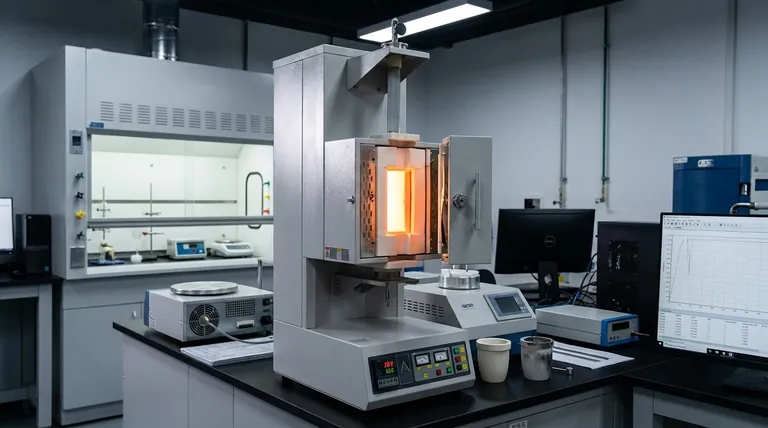
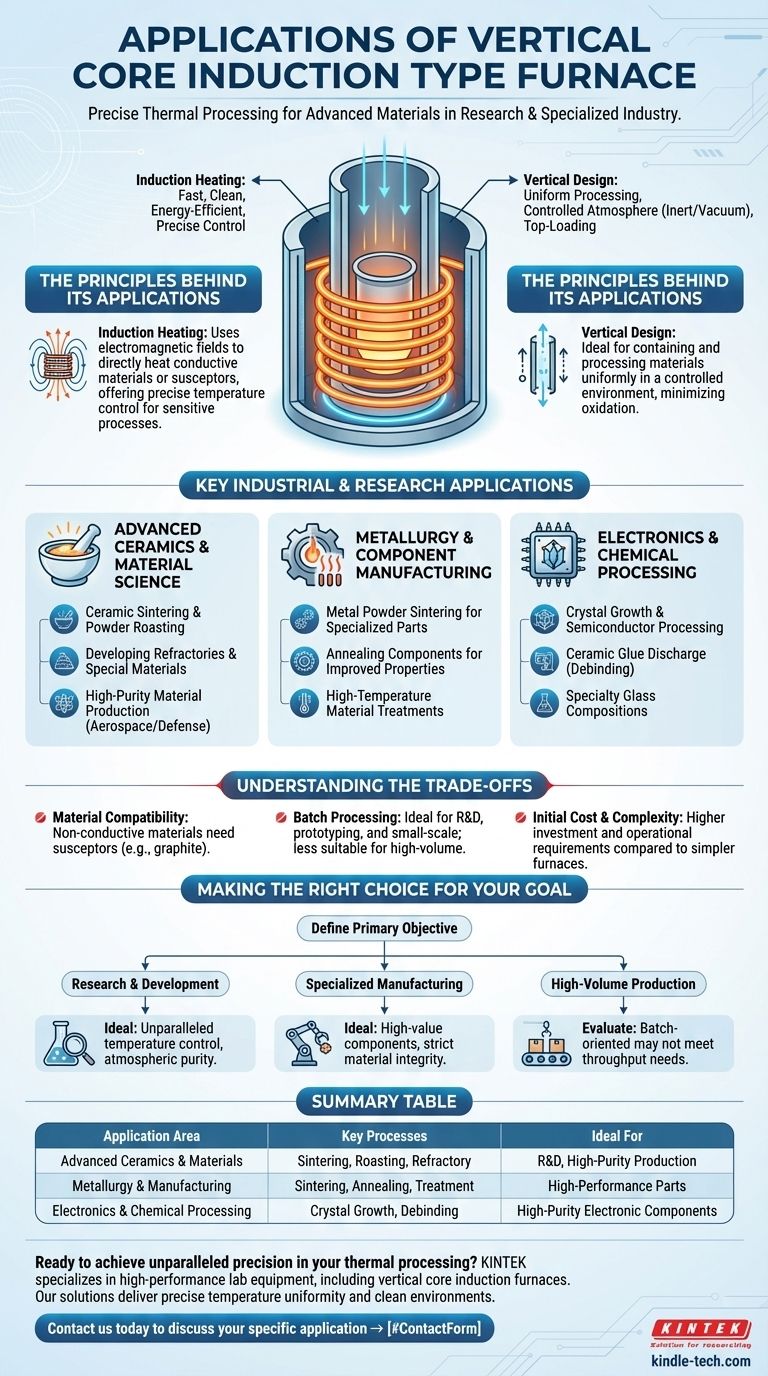
In short, a vertical core induction furnace is a specialized high-temperature tool used for precise thermal processing of materials. Its applications span across advanced research and specialized industrial manufacturing, including the sintering of ceramics, powder metallurgy, creating electronic components, and treating specialty materials in controlled environments.
