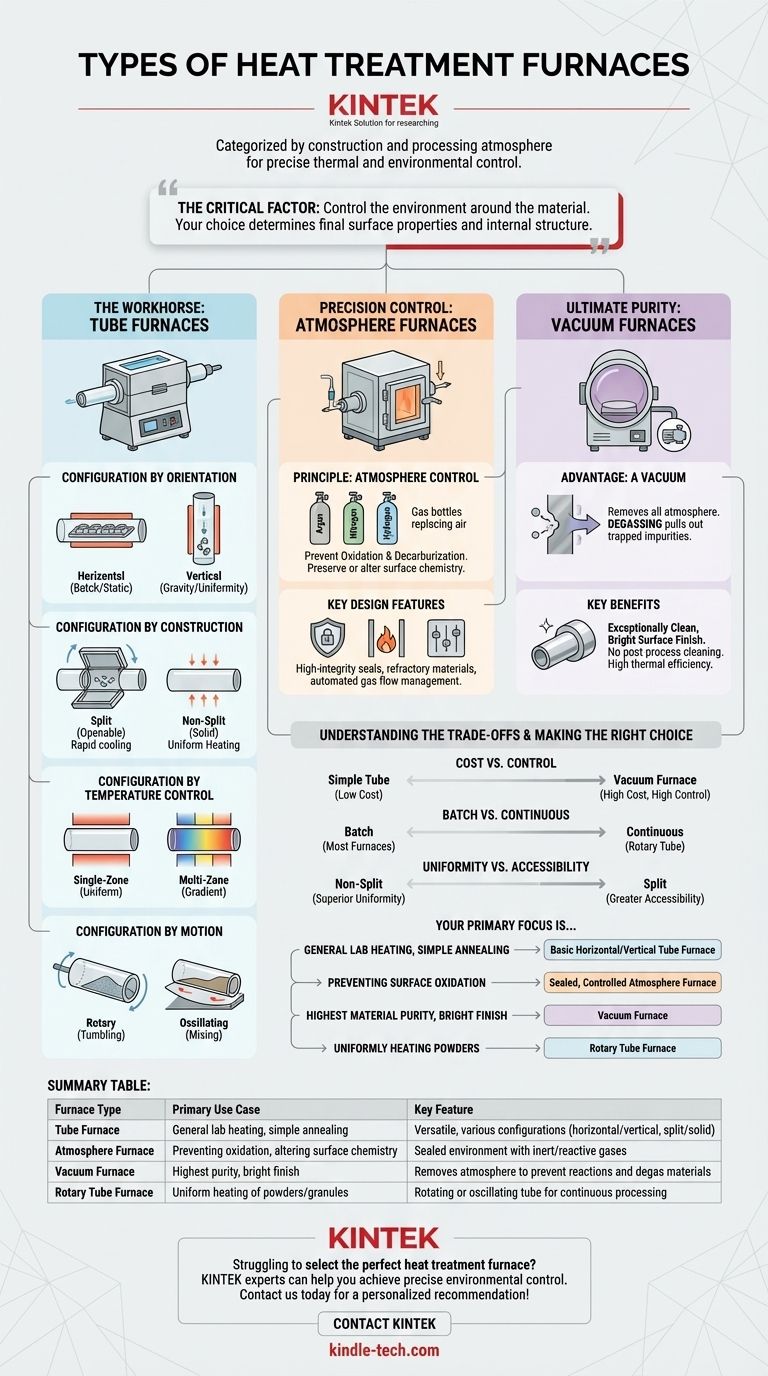
Heat treatment furnaces are primarily categorized by their physical construction and the type of atmosphere they use to process materials. The main types include highly versatile tube furnaces, specialized controlled atmosphere furnaces for preventing surface reactions, and high-purity vacuum furnaces. Each design is engineered to achieve a specific level of thermal and environmental control.
The critical factor in selecting a furnace is not just the temperature it can reach, but the degree to which it can control the environment around the material. Your choice—from a simple tube furnace to a complex vacuum system—directly determines the final surface properties and internal structure of your part.

The Workhorse: Tube Furnaces
Tube furnaces are exceptionally common in laboratory and small-scale production settings due to their versatility. The material is processed inside a contained work tube, which can be made from quartz, alumina, or metal alloys depending on the temperature requirements.
Configuration by Orientation: Horizontal vs. Vertical
Horizontal tube furnaces are the most common configuration, ideal for processing static samples or batches of components arranged on a tray.
Vertical tube furnaces are used when gravity is beneficial, such as for drop-quenching samples, growing crystals, or minimizing the effects of convection currents for highly uniform heating.
