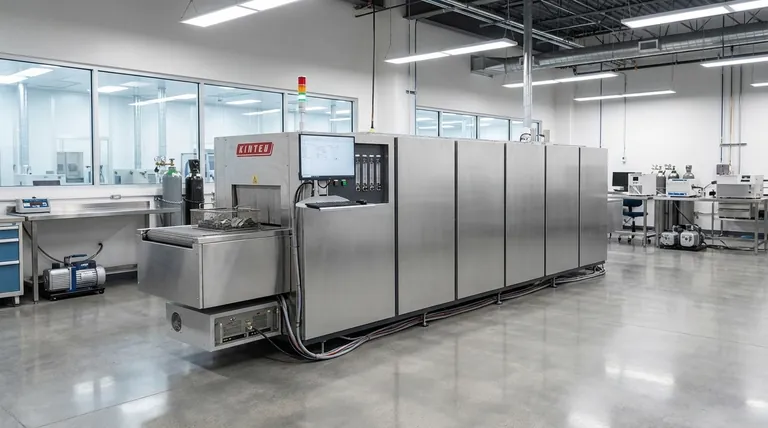
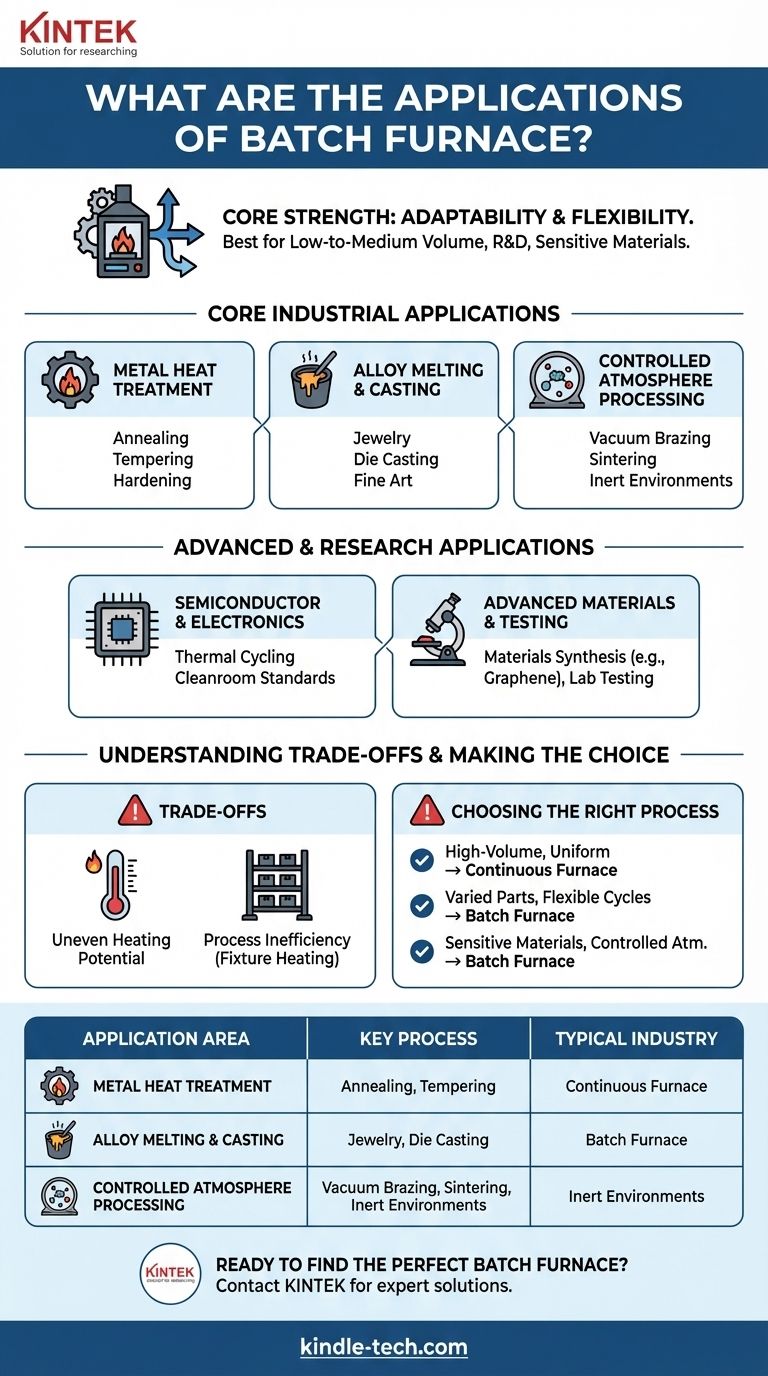
In short, batch furnaces are used for a wide range of thermal processes where flexibility is more important than high-volume throughput. Their applications span from fundamental metal heat treatments and alloy melting to highly specialized tasks like semiconductor manufacturing, advanced materials research, and vacuum brazing.
