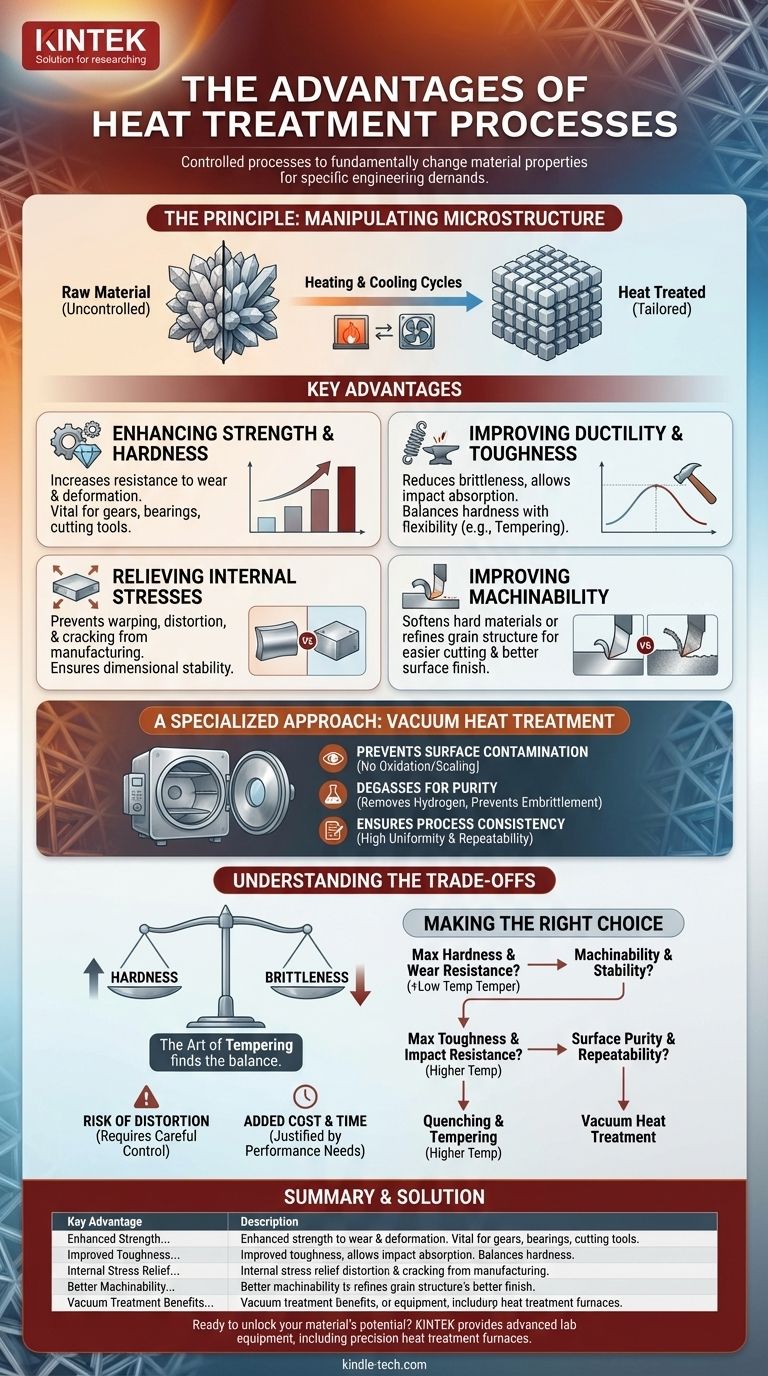
At its core, heat treatment is a group of controlled processes used to fundamentally change a material's properties to meet specific engineering demands. Its primary advantages are the ability to increase strength and wear resistance, improve toughness by reducing brittleness, and relieve internal stresses to make components easier to machine and more stable in service. This deliberate modification of a material's internal structure is what transforms a standard metal into a high-performance component.
Heat treatment is not merely a finishing step; it is a critical engineering tool. It provides precise control over a material's internal microstructure, allowing you to tailor its mechanical and physical properties for a specific application.

The Principle: Manipulating a Material's Internal Structure
Heat treatment works by subjecting a material, typically metal, to a carefully controlled cycle of heating and cooling. This thermal cycle is not arbitrary; it is designed to alter the material's internal crystalline structure, known as its microstructure.
How Heating and Cooling Change Everything
The size, shape, and composition of the crystals within a metal dictate its properties. By controlling the temperature, soaking time, and cooling rate, you can force these crystals to change, thereby changing the material's overall behavior. This is the fundamental advantage of heat treatment: it gives you direct influence over a material's final performance.
Key Advantages in Manufacturing and Engineering
By manipulating the microstructure, heat treatment unlocks several critical benefits that are essential across industries from aerospace and automotive to medical and tooling.
Enhancing Mechanical Strength and Hardness
Many processes, like hardening and quenching, are designed to make a material significantly harder and stronger. This increases its resistance to deformation and surface abrasion. This is vital for components like gears, bearings, and cutting tools that must withstand immense pressure and wear.