Configuration by Construction: Split vs. Non-Split
Split tube furnaces, often called openable or clamshell furnaces, are hinged to open into two halves. This design allows for easy placement and rapid cooling of the work tube and sample.
Non-split (solid) tube furnaces offer better temperature uniformity along the length of the heating zone but require samples to be loaded and unloaded from the ends.
Configuration by Temperature Control: Single-Zone vs. Multi-Zone
A single-zone furnace has one set of heating elements and a single controller, providing a uniform hot zone in the center.
Multi-zone furnaces (e.g., dual-zone, three-zone) have multiple, independently controlled heating zones. This allows for excellent temperature uniformity over a longer length or for creating a specific temperature gradient across the sample.
Configuration by Motion: Rotary and Oscillating
Rotary tube furnaces are designed to process powders, granules, or small parts. The entire tube rotates, tumbling the material to ensure every particle is heated uniformly. They can be used for both batch and continuous processing.
Oscillating tube furnaces provide a similar mixing function but rock back and forth instead of performing a full rotation.
Precision Control: Atmosphere Furnaces
When a material's surface must be protected from air during heating, a controlled atmosphere furnace is required. These systems are designed to operate with specific inert or reactive gases.
The Principle of Atmosphere Control
The core purpose is to prevent undesirable chemical reactions like oxidation (rusting) or decarburization (loss of carbon from steel). By replacing the air with a gas like argon, nitrogen, or hydrogen, the material's surface chemistry can be preserved or intentionally altered.
Key Design Features
These furnaces demand high-integrity seals to prevent gas leaks. They often feature specialized refractory materials like anti-carburizing bricks, fire curtains at openings for safety, and a high degree of automation to manage gas flow and pressure.
Ultimate Purity: Vacuum Furnaces
For the most sensitive applications, even an inert gas atmosphere is insufficient. Vacuum furnaces remove virtually all atmosphere from the heating chamber, providing the purest possible processing environment.
The Advantage of a Vacuum
Operating in a vacuum completely prevents oxidation and decarburization. It also has the unique benefit of pulling out trapped gases and impurities from within the material itself, a process known as degassing.
Key Benefits
This results in an exceptionally clean, bright surface finish with no need for post-process cleaning. Vacuum furnaces also offer high thermal efficiency, enabling very rapid and controlled heating and cooling cycles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right furnace involves balancing capability against complexity and cost. No single design is best for every task.
Cost vs. Control
A simple, single-zone tube furnace represents the lowest cost and complexity. Controlled atmosphere furnaces add significant cost for gas handling and sealing, while vacuum furnaces are the most expensive due to their vacuum pumps, robust chambers, and complex controls.
Batch vs. Continuous Processing
Most tube, vacuum, and atmosphere furnaces are designed for batch processing, where one load is treated at a time. Rotary tube furnaces are a key exception, excelling at the continuous processing of bulk materials.
Temperature Uniformity vs. Accessibility
A non-split tube furnace generally offers superior temperature uniformity. However, a split tube furnace provides far greater accessibility, which can be critical for certain experimental setups or when rapid cooling is desired.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your final decision should be driven by the required outcome for your material.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab heating or simple annealing: A basic horizontal or vertical tube furnace is a versatile and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is preventing surface oxidation or altering surface chemistry: A sealed, controlled atmosphere furnace is essential.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest material purity and a bright finish: A vacuum furnace is the definitive solution.
- If your primary focus is uniformly heating powders or granular materials: A rotary tube furnace is the ideal design for the job.
Ultimately, selecting the correct furnace is about matching its level of environmental control to the specific properties you need to achieve in your finished material.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Use Case | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Tube Furnace | General lab heating, simple annealing | Versatile, various configurations (horizontal/vertical, split/solid) |
| Atmosphere Furnace | Preventing oxidation, altering surface chemistry | Sealed environment with inert/reactive gases |
| Vacuum Furnace | Highest purity, bright finish | Removes atmosphere to prevent reactions and degas materials |
| Rotary Tube Furnace | Uniform heating of powders/granules | Rotating or oscillating tube for continuous processing |
Struggling to select the perfect heat treatment furnace for your specific material requirements? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between tube, atmosphere, and vacuum furnaces to ensure you achieve the precise environmental control, surface properties, and internal structure your materials demand. Contact us today via the form below to discuss your application and receive a personalized recommendation! Contact KINTEK
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the structure of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components & Functions
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries
- What is a vacuum furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Contamination-Free Thermal Processing
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance



















