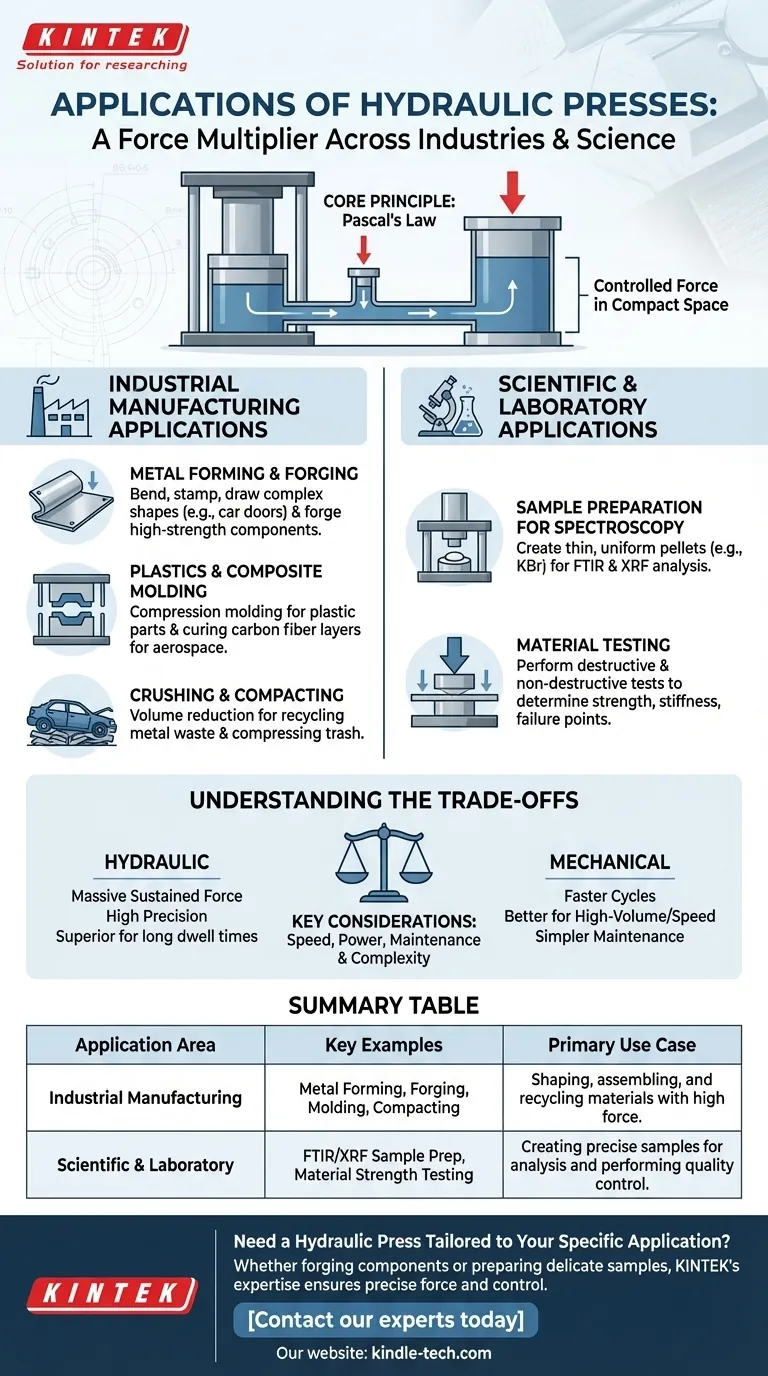
At its core, a hydraulic press is a force multiplier. It is a fundamental tool used across countless industries and scientific fields, applied anywhere a large, controlled force is needed in a compact space. Common examples range from massive industrial machines that forge metal and mold car parts to small, manual presses in laboratories used to prepare samples for chemical analysis.
The true value of the hydraulic press lies in its versatility, which stems from a simple principle: Pascal's Law. This allows it to generate immense, precisely controlled pressure for tasks as different as shaping a steel beam and creating a tiny, transparent pellet for spectroscopy.