The core strength of a batch furnace is its adaptability. It excels in environments that require varied temperature profiles, cycle times, or controlled atmospheres, making it the default choice for low-to-medium volume production, R&D, and processes involving sensitive materials.

Core Industrial Applications
The versatility of batch furnaces makes them a cornerstone in many foundational industrial processes. They are valued for their relative simplicity, lower initial cost, and ability to handle a variety of part sizes and requirements.
Metal Heat Treatment and Stress Relief
Batch furnaces are commonly used to alter the physical and chemical properties of metals. This includes processes like annealing, tempering, and hardening to improve strength and durability.
Units like box furnaces and car-bottom furnaces can reach temperatures between 1200°F and 2500°F, accommodating a wide range of metals and alloys.
Alloy Melting and Casting
Many electric furnaces used for melting metallic alloys are batch-type systems. This is fundamental for operations that produce new materials or cast parts.
These applications are critical in industries like jewelry making, die casting operations, and fine art studios, where melts are performed on a per-job or per-day basis.
Controlled Atmosphere Processing
Batch furnaces are exceptionally well-suited for processes that must occur in a non-reactive environment. Their sealed nature makes them ideal for creating a vacuum or introducing a protective atmosphere.
This capability is essential for applications like vacuum brazing, sintering, and heat-treating reactive metals that would be damaged by exposure to oxygen at high temperatures.
Advanced and Research Applications
Beyond traditional industry, batch furnaces are critical tools in technology development and scientific research, where precision and process control are paramount.
Semiconductor and Electronics Manufacturing
The production of semiconductors, batteries, and other electronic components often relies on the precise thermal cycling provided by tube furnaces, a common type of batch furnace.
Their suitability for cleanroom standards and inert atmosphere applications makes them essential for preventing contamination during these sensitive manufacturing steps.
Advanced Materials and Testing
Batch furnaces are indispensable in research and development. They are used to create or test materials like solid oxide fuel cells, polymer composites, and graphene.
Labs also use them for aerospace materials testing, oil and gas analysis, and environmental testing of water, waste, and soil samples.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly flexible, the batch processing model introduces specific operational challenges and inefficiencies that must be considered.
Uneven Heating Potential
In a batch furnace, parts closest to the heat source will heat faster than those in the center of the load. This can lead to a lack of temperature uniformity across the entire batch.
Achieving uniform heating often requires careful placement of parts and potentially longer cycle times to allow the entire load to "soak" at the target temperature.
Process Inefficiency
Batch processing requires parts to be grouped together for loading, often using heavy fixtures like baskets, racks, or carts.
These fixtures must also be heated and cooled with every cycle, which consumes significant energy and increases the overall heat load beyond that required for the parts themselves. This parasitic energy use is a key inefficiency of the batch model.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the right furnace technology depends entirely on your operational goals for volume, flexibility, and uniformity.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, uniform production of a single part: The inefficiencies of batch processing may be a significant drawback; a continuous furnace is likely a better solution.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility for varied parts and cycles: The ability to completely change the temperature, atmosphere, and duration for each load makes a batch furnace the ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is working with sensitive materials in a controlled atmosphere: Batch furnaces provide the sealed, highly controlled environment necessary for vacuum or inert gas processing.
By understanding these core capabilities and trade-offs, you can confidently determine if a batch furnace aligns with your specific thermal processing goals.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Processes | Typical Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Metal Heat Treatment | Annealing, Tempering, Hardening | Automotive, Aerospace, Tooling |
| Alloy Melting & Casting | Metal Melting, Casting | Jewelry, Die Casting, Fine Art |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Vacuum Brazing, Sintering | Medical Devices, Aerospace |
| Semiconductor Manufacturing | Thermal Cycling, Cleanroom Processing | Electronics, Battery Production |
| Advanced Materials Research | Materials Synthesis, Testing | R&D Labs, Universities, Aerospace |
Ready to find the perfect batch furnace for your specific application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your unique thermal processing needs. Whether you're in R&D, semiconductor manufacturing, or metal heat treatment, our experts can help you select the ideal batch furnace for precise temperature control, atmosphere management, and process flexibility.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is precise temperature control in a sintering furnace critical for NASICON electrolytes? Ensure Material Purity
- What is the role of an atmosphere-controlled tube furnace in Cu-Mo sintering? Achieve High-Purity Densification
- What advantages does a high-temperature atmosphere sintering furnace offer for UO2? Precision Fuel Densification
- What is the core function of a high-temperature atmosphere sintering furnace in the fabrication of Ni-Al2O3-TiO2 composites?
- Why is a horizontal tube furnace with a H2-N2 atmosphere used for NiO pre-treatment? Key to Catalyst Activation



















