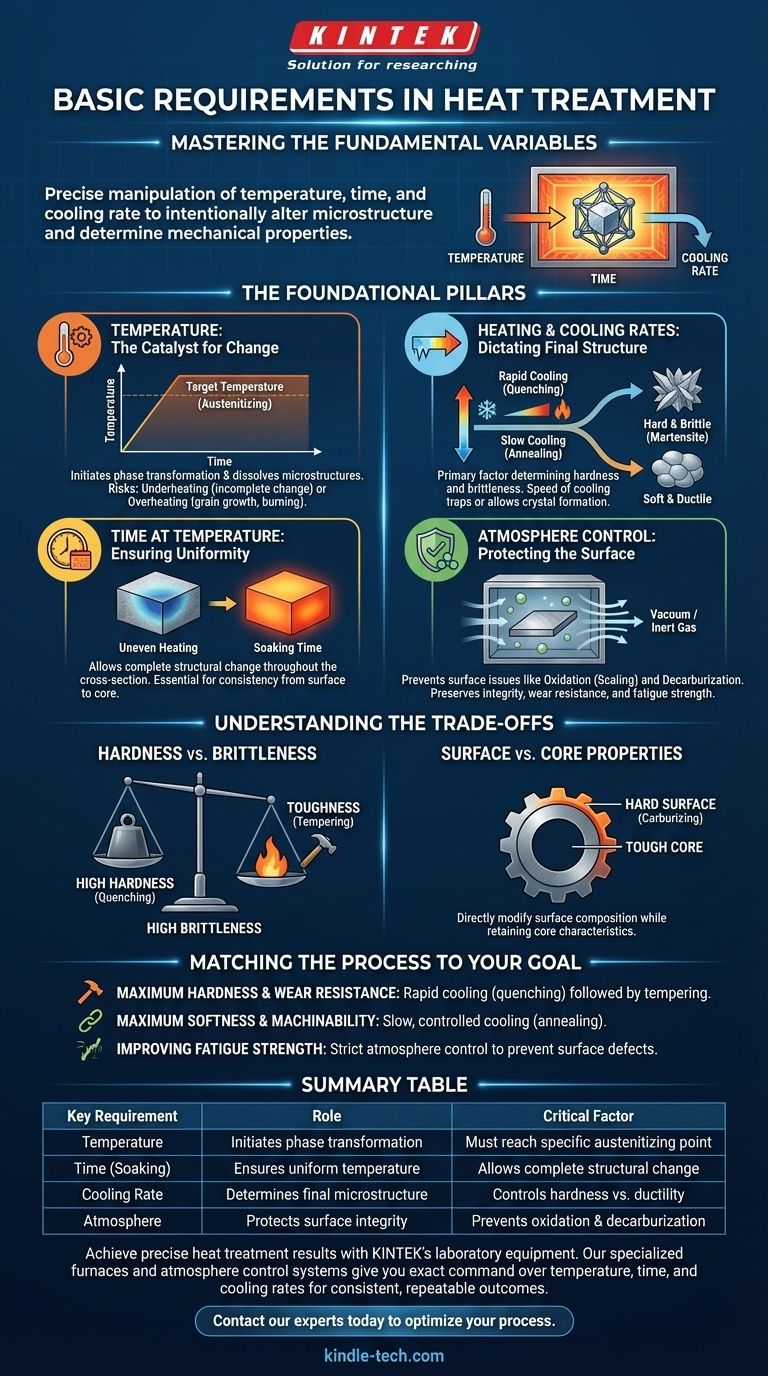
At its core, successful heat treatment hinges on the precise manipulation of three fundamental variables: temperature, time, and the rate of cooling. These factors work in concert to intentionally alter a metal's internal microstructure, which in turn determines its final mechanical properties like hardness, strength, and ductility.
The goal of any heat treatment process is not merely to heat and cool a material, but to predictably control its phase transformation. Mastering the relationship between temperature, time, cooling rates, and atmospheric conditions is the key to achieving a desired engineering outcome.
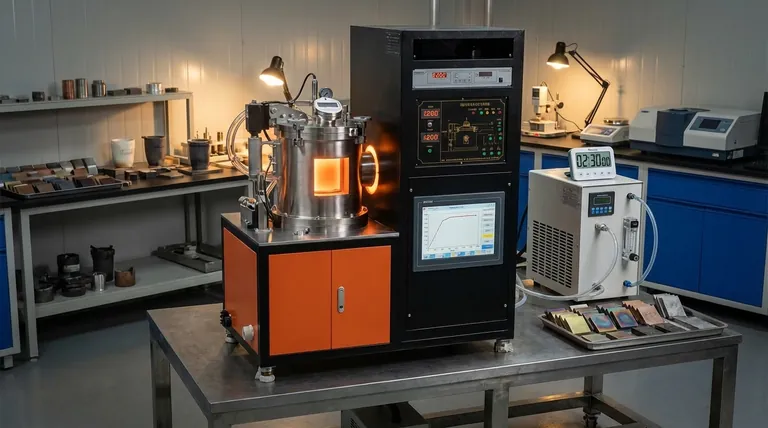

The Foundational Pillars of Heat Treatment
To achieve consistent and reliable results, every heat treatment process must be built upon a clear understanding of its core requirements. These are the levers you control to dictate the final properties of the material.
