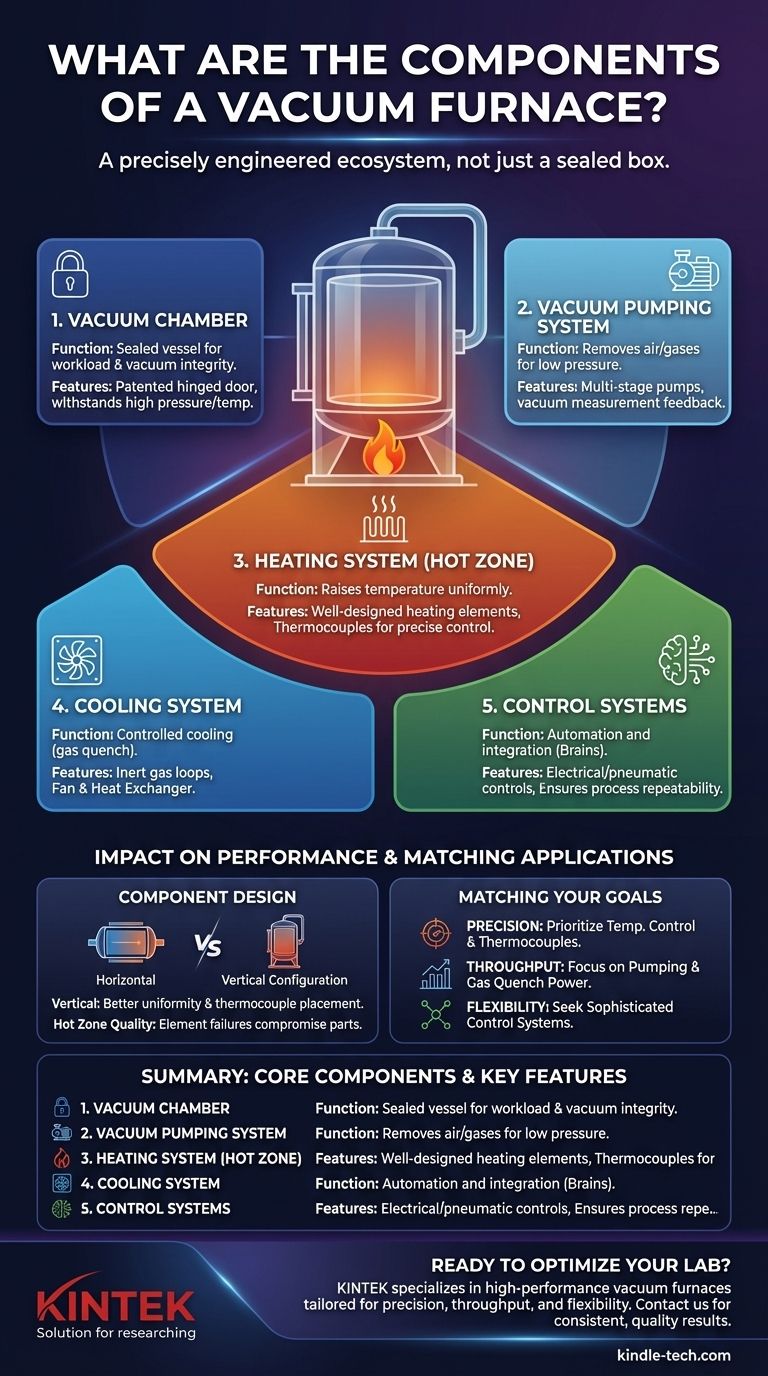
A vacuum furnace is an integrated set of sophisticated systems working in unison. Its primary components are the vacuum chamber, the vacuum pumping and measurement system, the heating and temperature control system, and the cooling system. These are all governed by electrical and pneumatic control systems to create a highly controlled environment for heat treating materials.
A vacuum furnace isn't just a sealed box that gets hot. It's a precisely engineered ecosystem where each component—from the chamber to the cooling circuit—plays a critical role in controlling the atmosphere and thermal cycle to achieve specific material properties.
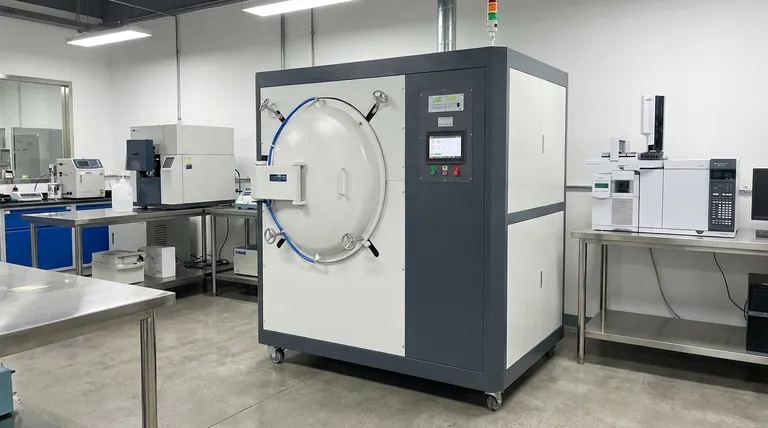

The Core Systems of a Vacuum Furnace
Understanding a vacuum furnace requires looking at it as a collection of distinct, yet interconnected, systems. Each one must perform its function flawlessly for the entire process to succeed.
