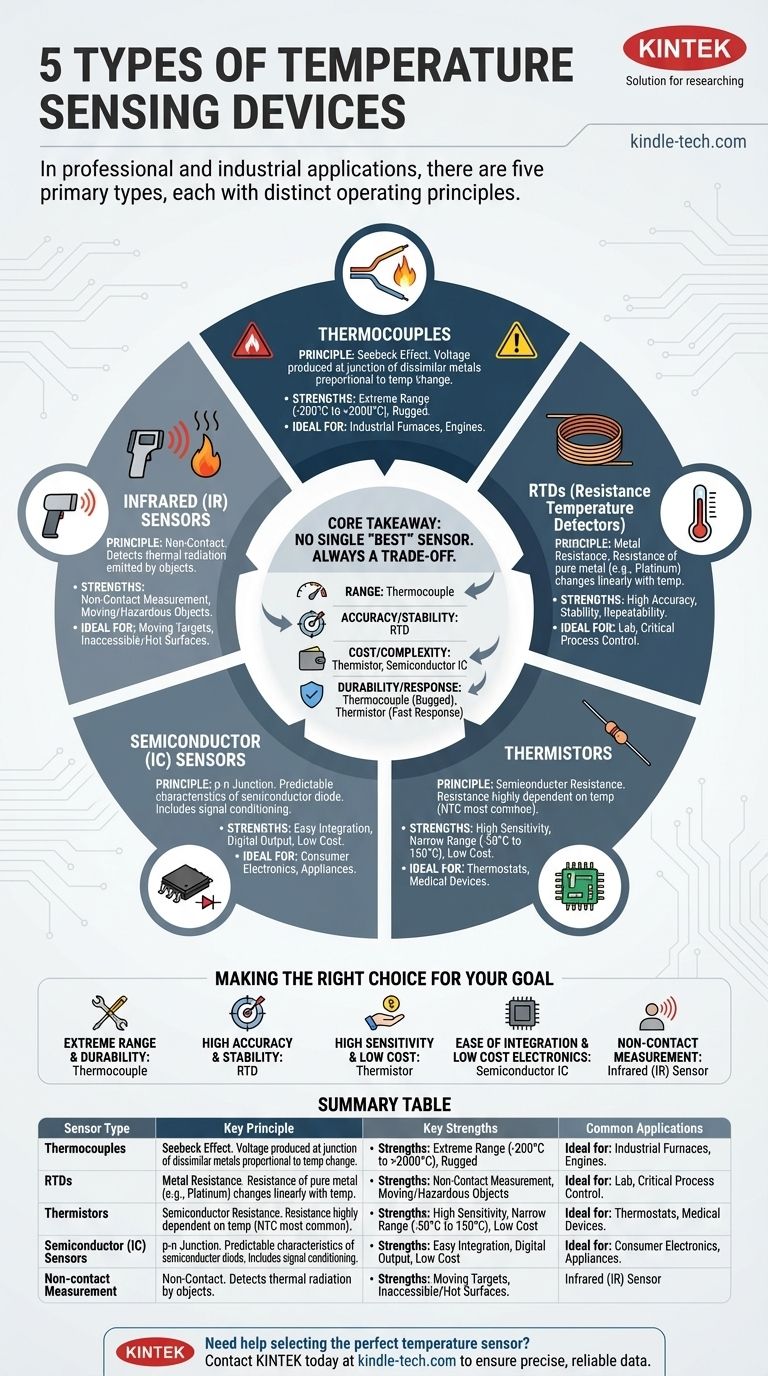
In professional and industrial applications, there are five primary types of electronic temperature sensors, each operating on a distinct physical principle. These are thermocouples, Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs), thermistors, semiconductor-based sensors, and infrared sensors. Choosing the correct one is critical, as they offer vastly different performance in terms of temperature range, accuracy, cost, and durability.
The core takeaway is that there is no single "best" temperature sensor. The ideal choice is always a trade-off, forcing a decision between factors like the extreme range of a thermocouple, the precision of an RTD, or the low cost of a thermistor.

How Each Sensor Works: The Core Principles
Understanding the fundamental operating principle of each sensor is the first step toward selecting the right tool for your specific application.
Thermocouples: The Seebeck Effect
A thermocouple is created by joining two wires made of dissimilar metals. When this junction is heated or cooled, it produces a small voltage that is proportional to the temperature change.
This phenomenon is known as the Seebeck effect. Because of their simple construction, thermocouples are extremely rugged and can measure a very wide range of temperatures, often from hundreds of degrees below zero to well over 2000°C.
Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs): Precision Through Resistance
An RTD leverages the principle that the electrical resistance of a pure metal changes in a highly predictable and linear way with temperature.
