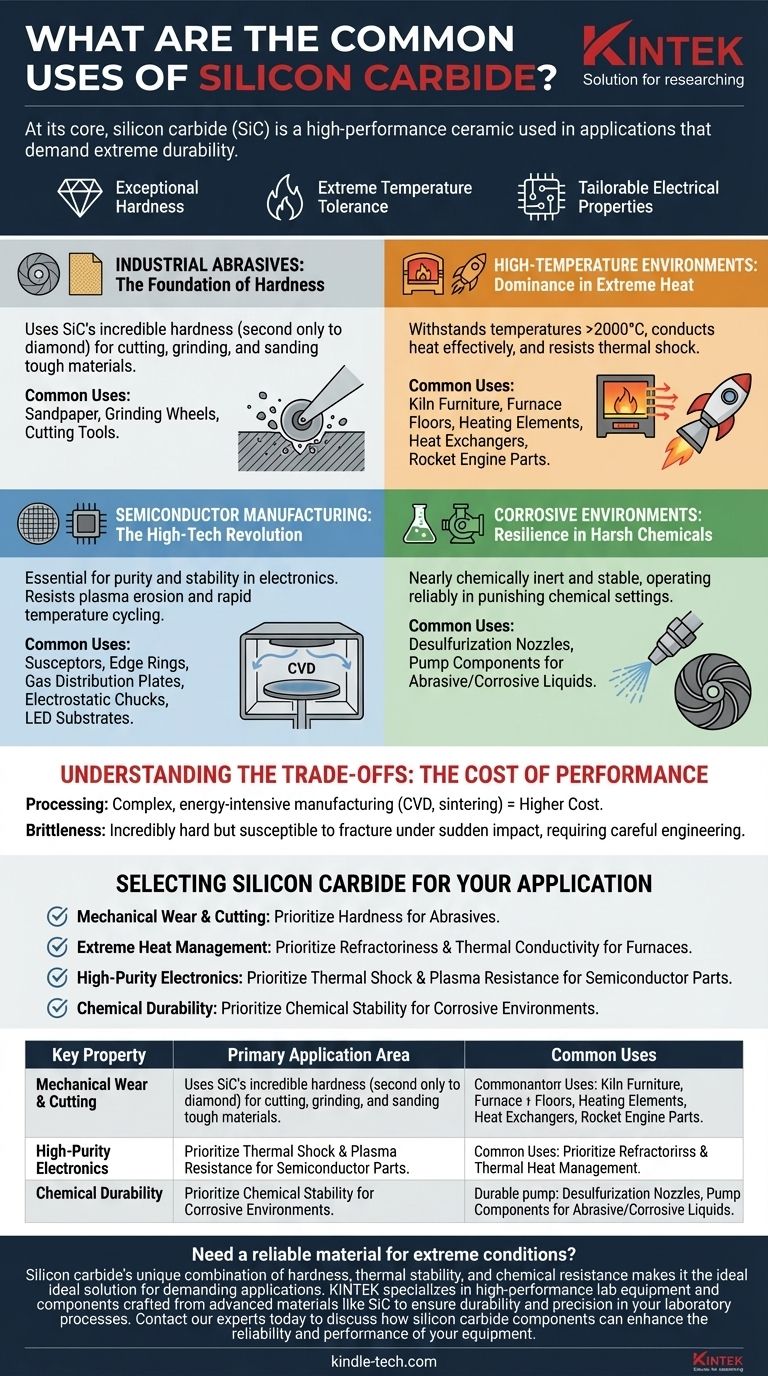
At its core, silicon carbide (SiC) is a high-performance ceramic used in applications that demand extreme durability. Its most common uses span four key areas: industrial abrasives, components for high-temperature furnaces and engines, critical parts for semiconductor manufacturing, and chemically resistant hardware for corrosive environments.
The versatility of silicon carbide isn't accidental. Its widespread adoption stems from a unique and powerful combination of exceptional hardness, extreme temperature tolerance, and tailorable electrical properties that few other materials can match.
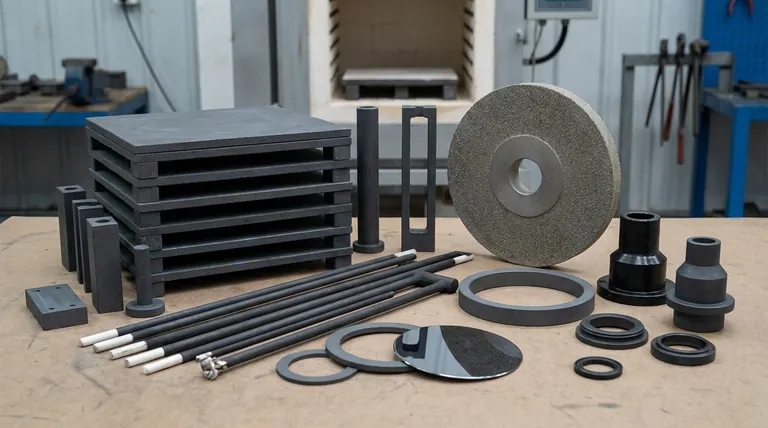

The Foundation: Hardness and Abrasive Power
The original and most traditional use of silicon carbide is rooted in its incredible hardness, second only to diamond.
