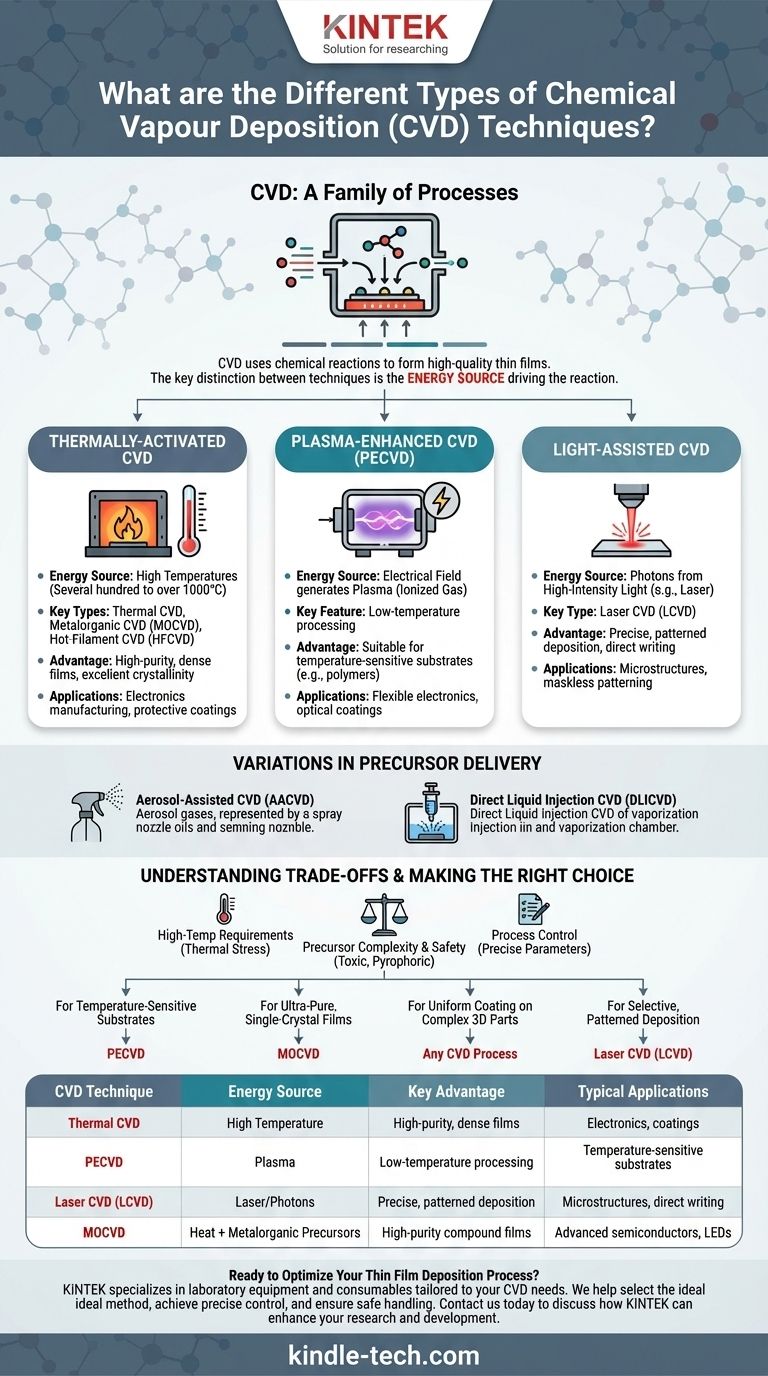
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a family of processes, not a single technique. The primary types are distinguished by how they supply the energy needed to drive the chemical reaction that forms the thin film. Key methods include thermally-activated CVD which uses heat, Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) which uses plasma, and light-assisted CVD which uses sources like lasers.
The fundamental difference between various CVD techniques is the energy source used to initiate the chemical reaction. Choosing a method is a matter of balancing the required film properties, the substrate's heat tolerance, and the complexity of the precursor materials.

The Core Principle of Chemical Vapor Deposition
What is CVD?
Chemical Vapor Deposition is a process used to create high-quality, high-performance solid thin films. It involves introducing one or more volatile precursor gases into a reaction chamber.
These gases decompose or react on a heated substrate surface, leaving behind a solid material layer.
Chemical Reaction is Key
The defining feature of CVD is the use of a chemical reaction to form the film. This distinguishes it from Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) techniques, which typically involve evaporating or sputtering a solid material onto the substrate.