Improving Ductility and Toughness
Conversely, processes like annealing and tempering are used to soften a material, increase its ductility (ability to deform without breaking), and improve its overall toughness. A hardened part is often brittle, but tempering reduces that brittleness to achieve a balance between hardness and the ability to absorb impact.
Relieving Internal Stresses
Manufacturing processes like welding, casting, and heavy machining introduce significant internal stresses into a part. These stresses can lead to warping, distortion, or even cracking over time. A stress-relief heat cycle gently heats the component and allows it to cool slowly, relaxing these internal forces and ensuring dimensional stability.
Improving Machinability
Some materials are too hard or too soft to be machined efficiently. An annealing heat treatment can soften a hard material to make it easier to cut, while a normalizing process can refine the grain structure of a soft material to produce a better surface finish during machining.
A Specialized Approach: Vacuum Heat Treatment
For applications demanding the highest level of precision and purity, vacuum heat treatment offers distinct advantages. By processing parts in a near-vacuum environment, several common problems are eliminated.
Preventing Surface Contamination
The vacuum prevents surface reactions like oxidation (scaling) and decarburization (loss of carbon from the surface of steel). This results in a clean, bright part that often requires no subsequent cleaning, preserving precise dimensions and surface finish.
Degassing for Purity and Performance
The vacuum environment effectively pulls dissolved gases, such as hydrogen and oxygen, out of the metal. Removing hydrogen is particularly crucial for preventing hydrogen embrittlement, a catastrophic failure mode in high-strength steels.
Ensuring Process Consistency
Vacuum furnaces offer exceptional temperature uniformity and process control. This leads to highly repeatable and reliable results from batch to batch, which is critical for aerospace, medical, and other high-stakes industries.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Heat treatment is powerful, but it involves inherent compromises that must be managed by an expert. Understanding these trade-offs is key to successful application.
The Hardness vs. Brittleness Balance
The most fundamental trade-off in metallurgy is that as hardness increases, toughness (and ductility) typically decreases. A fully hardened steel part is extremely wear-resistant but can be as brittle as glass. The art of heat treatment, especially tempering, lies in finding the precise point on that spectrum that delivers the required hardness without unacceptable brittleness.
The Risk of Distortion
Rapid heating or cooling is the source of many beneficial property changes, but it also creates thermal stress. If not managed correctly, this stress can cause a part to warp, twist, or even crack during the process. Proper part support, furnace loading, and quench control are essential to minimize this risk.
Added Cost and Production Time
Heat treatment is an additional manufacturing step that requires specialized equipment and expertise. It adds both cost and lead time to a project. Therefore, it should be specified only when the performance requirements of the component justify the investment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The right heat treatment process depends entirely on the intended function of the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance: Use a hardening and quenching process, often followed by a low-temperature temper for parts like cutting tools or ball bearings.
- If your primary focus is machinability and stability: Use an annealing or normalizing process before machining to soften the material and relieve internal stresses.
- If your primary focus is maximum toughness and impact resistance: Use a quenching and tempering process, where the tempering temperature is higher to sacrifice some hardness for a significant gain in toughness.
- If your primary focus is surface purity and process repeatability: Use vacuum heat treatment, especially for critical components in the aerospace, medical, or semiconductor industries.
Ultimately, heat treatment allows you to unlock the full engineering potential hidden within a raw material.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Strength & Hardness | Increases resistance to wear and deformation for components like gears and cutting tools. |
| Improved Toughness & Ductility | Reduces brittleness, allowing materials to absorb impact without breaking. |
| Internal Stress Relief | Prevents warping and distortion, ensuring dimensional stability. |
| Better Machinability | Softens or refines materials for easier and more efficient machining. |
| Vacuum Treatment Benefits | Prevents surface oxidation, removes gases, and ensures high process consistency. |
Ready to unlock the full potential of your materials?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables, including precision heat treatment furnaces, to help you achieve superior material properties. Whether you're in aerospace, automotive, medical, or tooling, our solutions ensure consistent, high-quality results that enhance component performance and durability.
Contact us today to discuss your specific heat treatment needs and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum oven required for LFP cathode sheets? Ensure Peak Battery Performance and Safety
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Tailor Material Properties for Peak Performance
- What is the temperature of the heat of the arc in arc welding? Mastering Extreme Heat for Perfect Welds
- What is a vacuum furnace operator? The Key to Precision Heat Treatment Success
- Why is it necessary for a high-temperature furnace to maintain a constant 750°C for Sc1/3Zr2(PO4)3 DC electrolysis?
- How do annular steam pipes improve activation furnace efficiency? Maximize Carbon Reaction Rates and Quality
- What is an example of quenching? Achieve Optimal Hardness with Precise Cooling
- What role do furnaces play in argyrodite electrolytes? Essential Tools for High-Performance Phase Formation



















