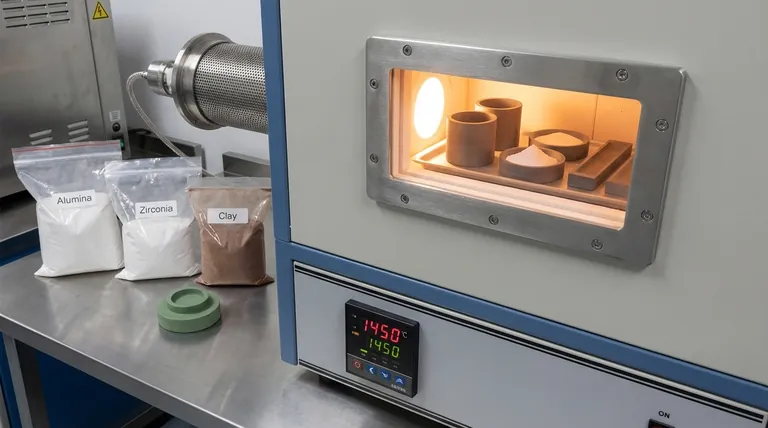
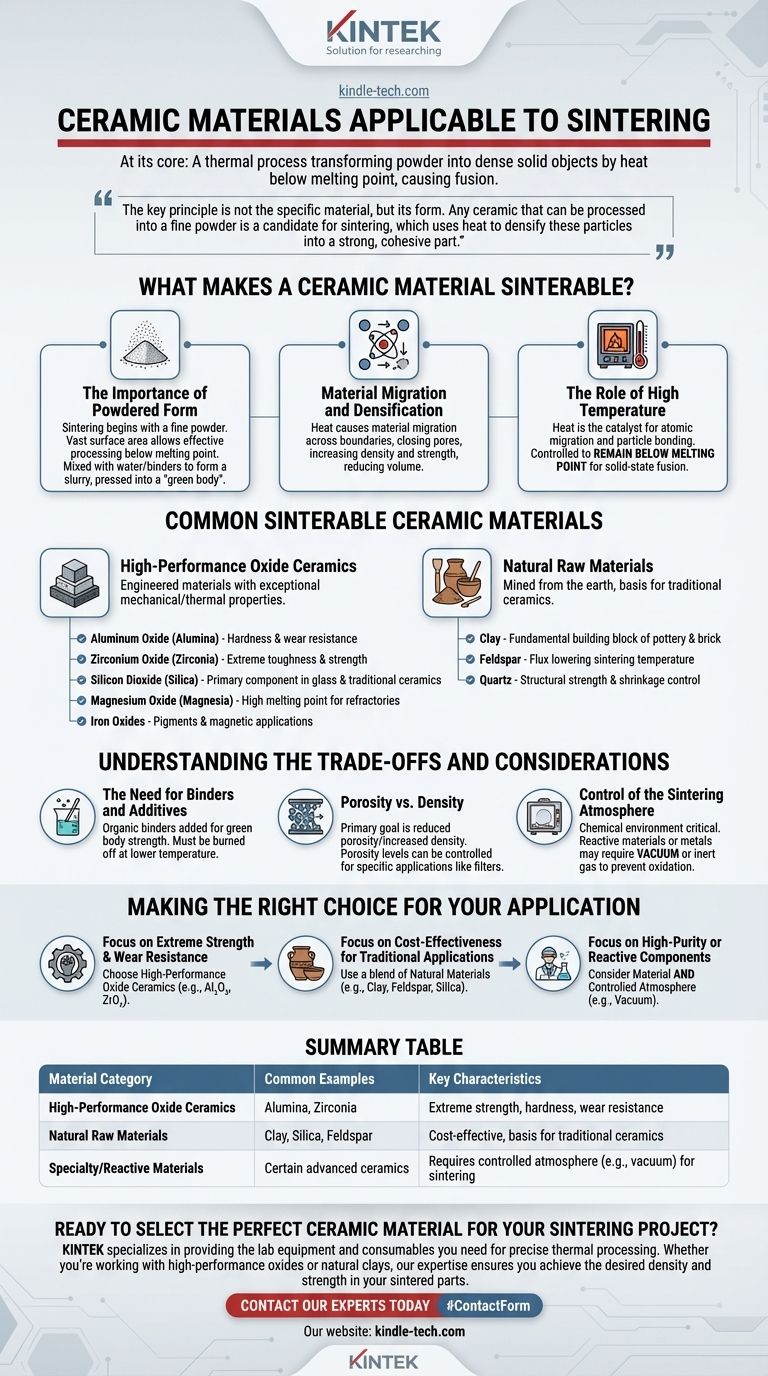
At its core, sintering is a thermal process applicable to a wide range of ceramic materials, most notably oxides like alumina and zirconia, as well as natural materials such as clay and silica. The process transforms these materials from a powdered state into a solid, dense object by applying high heat below their melting point, causing the individual particles to fuse together.