The chemical nature of the process allows for the creation of highly pure, dense, and well-crystallized films.
Creating Conformal Coatings
A significant advantage of CVD is its ability to produce conformal films. Because the precursor gases surround an object, the deposition process happens uniformly on all surfaces.
This "wrap-around" effect is ideal for coating complex, three-dimensional shapes, which is difficult for line-of-sight PVD methods.
Major Categories of CVD Techniques
The most effective way to understand the different types of CVD is to group them by the energy source that drives the critical chemical reaction.
Thermally-Activated CVD
This is the most traditional form of CVD, relying on high temperatures (often several hundred to over a thousand degrees Celsius) to provide the energy for the reaction.
Specific types include Thermal CVD, Metalorganic CVD (MOCVD), which uses metal-organic precursors and is vital for manufacturing advanced electronics, and Hot-Filament CVD (HFCVD).
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD)
Instead of relying solely on high heat, PECVD uses an electrical field to generate a plasma (an ionized gas).
The highly reactive species within the plasma can initiate the chemical reaction at much lower temperatures than thermal CVD. This makes PECVD suitable for depositing films on substrates that cannot withstand high heat, such as plastics.
Light-Assisted CVD
This category uses photons from a high-intensity light source to provide the reaction energy.
The most common example is Laser CVD (LCVD), where a focused laser beam can selectively deposit material in a very precise pattern, allowing for direct writing of microstructures.
Variations in Precursor Delivery
Some CVD methods are distinguished not by the energy source, but by how the chemical precursor is introduced into the reaction chamber.
Aerosol-Assisted CVD (AACVD) uses an aerosol to transport the precursor, while Direct Liquid Injection CVD (DLICVD) vaporizes a precise amount of a liquid precursor directly inside a heated chamber.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, CVD is not without its challenges. Understanding the limitations of each method is key to making an informed decision.
High-Temperature Requirements
The primary drawback of traditional thermal CVD is the need for very high temperatures. This limits the types of substrate materials that can be used and can introduce thermal stress into the final product.
Precursor Complexity and Safety
CVD processes depend on volatile chemical precursors, which can be expensive, toxic, or pyrophoric (igniting spontaneously in air). This requires careful handling, storage, and exhaust management systems.
Process Control
Achieving a specific film thickness, composition, and crystalline structure requires precise control over numerous parameters. These include temperature, pressure, gas flow rates, and precursor concentrations, which can make process optimization complex.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate CVD method depends entirely on the material you are depositing and the substrate you are coating.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive substrate (like a polymer): You need a low-temperature process, making PECVD the ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is creating ultra-pure, single-crystal films for high-end electronics: The precise control offered by MOCVD is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is uniformly coating a complex, 3D part: The inherent conformal nature of any CVD process makes it a superior choice over line-of-sight PVD methods.
- If your primary focus is selective, patterned deposition without masks: The precision of Laser CVD (LCVD) allows you to write patterns directly onto a surface.
Ultimately, the diverse family of CVD techniques provides a highly versatile toolkit for engineering materials at the atomic level.
Summary Table:
| CVD Technique | Energy Source | Key Advantage | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal CVD | High Temperature | High-purity, dense films | Electronics, coatings |
| Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) | Plasma | Low-temperature processing | Temperature-sensitive substrates |
| Laser CVD (LCVD) | Laser/Photons | Precise, patterned deposition | Microstructures, direct writing |
| Metalorganic CVD (MOCVD) | Heat + Metalorganic Precursors | High-purity compound films | Advanced semiconductors, LEDs |
| Aerosol-Assisted CVD (AACVD) | Heat + Aerosol Delivery | Versatile precursor options | Complex material compositions |
Ready to Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition Process?
Choosing the right Chemical Vapor Deposition technique is critical for achieving your desired film properties and performance. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing laboratory equipment and consumables tailored to your specific CVD needs.
We help you:
- Select the ideal CVD method for your substrate and application
- Achieve precise film thickness and composition control
- Implement safe handling of volatile precursors
- Optimize process parameters for superior results
Whether you're working with temperature-sensitive materials or require ultra-pure coatings for advanced electronics, our expertise ensures you get the right solution for your laboratory requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK's CVD solutions can enhance your research and development!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between thermal CVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- How plasma is generated in PECVD? A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Process
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What is the difference between CVD and PVD process? A Guide to Choosing the Right Coating Method
- What is the precursor gas in PECVD? The Key to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