From Sandpaper to Cutting Tools
Historically, SiC's primary application was as an abrasive. Its sharp, hard crystalline structure makes it highly effective for grinding, sanding, and cutting tough materials. This is why it remains a key component in sandpapers, grinding wheels, and cutting tools.
Dominance in High-Temperature Environments
Silicon carbide excels where other materials melt or fracture. Its ability to withstand and conduct heat makes it indispensable for high-temperature industrial processes.
Furnace and Kiln Components
SiC has a very high refractoriness, meaning it can resist temperatures over 2000°C without degrading. This makes it an ideal material for kiln furniture—the shelves and supports used in firing ceramics and glass—as well as for furnace floors and guide rails.
Heating Elements and Heat Exchangers
Beyond just withstanding heat, SiC conducts it very effectively. Recrystallized silicon carbide, a pure and porous form, is used to make heating elements for industrial furnaces, combustion nozzles, and highly efficient heat exchangers. Its high thermal conductivity allows for rapid and uniform heat transfer.
Extreme Thermal Shock Resistance
In applications like rocket engines, materials must endure rapid and dramatic temperature changes. SiC’s excellent thermal shock resistance prevents it from cracking under this stress, making it a reliable choice for mission-critical engine parts.
The Semiconductor Revolution
In the world of high-tech electronics, purity and stability are paramount. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) silicon carbide provides the performance needed to manufacture modern semiconductors.
Semiconductor Processing Components
Manufacturing microchips involves high-energy plasmas and rapid temperature cycling. SiC is used for essential chamber components like susceptors, edge rings, and gas distribution plates because it resists erosion from plasma and withstands the thermal shock of processes like Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP).
Heaters and Substrates
Low-resistivity SiC can be engineered to act as a highly durable and uniform heating element, such as an electrostatic chuck or heater. It is also used as a semiconducting substrate, forming the foundational layer upon which devices like high-efficiency light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are built.
Resilience in Corrosive Environments
Silicon carbide is nearly as chemically inert as it is physically hard. This stability allows it to operate reliably in harsh chemical settings.
Desulfurization and Pumping
In power plants and large boilers, hot, corrosive gases must be treated. SiC is fabricated into desulfurization nozzles that can endure this punishing environment without degrading. This same chemical resilience makes it suitable for durable parts in industrial pumps that handle abrasive or corrosive liquids.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Cost of Performance
While silicon carbide's properties are exceptional, they do not come without practical considerations. Its primary drawback is cost and manufacturability.
The Challenge of Processing
Creating high-purity, precisely shaped SiC components through methods like CVD or sintering is an energy-intensive and complex process. This makes silicon carbide significantly more expensive than traditional metals or lower-grade ceramics.
Brittleness vs. Toughness
Like most ceramics, silicon carbide is brittle. While it is incredibly hard and resistant to wear, it can fracture under a sudden, sharp impact, unlike a metal which might bend or deform. This requires careful engineering and design to avoid catastrophic failure in certain mechanical applications.
Selecting Silicon carbide for Your Application
Choosing SiC is a decision to prioritize performance in extreme conditions. Your specific goal will determine which of its properties is most critical.
- If your primary focus is mechanical wear and cutting: You need SiC for its fundamental hardness, making it ideal for abrasives and cutting tools.
- If your primary focus is extreme heat management: You need SiC for its high refractoriness and thermal conductivity, essential for furnace components, heat exchangers, and heating elements.
- If your primary focus is high-purity electronics manufacturing: You need SiC for its thermal shock resistance, plasma erosion resistance, and controlled electrical properties for semiconductor chamber parts.
- If your primary focus is chemical durability: You need SiC for its chemical stability, which is critical for components like nozzles and pumps operating in corrosive environments.
Ultimately, silicon carbide is the material of choice when standard materials fail and long-term reliability in a harsh environment is the most important requirement.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Primary Application Area | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Hardness | Abrasives & Cutting Tools | Sandpaper, Grinding Wheels, Cutting Tools |
| High Temperature & Thermal Conductivity | High-Temperature Environments | Kiln Furniture, Heating Elements, Heat Exchangers, Rocket Engine Parts |
| Thermal Shock & Plasma Resistance | Semiconductor Manufacturing | Susceptors, Edge Rings, Electrostatic Chucks, LED Substrates |
| Chemical Inertness | Corrosive Environments | Desulfurization Nozzles, Pump Components for Abrasive/Corrosive Liquids |
Need a reliable material for extreme conditions?
Silicon carbide's unique combination of hardness, thermal stability, and chemical resistance makes it the ideal solution for demanding applications where other materials fail. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including components crafted from advanced materials like SiC to ensure durability and precision in your laboratory processes.
Contact our experts today to discuss how silicon carbide components can enhance the reliability and performance of your equipment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature for silicon carbide heating element? The Real Limit for Your High-Temp Furnace
- What is the maximum temperature for a SiC heating element? Unlock the Key to Longevity and Performance
- What are silicon carbide heating elements used for? Reliable High-Temp Heating for Industrial Processes
- What is SiC elements? The Ultimate High-Temperature Heating Solution
- What is silicon carbide rod heated to high temperature used as? A Premier Heating Element for Extreme Environments



