The key principle is not the specific material, but its form. Any ceramic that can be processed into a fine powder is a candidate for sintering, which uses heat to densify these particles into a strong, cohesive part.

What Makes a Ceramic Material Sinterable?
The ability to sinter a material is less about its chemical name and more about its physical form and how it behaves under heat. The entire process is built on a few fundamental principles.
The Importance of Powdered Form
Sintering begins with a fine powder. The vast surface area of these tiny particles is what allows the process to work effectively at temperatures below the material's melting point.
The process often involves mixing this powder with water and binders to form a slurry, which is then dried and pressed into the desired shape, known as a "green body."
Material Migration and Densification
When the green body is heated in a furnace, atoms move across the boundaries of the particles in a process called material migration.
This atomic movement closes the gaps (or pores) between particles. The result is a significant increase in the material's density and strength, and a reduction in its overall volume.
The Role of High Temperature
Heat is the catalyst for sintering. It provides the energy needed for atoms to migrate and for the particles to bond.
However, this temperature is carefully controlled to remain below the material's melting point. The goal is to fuse the particles together in a solid state, not to melt the material into a liquid.
Common Sinterable Ceramic Materials
While many ceramics can be sintered, they generally fall into a few key categories based on their composition and origin.
High-Performance Oxide Ceramics
These are engineered materials known for their exceptional mechanical and thermal properties. Common examples include:
- Aluminum Oxide (Alumina): Valued for its hardness and wear resistance.
- Zirconium Oxide (Zirconia): Known for its extreme toughness and strength.
- Silicon Dioxide (Silica): A primary component in many glasses and traditional ceramics.
- Magnesium Oxide (Magnesia): Used in refractory applications due to its high melting point.
- Iron Oxides: Often used as pigments or in magnetic applications.
Natural Raw Materials
These materials are mined from the earth and form the basis of traditional ceramics like porcelain and earthenware.
- Clay: The fundamental building block of most traditional pottery and brick.
- Feldspar: Acts as a flux, lowering the sintering temperature of clay bodies.
- Quartz: Provides structural strength and controls shrinkage during firing.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
Successfully sintering a ceramic part requires more than just heat. Several factors must be managed to achieve the desired outcome.
The Need for Binders and Additives
Some ceramic powders do not mix well with water or hold their shape after being pressed. In these cases, organic binders are added to the initial mix.
These binders give the green body strength but must be completely burned off at a lower temperature before the final high-temperature sintering begins.
Porosity vs. Density
The primary goal of sintering is to reduce porosity and increase density. A fully densified part is stronger and less permeable to fluids.
However, some applications, like filters, require a specific level of controlled porosity. The sintering time and temperature can be adjusted to achieve this balance.
Control of the Sintering Atmosphere
The chemical environment inside the furnace is critical. Most ceramics are sintered in air, but reactive materials require a specific atmosphere.
For example, certain advanced ceramics or metals are sintered in a vacuum or an inert gas to prevent oxidation or other unwanted chemical reactions that could compromise the final part's integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of ceramic material depends entirely on the performance requirements of the final product.
- If your primary focus is extreme strength and wear resistance: Choose high-performance oxide ceramics like Alumina (Al₂O₃) or Zirconia (ZrO₂).
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for traditional applications: Use a blend of natural materials like clay, feldspar, and silica.
- If your primary focus is high-purity or reactive components: You must consider not only the material but also the necessity of a controlled sintering atmosphere, such as a vacuum.
Ultimately, mastering sintering comes from understanding that the final properties of a ceramic part are directly controlled by the starting powder and the precise application of heat.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Common Examples | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| High-Performance Oxide Ceramics | Alumina (Al₂O₃), Zirconia (ZrO₂) | Extreme strength, hardness, wear resistance |
| Natural Raw Materials | Clay, Silica, Feldspar | Cost-effective, basis for traditional ceramics |
| Specialty/Reactive Materials | Certain advanced ceramics | Requires controlled atmosphere (e.g., vacuum) for sintering |
Ready to select the perfect ceramic material for your sintering project?
KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables you need for precise thermal processing. Whether you're working with high-performance oxides or natural clays, our expertise ensures you achieve the desired density and strength in your sintered parts.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of brazing? A Guide to Strong, Clean Metal Joining
- What is the main difference between soldering and brazing? Choose the Right Metal Joining Method
- What are the classification of ceramic materials? A Guide to Oxides, Non-Oxides, and Composites
- What are 4 disadvantages of brazing? Understanding the Critical Limitations of This Joining Method
- Why is a hexagonal Boron Nitride (h-BN) layer required for LATP? Protect Your Samples from Carbon Contamination



















