At its core, an industrial furnace is a highly controlled thermal processing device used to fundamentally alter the physical and chemical properties of materials. Its applications span nearly every sector of modern manufacturing, from creating aerospace components and 3D-printed metal parts to producing everyday ceramics and heat-treating steel tools.
The true role of an industrial furnace isn't just to generate heat; it's to provide the precise thermal environment required to join, shape, harden, or create materials, making it an indispensable tool for both mass production and scientific research.

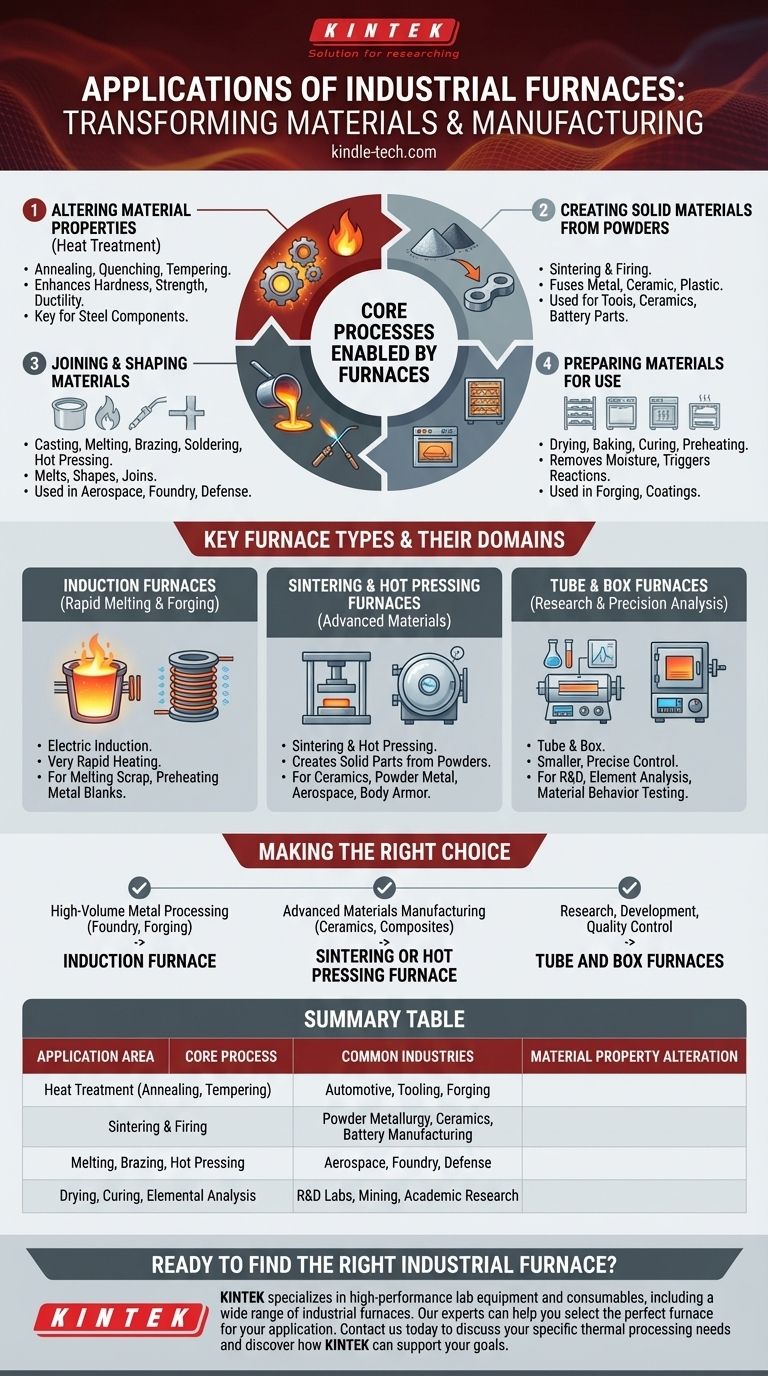
Core Processes Enabled by Furnaces
Industrial furnaces are best understood not by a list of applications, but by the fundamental processes they facilitate. These processes are the building blocks of modern material science and manufacturing.
