely and convert it to heat according to
P = V²/R. - If your primary focus is durability and a long lifespan: The choice of material is paramount. You need an alloy like nichrome or Kanthal with high resistivity, a high melting point, and excellent oxidation resistance.
- If your primary focus is operational safety: You must distinguish between the element's designed resistance and its resistance-to-ground, which is a critical measure of insulation integrity.
Ultimately, effective heating is achieved not by simply choosing "high" or "low" resistance, but by engineering an element from the right material with the optimal resistive properties for its specific voltage and application.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Why It Matters | Ideal Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Resistance | Determines power (heat) output via P=I²R | High (Optimal for fixed voltage) |
| Material Resistivity | Enables high resistance in a practical size | High (e.g., Nichrome, Kanthal) |
| Melting Point | Prevents element failure at high temperatures | Very High |
| Oxidation Resistance | Extends operational lifespan at high heat | High (forms protective layer) |
Need a reliable heating element for your laboratory equipment?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables. Our expertise ensures you get heating elements with the optimal resistance and material properties for precise temperature control, durability, and safety in your applications.
Let us help you achieve efficient and reliable heat generation. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the working temperature of a heating element? Match Material to Your Application's Heat Needs
- How are tubular heating elements made? A Guide to Durable & Efficient Heating
- What advantages do carbon/carbon (C/C) composite resistors offer? High-Resilience Heating for Si2N2O Synthesis
- Is tungsten the most heat resistant material? It depends on your application's environment.
- How do you control the temperature of a resistance? Master Voltage, Resistance, and PWM Methods
- Why are platinum and nickel-chromium wires used in TGA? Ensure High-Temperature Data Accuracy
- How long does fiber insulation last? The Truth About Its Real Lifespan & Performance
- What are the common materials used as heating elements? Find the Right Material for Your Temperature Needs



















