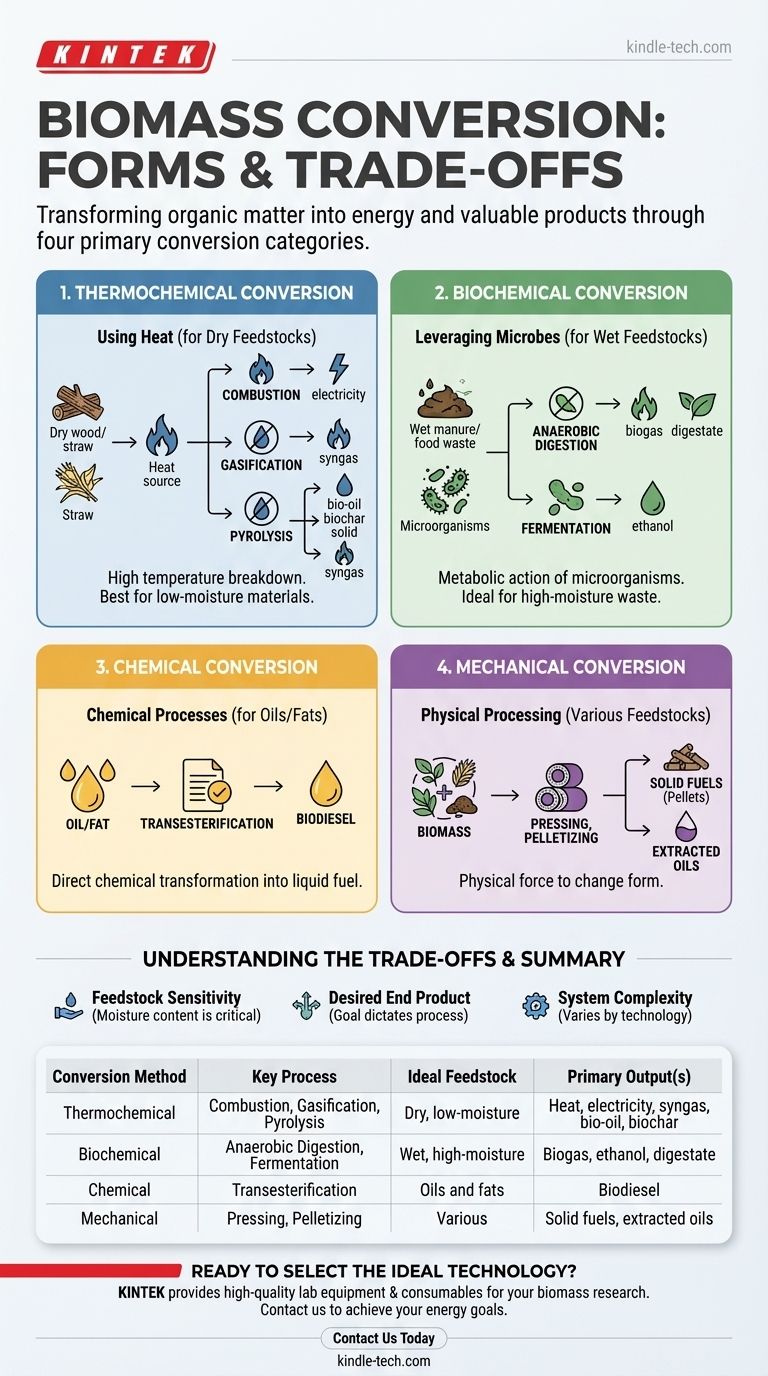
The primary forms of biomass conversion fall into four main categories: thermochemical, biochemical, chemical, and mechanical. These processes use different agents—such as heat, microbes, or physical force—to break down organic matter and transform it into a usable form of energy or other valuable products.
The optimal conversion method is not universal; it depends entirely on the type of biomass you have (the "feedstock") and the specific energy product you need, whether it's direct heat, electricity, liquid fuel, or gas.

Thermochemical Conversion: Using Heat to Break Down Biomass
Thermochemical processes use high temperatures to convert biomass. These methods are generally best suited for dry, low-moisture feedstocks like wood, straw, or other agricultural residues.