Altering Material Properties (Heat Treatment)
Many applications revolve around modifying a material's internal structure to improve its characteristics.
Heat treatment involves controlled heating and cooling to enhance properties like hardness, strength, or ductility. Key processes include annealing (softening), quenching (hardening), and tempering (reducing brittleness).
These techniques are critical in the heat treatment and forging industries, especially for steel components.
Creating Solid Materials from Powders
Furnaces are essential for turning powdered materials into solid, functional parts.
Firing and sintering use heat to fuse particles of metal, ceramic, or plastic together without reaching their melting point. This is the foundational process for the powder metallurgy, advanced ceramics, and battery manufacturing industries.
Applications range from producing stainless-steel tools and aircraft hydraulic parts to creating the durable bases for skis and snowboards.
Joining and Shaping Materials
High temperatures allow for the melting, shaping, and joining of materials.
Processes like casting and melting are central to the foundry industry for recycling and creating new metal parts. Brazing and soldering use heat to join different components, while hot pressing uses heat and pressure to form high-strength parts.
These methods are common in aerospace, automotive, and defense manufacturing for creating everything from vehicle armor to engine components.
Preparing Materials for Use
Simpler thermal processes are used to prepare materials for subsequent steps or final use.
Drying, baking, and curing involve applying heat to remove moisture or trigger a chemical reaction in coatings, adhesives, or composites. Preheating is used extensively in the forging industry to make metal blanks easier to shape.
Key Furnace Types and Their Domains
Different industrial processes demand specialized equipment. The type of furnace used is directly linked to the material, required temperature, and the specific outcome desired.
Induction Furnaces: For Rapid Melting and Forging
Electric induction furnaces use electromagnetic induction to generate heat directly within the metal itself. This allows for very rapid and efficient heating.
They are a cornerstone of the foundry industry for melting scrap metal and in the forging industry for preheating metal blanks before shaping.
Sintering & Hot Pressing Furnaces: For Advanced Materials
These furnaces are designed for processes that create solid parts from powders. Sintering furnaces are critical for producing ceramics and powder metal parts.
Hot pressing furnaces add pressure to the heating process, creating exceptionally dense and strong components used in aerospace and body armor manufacturing.
Tube & Box Furnaces: For Laboratories and Precision Analysis
Tube furnaces and box furnaces are typically smaller and offer extremely precise temperature control, making them ideal for research and development.
They are widely used in academic, mining, and scientific settings for element analysis and for determining how materials behave under specific thermal conditions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection of a furnace is driven entirely by the industrial goal, as each type is optimized for a specific set of thermal processes and materials.
- If your primary focus is high-volume metal processing (foundry or forging): An induction furnace is the industry standard for its speed and efficiency in melting and preheating.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials manufacturing (ceramics, composites): Sintering or hot pressing furnaces provide the necessary control for creating high-performance parts from powders.
- If your primary focus is research, development, or quality control: Tube and box furnaces offer the precision and versatility required for material testing and analysis.
Ultimately, the industrial furnace is the enabling technology that transforms raw materials into the high-performance products that define our modern world.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Core Process | Common Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Material Property Alteration | Heat Treatment (Annealing, Tempering) | Automotive, Tooling, Forging |
| Creating Solid Parts | Sintering & Firing | Powder Metallurgy, Ceramics, Battery Manufacturing |
| Joining & Shaping Materials | Melting, Brazing, Hot Pressing | Aerospace, Foundry, Defense |
| Material Preparation & Research | Drying, Curing, Elemental Analysis | R&D Labs, Mining, Academic Research |
Ready to find the right industrial furnace for your application?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a wide range of industrial furnaces tailored for heat treatment, sintering, melting, and R&D. Our experts can help you select the perfect furnace to enhance your manufacturing process, improve material properties, and boost efficiency.
Contact us today to discuss your specific thermal processing needs and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control



