These sensors typically use a coil or film of platinum due to its exceptional stability. RTDs are known for their high accuracy, repeatability, and stability over long periods, making them a standard for laboratory and critical industrial processes.
Thermistors: High Sensitivity, Narrow Range
A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance is highly dependent on temperature. The most common type is the Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) thermistor, where resistance decreases as temperature increases.
Made from semiconductor materials (like metallic oxides), thermistors offer the highest sensitivity of any sensor but operate over a much narrower temperature range. They provide a large signal change for a small temperature change, making them ideal for high-resolution measurements.
Semiconductor (IC) Sensors: The Digital Choice
These are modern sensors built on silicon integrated circuits (ICs). They function by using the predictable temperature characteristics of a semiconductor p-n junction (like a diode).
Their primary advantage is that the signal conditioning and even analog-to-digital conversion circuitry can be included on the same chip. This makes them easy to integrate, low-cost, and available with simple voltage or digital outputs.
Infrared (IR) Sensors: Non-Contact Measurement
Unlike the other types, an infrared (IR) sensor measures temperature without physical contact. It works by detecting and quantifying the thermal radiation (infrared energy) emitted by an object.
This is the only way to measure the temperature of moving objects, dangerously hot surfaces, or objects in a vacuum. Its accuracy can be affected by the surface properties (emissivity) of the object being measured.
Understanding the Trade-offs: A Comparative Look
No sensor excels in all areas. Your decision will be driven by which compromises you are willing to make based on your project's needs.
Temperature Range
Thermocouples are the clear winners for range, with some types capable of measuring up to 2300°C. RTDs offer a wide, practical range (e.g., -200°C to 850°C), while thermistors and semiconductor ICs are limited to a much narrower band, typically around -50°C to 150°C.
Accuracy and Stability
RTDs are the most accurate and stable sensors over time. Precision thermistors can be highly accurate over their limited range, but thermocouples are more prone to drift and have lower base accuracy, often requiring careful calibration.
Cost and Complexity
Thermistors and semiconductor IC sensors are generally the lowest-cost options. RTDs and the required measurement instruments are more expensive. While the thermocouple sensor itself is inexpensive, the special extension wires and signal conditioning electronics add to the overall system cost and complexity.
Durability and Response Time
Thermocouples are exceptionally rugged and can withstand significant vibration and mechanical shock. Thermistors, with their small size, typically have the fastest response time to a change in temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your sensor based on the single most critical requirement of your application.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature range and durability: A thermocouple is the only practical choice for very high-temperature industrial environments like furnaces or engines.
- If your primary focus is high accuracy and stability: An RTD is the standard for scientific research, calibration, and critical process control where precision is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is high sensitivity within a limited range at low cost: A thermistor is ideal for applications like digital thermostats, medical devices, and battery temperature monitoring.
- If your primary focus is ease of integration and low-cost electronics: A semiconductor IC sensor is perfect for high-volume consumer electronics, appliances, and board-level temperature monitoring.
- If your primary focus is non-contact measurement: An infrared sensor is the definitive solution for measuring moving targets, inaccessible surfaces, or extremely hot objects from a safe distance.
Ultimately, matching the sensor's inherent strengths to the demands of your specific problem is the key to a successful measurement system.
Summary Table:
| Sensor Type | Key Principle | Key Strengths | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermocouple | Seebeck Effect (dissimilar metals) | Extreme temperature range, ruggedness | Industrial furnaces, engines |
| RTD | Change in metal resistance | High accuracy, stability, repeatability | Laboratory, process control |
| Thermistor | Change in semiconductor resistance | High sensitivity, low cost | Medical devices, thermostats |
| Semiconductor IC | p-n junction characteristics | Easy integration, digital output | Consumer electronics, appliances |
| Infrared (IR) | Detection of thermal radiation | Non-contact measurement | Moving objects, hazardous surfaces |
Need help selecting the perfect temperature sensor for your lab or process? The right sensor is critical for accurate results and process efficiency. At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables, including a wide range of temperature sensing solutions. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between range, accuracy, and cost to find the ideal match for your specific laboratory needs. Contact us today to discuss your application and ensure you get the precise, reliable data you require.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Beaker and Lids
- Lithium Battery Tab Tape for Battery Lab Applications
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range of a MoSi2 heating element? Unlock 1900°C Performance for Your Lab
- What is molybdenum disilicide used for? Powering High-Temperature Furnaces Up to 1800°C
- What is the temperature range of molybdenum disilicide heating elements? Choose the Right Grade for Your High-Temp Needs
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process
- Which high temperature furnace elements to be used in oxidizing atmosphere? MoSi2 or SiC for Superior Performance



















