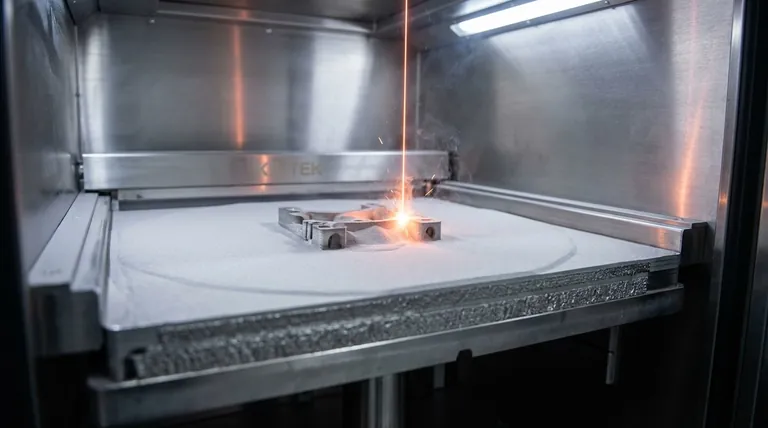
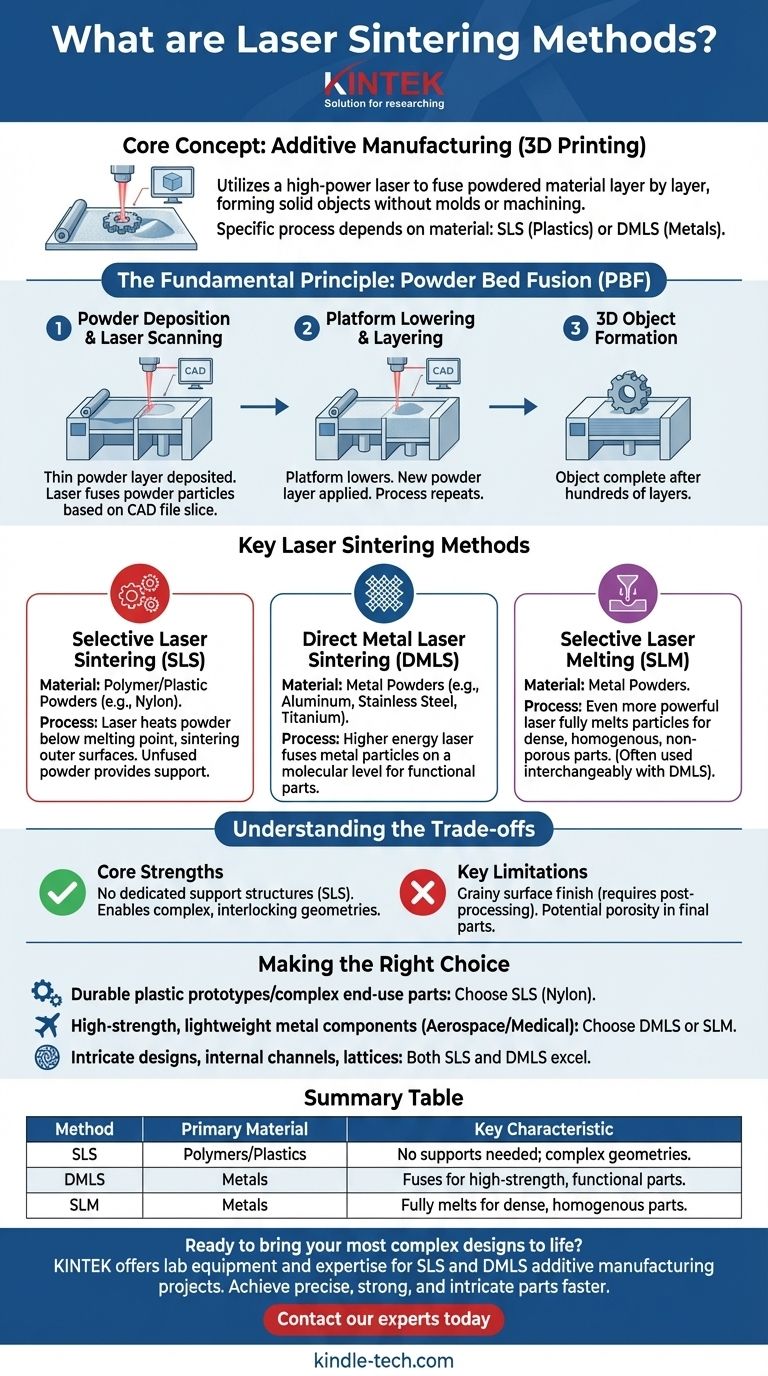
At its core, laser sintering is a method of additive manufacturing, or 3D printing. It employs a high-power laser to fuse powdered material together, layer by layer, based on a digital 3D model. The laser selectively heats the powder particles to their melting or sintering point, causing them to bond and form a solid object without the need for molds or traditional machining.