The Vacuum Chamber
The vacuum chamber is the physical heart of the furnace. It's the sealed vessel that contains the workload and maintains the integrity of the vacuum environment.
Chambers are built to withstand immense external atmospheric pressure and extreme internal temperatures. They often feature a patented hinged door for easy loading and a design that optimizes the flow of gases during the cooling phase.
The Vacuum Pumping System
This system is what puts the "vacuum" in vacuum furnace. Its job is to remove air and other gases from the chamber to create the necessary low-pressure environment.
This is typically a multi-stage system, using different types of pumps to efficiently reduce the pressure from atmospheric levels down to the required vacuum level for the specific metallurgical process. A vacuum measurement system provides constant feedback to ensure the correct pressure is maintained.
The Heating and Temperature Control System
This is the "furnace" component, often referred to as the hot zone. It is responsible for raising the temperature of the workload according to a precise profile.
Key elements include the heating elements, which must be well-designed and installed to ensure temperature uniformity. Temperature control is managed by sensors, most commonly thermocouples, which are strategically placed to accurately measure the temperature of the workload. The configuration of the furnace (e.g., vertical) can make placing these sensors easier.
The Cooling System
After the heating cycle is complete, the workload must be cooled at a controlled rate. The cooling system handles this critical step, often by using a high-pressure gas quench.
This typically involves inert gas cooling loops. A powerful fan circulates an inert gas like nitrogen or argon through the chamber and over a heat exchanger to rapidly and uniformly cool the material, locking in the desired metallurgical properties.
The Control Systems
The electrical and pneumatic control systems are the brains and nervous system of the furnace. They integrate and automate the operation of all other components.
These systems manage everything from pump activation and valve control to executing the heating and cooling profiles with high accuracy. This ensures process repeatability and safe operation.
Component Design and Its Impact on Performance
The quality of individual components has a direct and significant impact on the furnace's overall performance, reliability, and the final quality of the treated product.
The Critical Role of the Hot Zone
Poorly designed or installed heating elements are a primary source of failure. They can lead to non-uniform heating, which compromises the integrity of the heat-treated parts and can damage other critical hot zone components over time.
Horizontal vs. Vertical Configuration
The physical orientation of the furnace influences its operational characteristics. Horizontal furnaces are often praised for their compact design and ease of loading.
Vertical furnaces, on the other hand, can offer superior temperature uniformity for certain load shapes and make it easier to place thermocouples in hard-to-reach areas, ensuring more accurate process control.
The Importance of System Integration
A high-performance vacuum furnace is more than the sum of its parts. True efficiency and repeatability come from how well the vacuum, heating, and cooling systems are integrated and controlled, allowing for rapid cycles and precise results.
Matching Components to Your Application
When evaluating a vacuum furnace, consider how its systems align with your primary operational goals.
- If your primary focus is process precision and repeatability: The quality of the temperature control system, including the number and placement of thermocouples, is paramount.
- If your primary focus is high throughput: Pay close attention to the efficiency of the vacuum pumping system and the power of the gas quench cooling system, as these dictate cycle times.
- If your primary focus is operational flexibility: Look for a furnace with sophisticated control systems that allow for easy programming of complex heat treatment recipes for a variety of materials.
Ultimately, understanding how each system contributes to the whole empowers you to select and operate a furnace that delivers consistent, high-quality results.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Chamber | Sealed vessel for workload | Hinged door, withstands high pressure/temperature |
| Vacuum Pumping System | Creates low-pressure environment | Multi-stage pumps, vacuum measurement |
| Heating System | Raises temperature uniformly | Heating elements, thermocouples, precise control |
| Cooling System | Controlled cooling after heating | Inert gas quench, heat exchanger, fan circulation |
| Control Systems | Automation and integration | Electrical/pneumatic controls, process repeatability |
Ready to optimize your lab's thermal processing with a precision vacuum furnace? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including vacuum furnaces tailored for your specific needs—whether for process precision, high throughput, or operational flexibility. Our systems ensure superior temperature control, rapid cooling, and reliable integration for consistent, high-quality results. Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does arc melting equipment facilitate the preparation of refractory multi-principal element alloys (RMPEAs)?
- What is deposition of a vapor? A Guide to High-Precision Thin Film Coating
- What materials are used in high temperature furnace? Uncover the Key Components for Extreme Heat
- What kind of material is full annealing applied to? Optimize Steel for Maximum Machinability
- Why are vacuum drying ovens essential for health monitoring sensors? Ensure Superior Stability and Biological Safety
- How do induction heating systems with graphite hot zones function during mechanical testing? Achieve Ultra-High 2573 K
- How does a reaction furnace contribute to the synthesis of uranium nitride precursor (U2N3) powder? High-Purity Controls
- How is heating done in sintering operation? Master the Core Methods for Dense, Strong Parts



