The core value of a vertical core induction furnace lies not in its versatility, but in its precision. It excels at applying uniform, high-intensity heat to materials, particularly powders and small components, within a tightly controlled atmosphere, making it essential for developing and producing advanced materials.

The Principles Behind Its Applications
To understand its uses, you must first understand its design. Unlike a general-purpose oven, this furnace combines two key principles: induction heating and a vertical orientation.
The Role of Induction Heating
Induction heating uses electromagnetic fields to directly heat an electrically conductive material placed inside a coil. This process is incredibly fast, clean, and energy-efficient because it heats the material itself, not the air around it.
This direct heating method provides the precise temperature control needed for sensitive processes like sintering and annealing.
The Significance of the Vertical Design
The vertical "core" or "tube" design is ideal for containing and processing materials in a uniform manner. It allows for easy top-loading of materials, often held within a crucible.
This configuration is particularly effective for creating a controlled atmosphere (such as inert gas or a vacuum), which is critical for preventing oxidation and contamination when working with high-purity or reactive materials.
Key Industrial and Research Applications
The combination of precise heating and a controlled environment makes this furnace a critical tool in several high-tech fields.
Advanced Ceramics and Material Science
This is a primary application area. The furnace provides the extreme temperatures and controlled conditions needed to transform powders into solid, dense objects.
Specific uses include ceramic sintering, powder roasting, and developing refractories and other special materials for aerospace, defense, and industrial machinery.
Metallurgy and Component Manufacturing
In metallurgy, the furnace is used for processes that require strict thermal profiles and clean environments.
This includes sintering metal powders to create specialized parts, annealing components to improve their mechanical properties, and other high-temperature material treatments.
Electronics and Chemical Processing
The electronics and chemical industries rely on this technology to produce high-purity materials and components.
Applications range from growing crystals and processing semiconductor materials to ceramic glue discharge (debinding) and heat-treating small electronic parts. Its use in the glass industry involves creating specialty glass compositions that require high temperatures and purity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the vertical core induction furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Material Compatibility Challenges
Induction heating works best with electrically conductive materials. For non-conductive materials like many ceramics, a conductive crucible (often graphite) called a susceptor is required to absorb the energy and radiate heat to the sample. This adds a layer of complexity to the process.
Batch Processing Limitations
The vertical tube design is inherently suited for batch processing, where one sample or a small group of items is processed at a time. This makes it ideal for research, prototyping, and small-scale production of high-value parts.
However, it is generally not suitable for high-volume, continuous manufacturing, where other furnace designs may be more efficient.
Initial Cost and Complexity
Induction heating systems, with their power supplies and cooling requirements, typically have a higher initial investment cost and operational complexity compared to simpler resistance-heated furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding if this furnace fits your needs depends entirely on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is research and development: This furnace offers the unparalleled temperature control and atmospheric purity required for experimenting with and creating new, advanced materials.
- If your primary focus is specialized manufacturing: It is the ideal tool for producing high-value, high-performance components where material integrity and precise properties are non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost production: You should carefully evaluate if a batch-oriented induction furnace can meet your throughput needs compared to continuous belt or rotary furnaces.
Ultimately, the vertical core induction furnace is a precision instrument for tasks where material quality and process control are paramount.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Processes | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Ceramics & Materials | Sintering, Powder Roasting, Refractory Development | R&D, High-Purity Material Production |
| Metallurgy & Manufacturing | Metal Powder Sintering, Annealing, Component Treatment | Creating High-Performance Specialized Parts |
| Electronics & Chemical Processing | Crystal Growth, Semiconductor Processing, Ceramic Glue Discharge | Producing High-Purity Electronic Components |
Ready to achieve unparalleled precision in your thermal processing?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including vertical core induction furnaces. Whether you are in R&D developing new advanced ceramics or in specialized manufacturing requiring strict atmospheric control, our solutions deliver the precise temperature uniformity and clean environments your work demands.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your material science and production processes. Let's talk about your specific application → #ContactForm
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan



