The term "laser sintering" is often used as a general category, but its true meaning depends on the material. The specific process is typically called Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) when working with plastics and Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) when working with metals.
The Fundamental Principle: Powder Bed Fusion
All laser sintering methods fall under a broader manufacturing category called powder bed fusion (PBF). The underlying principle is consistent across all variations of the technology.
How the Process Works
A machine deposits an extremely thin layer of powdered material onto a build platform. A high-power laser, guided by a computer-aided design (CAD) file, then scans a cross-section of the part, fusing the powder particles together. The platform then lowers by one layer's thickness, a new layer of powder is applied, and the process repeats until the object is complete.
The Role of the CAD File
The entire operation is directed by a 3D CAD model. This digital file is "sliced" into hundreds or thousands of digital layers. Each slice serves as a precise blueprint, telling the laser exactly where to fire to create that specific cross-section of the final part.
Key Laser Sintering Methods Explained
While the general process is similar, the specific terminology changes based on the material being used. This distinction is critical for engineering applications.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
This term almost exclusively refers to the sintering of polymer and plastic powders, most commonly nylon. In SLS, the laser heats the powder to just below its melting point, causing the particles' outer surfaces to fuse—a process known as sintering. The surrounding, unfused powder provides support for the part as it is built.
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
When working with metal powders, such as aluminum, stainless steel, or titanium, the process is called DMLS. The laser's energy is significantly higher, heating the metal particles to a point where they fuse on a molecular level. This creates parts with mechanical properties comparable to those made through traditional manufacturing.
A Note on Selective Laser Melting (SLM)
SLM is a closely related process for metals that uses an even more powerful laser to fully melt the powder particles, creating a completely homogenous, non-porous part. While technically distinct from DMLS (sintering vs. melting), the terms are often used interchangeably in the industry.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Laser sintering offers powerful advantages, but it's essential to recognize its limitations to determine if it's the right choice for a given application.
Core Strengths
The single greatest advantage of laser sintering (specifically SLS) is that it requires no dedicated support structures. The unused powder in the build chamber supports overhanging features, allowing for the creation of extremely complex, interlocking geometries that are impossible to produce with other methods.
Key Limitations to Consider
Parts produced via laser sintering often have a grainy surface finish right out of the machine and may require post-processing steps like media tumbling or sanding to achieve a smooth surface. Additionally, the final parts can have a degree of porosity, which may be a factor for certain high-performance applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct process requires aligning your material needs with the capabilities of each technology.
- If your primary focus is durable plastic prototypes or complex end-use parts: SLS is the definitive choice for its design freedom and the functional strength of materials like nylon.
- If your primary focus is high-strength, lightweight metal components for aerospace or medical applications: DMLS or SLM provide the necessary material integrity and performance characteristics.
- If your goal is to produce intricate designs that cannot be traditionally machined: Both SLS and DMLS excel at creating complex internal channels, lattices, and organic shapes.
Understanding these distinctions allows you to select the precise powder bed fusion technology that meets your specific engineering requirements.
Summary Table:
| Method | Primary Material | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) | Polymers/Plastics (e.g., Nylon) | No support structures needed; ideal for complex geometries |
| Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) | Metals (e.g., Stainless Steel, Titanium) | Fuses metal particles for high-strength, functional parts |
| Selective Laser Melting (SLM) | Metals | Fully melts powder for dense, homogenous parts |
Ready to bring your most complex designs to life?
Whether you need durable plastic prototypes via SLS or high-performance metal components via DMLS, KINTEK has the lab equipment and expertise to support your additive manufacturing projects. Our solutions help you achieve precise, strong, and intricate parts faster and more efficiently.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our sintering technologies can meet your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
People Also Ask
- What is the operating procedure of a sieve shaker? Master Accurate Particle Size Analysis
- What are the applications of sieving machine? From Mining to Pharmaceuticals
- What are the components of a sieving machine? Unlock the Anatomy of Precision Particle Separation
- What is the principle of sieving machine? Achieve Accurate Particle Size Separation
- What is the use of vibrating sieve machine? Achieve Precise Particle Size Analysis for Your Lab



















