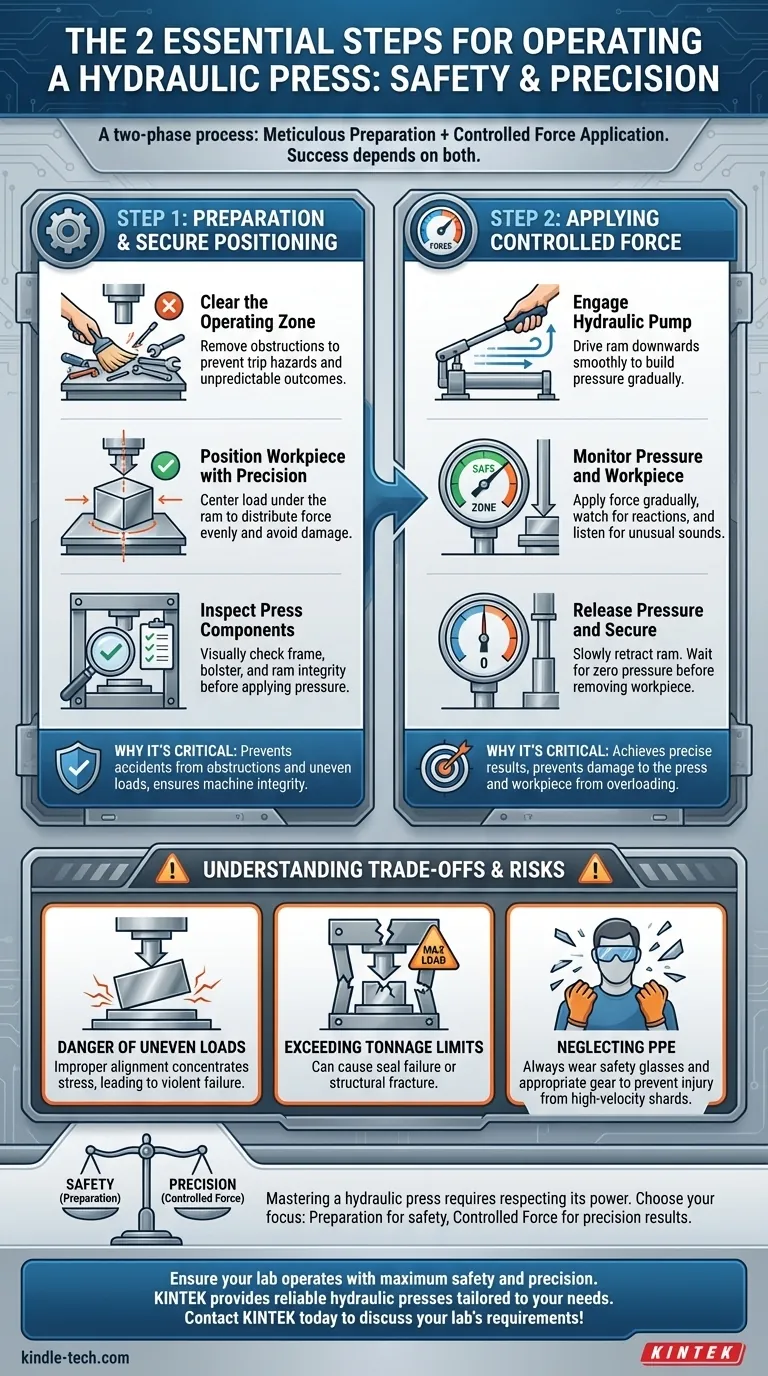
At its core, operating a hydraulic press is a two-phase process. The first phase involves meticulous preparation of the workspace and workpiece, while the second is the controlled application of force. Success and safety depend entirely on executing both phases with precision.
While a hydraulic press seems simple—just apply force—the critical steps are not in the pressing action itself, but in the careful preparation and constant monitoring that precede and accompany it. Ignoring these foundational steps is the primary cause of failure and accidents.

Step 1: Preparation and Secure Positioning
Before any force is applied, your first responsibility is to establish a safe and stable environment. This setup phase dictates the quality and safety of the entire operation.