Combustion
Combustion is the simplest and most common method. It is the direct burning of biomass in the presence of oxygen to release heat.
This heat can be used directly for heating applications or to produce steam that turns a turbine, generating electricity.
Gasification
Gasification involves heating biomass to high temperatures with a limited and controlled amount of oxygen.
Instead of burning completely, the biomass converts into a combustible gas mixture called syngas (synthesis gas), which can then be used to generate electricity or be processed into liquid fuels and chemicals.
Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is the process of heating biomass in the complete absence of oxygen.
This process breaks down the organic material into three key products: a liquid known as bio-oil (or pyrolysis oil), a solid charcoal-like substance called biochar, and a syngas. Bio-oil can be upgraded into transportation fuels, while biochar is a valuable soil amendment.
Biochemical Conversion: Leveraging Biological Processes
Biochemical conversion uses the metabolic action of microorganisms—like bacteria and yeast—to break down biomass. These methods are ideal for wet, high-moisture feedstocks such as animal manure, sewage sludge, and food waste.
Anaerobic Digestion
This process uses microorganisms to decompose wet organic matter in an oxygen-free environment.
The primary output is biogas, a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide, which can be burned to generate heat and electricity. The remaining solid and liquid material, called digestate, is a nutrient-rich fertilizer.
Fermentation
Fermentation uses yeast or bacteria to convert the carbohydrates and sugars in biomass directly into liquid fuels.
The most common application is the production of ethanol from crops like corn, sugarcane, or cellulosic materials. This ethanol is then blended with gasoline for use as a transportation fuel.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right biomass conversion technology requires understanding the inherent limitations and suitability of each process. There is no single "best" method.
Feedstock Sensitivity
The nature of your input material is the most critical factor. Dry, woody biomass is highly inefficient for biochemical processes but is perfect for thermochemical methods like combustion or gasification.
Conversely, attempting to burn wet manure is extremely inefficient. Its high moisture content makes it an ideal candidate for anaerobic digestion.
Desired End Product
Your goal dictates the process. If you need direct, on-site heat, combustion is the most direct route. If you need a liquid transportation fuel like ethanol, fermentation is the established pathway.
Processes like pyrolysis are more flexible, producing a mix of gas, liquid, and solid products that can serve different markets.
System Complexity and Scale
Combustion systems can be relatively simple and are proven at both small and large scales.
In contrast, technologies like gasification or pyrolysis require more sophisticated engineering, higher capital investment, and more precise operational control to be effective.
Matching the Process to Your Goal
Your choice of conversion technology should be a direct function of your available resources and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is generating heat or electricity from dry waste (like wood or crop residue): Combustion is the most straightforward and established pathway.
- If your primary focus is managing wet organic waste (like manure or food scraps) while producing gas: Anaerobic digestion is the ideal solution.
- If your primary focus is creating liquid biofuel (like ethanol) from sugar or starch-based crops: Fermentation is the standard biochemical process.
- If your primary focus is converting oils and fats into biodiesel: A chemical process known as transesterification is the required pathway.
Ultimately, selecting the right conversion technology is about aligning the specific characteristics of your biomass feedstock with your final energy goal.
Summary Table:
| Conversion Method | Key Process | Ideal Feedstock | Primary Output(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermochemical | Combustion, Gasification, Pyrolysis | Dry, low-moisture (e.g., wood, straw) | Heat, electricity, syngas, bio-oil, biochar |
| Biochemical | Anaerobic Digestion, Fermentation | Wet, high-moisture (e.g., manure, food waste) | Biogas, ethanol, digestate (fertilizer) |
| Chemical | Transesterification | Oils and fats | Biodiesel |
| Mechanical | Physical processing (e.g., pressing, pelletizing) | Various biomass types | Solid fuels (e.g., pellets), extracted oils |
Ready to select the ideal biomass conversion technology for your lab or facility? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to support your biomass research and energy production needs. Whether you're exploring thermochemical processes like pyrolysis or optimizing biochemical methods like anaerobic digestion, our solutions ensure precision, efficiency, and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can help you achieve your energy goals with the right equipment and expertise!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process



