Temperature: The Catalyst for Change
The temperature to which a metal is heated is the most critical factor. Reaching specific temperatures, such as the austenitizing temperature in steel, is necessary to dissolve existing microstructures and initiate the phase transformations that enable hardening or softening.
Heating that is insufficient will fail to produce the desired structural change, while overheating can lead to grain growth, burning, and degradation of mechanical properties.
Time at Temperature: Ensuring Uniformity
Simply reaching the target temperature is not enough. The material must be held at that temperature, a process known as soaking, for a sufficient duration.
This soaking time allows the temperature to become uniform throughout the entire cross-section of the part, ensuring the internal structural changes are complete and consistent from the surface to the core.
Heating and Cooling Rates: Dictating the Final Structure
The speed at which a material is heated and, more importantly, cooled determines the final microstructure. This rate is the primary factor that dictates the material's hardness and brittleness.
A very rapid cooling rate, known as quenching, "traps" a hard and brittle crystal structure (like martensite in steel). Conversely, a very slow cooling rate, as seen in annealing, allows for the formation of a soft and ductile structure.
Atmosphere Control: Protecting the Surface
The environment surrounding the part during heating is a critical, though sometimes overlooked, requirement. An uncontrolled atmosphere (like open air) can cause undesirable chemical reactions on the material's surface.
Proper atmosphere control, using vacuums, inert gases, or specific chemical compositions, prevents issues like oxidation (scaling) and decarburization. This preserves the part's surface integrity, wear resistance, and fatigue strength.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Heat treatment is not a process of universal improvement but one of calculated compromise. Enhancing one property often comes at the expense of another.
The Hardness vs. Brittleness Compromise
The most common trade-off is between hardness and toughness. A process like quenching can produce extreme hardness, but this almost always comes with a significant increase in brittleness and high internal stresses.
This is why a secondary heat treatment, tempering, is almost always performed after quenching. Tempering slightly reduces hardness but restores a crucial amount of toughness, making the part usable for its intended application.
Surface Properties vs. Core Properties
For many components, the desired properties at the surface (e.g., high wear resistance) are different from those needed in the core (e.g., toughness and ductility).
Treatments like carburizing are a direct answer to this challenge. They modify the chemical composition of the surface layer only, allowing the surface to be hardened to a high degree while the core retains its original, tougher characteristics.
Matching the Process to Your Goal
The right combination of heat treatment characteristics depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance: You will require a rapid cooling rate (quenching) from the correct austenitizing temperature, followed by a tempering cycle to reduce brittleness.
- If your primary focus is maximum softness and machinability: You will require a very slow and controlled cooling rate (annealing) from the proper temperature.
- If your primary focus is improving fatigue strength: You must prioritize strict atmosphere control to prevent surface defects like decarburization, which can initiate fatigue cracks.
Mastering these fundamental requirements transforms heat treatment from a simple procedure into a predictable and powerful engineering tool.
Summary Table:
| Key Requirement | Role in Heat Treatment | Critical Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Initiates phase transformation | Must reach specific austenitizing point |
| Time (Soaking) | Ensures uniform temperature | Allows complete structural change |
| Cooling Rate | Determines final microstructure | Controls hardness vs. ductility |
| Atmosphere | Protects surface integrity | Prevents oxidation and decarburization |
Achieve precise heat treatment results with KINTEK's laboratory equipment. Our specialized furnaces and atmosphere control systems give you exact command over temperature, time, and cooling rates—ensuring consistent, repeatable outcomes for your materials research or production needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your heat treatment processes and help you achieve your target material properties.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the DC sputtering mechanism? A Guide to Physical Vapor Deposition for Thin Films
- How do ULT freezers improve the storage life of medical components? Extend Sample Viability for Years
- What are the effects of heat treatment and temperature on properties of metals? Master Hardness, Toughness, and More
- What are the 5 types of heat treatment? Master Metal Properties for Better Performance
- How does heat treatment affect hardness? Master the Art of Controlled Hardening and Softening
- Why is argon used as a plasma gas? The Ideal Balance for Efficient Sputtering
- Why does casting need heat treatment? Transform Raw Castings into Reliable Components
- What happens to graphite at high temperatures? Unlock its Extreme Heat Resistance



