Clear the Operating Zone
First, ensure the area around the press is completely clear of any tools, materials, or unnecessary personnel. Obstructions create trip hazards and can interfere with the operation, leading to unpredictable and dangerous outcomes.
Position the Workpiece with Precision
The material you are working on must be placed securely on the press bed or bolster plate. It needs to be centered directly under the ram (the main pressing cylinder) to ensure the force is distributed evenly. An off-center load can damage the workpiece, the press itself, or even cause a catastrophic failure.
Inspect the Press Components
Visually check that the frame, bolster, and ram appear to be in good working order. A solid frame is what gives the press its strength, and the bolster is what supports the material. This quick inspection ensures the machine's structural integrity is sound before you put it under immense pressure.
Step 2: Applying Controlled Force
With the workpiece correctly positioned, the second phase involves the actual pressing operation. This is not about speed; it is about control.
Engage the Hydraulic Pump
Begin operating the pump to send hydraulic fluid into the cylinder. This action drives the ram downwards towards the workpiece. Whether manual or powered, this should be done smoothly to begin building pressure in the system.
Monitor Pressure and Workpiece Response
As the ram makes contact, watch the pressure gauge and the workpiece itself. Apply force gradually, paying close attention to how the material is reacting. Listen for unusual sounds and watch for any shifting. This constant feedback is your guide to a successful press.
Release Pressure and Secure the Machine
Once the operation is complete, slowly release the hydraulic pressure to retract the ram. Wait until the ram is fully retracted and the pressure gauge reads zero before attempting to remove the workpiece.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
A hydraulic press multiplies force to an incredible degree, but this power comes with inherent risks that must be managed. Misunderstanding these trade-offs is a common pitfall.
The Danger of Uneven Loads
The single most common mistake is improper workpiece alignment. An uneven or off-center load concentrates immense force on one part of the ram and frame, creating stresses the machine was not designed for. This can lead to equipment damage or sudden, violent failure.
Exceeding Tonnage Limits
Every press has a maximum rated tonnage. Attempting to apply more force than the machine is rated for can cause the hydraulic seals to fail or, in the worst case, fracture the frame. Always know the limits of your machine and your material.
Neglecting Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Operating a hydraulic press without safety glasses is unacceptable. Depending on the application, gloves and steel-toed boots may also be necessary. The forces involved can cause materials to fracture and eject shards at high velocity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to using a press should be guided by your end goal.
- If your primary focus is safety: Your most critical step is preparation. A clear area and a perfectly centered workpiece prevent the vast majority of accidents.
- If your primary focus is precision results: Your most critical step is controlled force application. Gradual pressure and constant monitoring ensure the workpiece conforms as intended without being damaged.
Ultimately, mastering a hydraulic press is about treating it with respect for the immense power it wields.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Why It's Critical |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Clear workspace, center workpiece, inspect press | Prevents accidents from obstructions and uneven loads, ensures machine integrity. |
| 2. Controlled Force | Engage pump smoothly, monitor pressure/workpiece, release slowly | Achieves precise results, prevents damage to the press and workpiece from overloading. |
Ensure your lab operates with maximum safety and precision. The proper use of a hydraulic press is fundamental to achieving consistent, high-quality results while protecting your personnel and equipment. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables, including hydraulic presses, tailored to meet the rigorous demands of your laboratory. Let our experts help you select the right press and understand best practices for your specific applications.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your lab's needs and enhance your operational safety and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Why is a hydraulic pellet press used for FTIR? Transform Nanofillers into Clear Data
- What is the use of manual hydraulic press? A Cost-Effective Tool for Lab Sample Preparation
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press utilized for electrolyte pelletizing? Unlock High Ionic Conductivity
- What is the function of a bench-top laboratory hydraulic press for XRF? Maximize Accuracy in Prosopis juliflora Analysis
- What is KBr disc method? A Complete Guide to IR Spectroscopy Sample Prep



