Industrial Manufacturing Applications
The most visible applications of hydraulic presses are in heavy industry, where their ability to generate thousands of tons of force is essential for shaping and assembling products.
Metal Forming and Forging
Hydraulic presses are the workhorses of metalworking. They are used to bend, stamp, and draw large sheets of metal into complex shapes, such as car doors and appliance bodies.
In forging, a press squeezes a heated metal billet into a die, shaping it into high-strength components like engine parts or industrial tools.
Plastics and Composite Molding
Many of the plastic items we use daily are formed using hydraulic presses. In compression molding, the press closes a heated mold onto a plastic material, forcing it to take the mold's shape.
This same principle applies to advanced composites, where presses are used to cure layers of carbon fiber or fiberglass under immense pressure and heat to create strong, lightweight parts for aerospace and automotive industries.
Crushing and Compacting
The raw power of a hydraulic press is ideal for volume reduction. Scrap metal yards use large hydraulic presses to compact old cars and other metal waste into dense, manageable blocks for recycling.
This application also extends to waste management, where hydraulic compactors are used to compress trash, and in manufacturing to create "pucks" from metal shavings for easier handling.
Scientific and Laboratory Applications
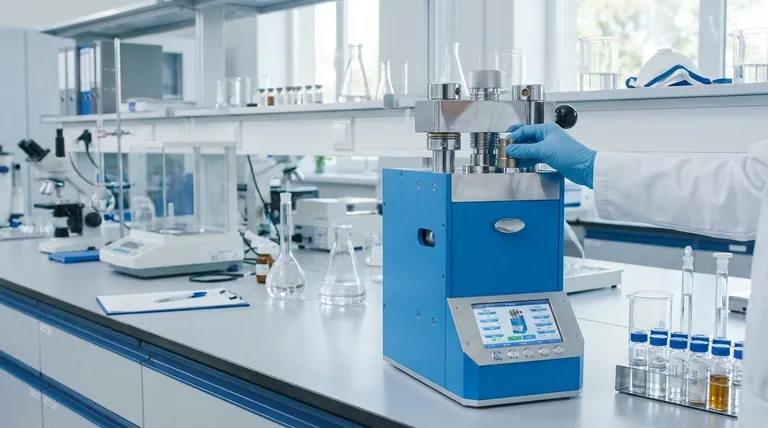
On a much smaller scale, hydraulic presses are indispensable tools in research and quality control labs, where precision is just as important as force.
Sample Preparation for Spectroscopy
This is a primary application for manual and mini hydraulic presses. Techniques like FTIR (Fourier-Transform Infrared) spectroscopy require a sample to be very thin and uniform for infrared light to pass through.
Scientists mix a small amount of their sample with a salt powder (KBr) and use a hydraulic press to create a small, transparent pellet. The press ensures the pellet is solid and consistent, which is critical for accurate analysis.
A similar process is used to create sample pellets for XRF (X-ray Fluorescence) analysis, which identifies the elemental composition of a material.
Material Testing
In materials science and engineering labs, hydraulic presses are used to perform destructive and non-destructive testing.
By applying a controlled compressive force, researchers can determine a material's strength, stiffness, and failure points. This is essential for quality control and the development of new polymers, composites, and alloys.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly powerful and versatile, hydraulic systems are not the solution for every application. Understanding their limitations is key to using them effectively.
Speed vs. Power
Hydraulic presses excel at delivering massive, sustained force. However, they are generally slower than mechanical presses, which complete a cycle more rapidly.
For high-speed, high-volume operations like stamping small metal parts, a mechanical press is often a better choice. For tasks requiring immense force or a long "dwell" time under pressure, hydraulic is superior.
Maintenance and Complexity
Hydraulic systems rely on fluid, pumps, hoses, and seals. This introduces a level of complexity that requires regular maintenance to prevent leaks and ensure consistent performance.
Fluid contamination or a leak can lead to a loss of pressure and system failure, demanding a more rigorous maintenance schedule compared to simpler mechanical systems.
Matching the Press to the Task
The right hydraulic press is entirely dependent on your specific goal, whether you are shaping tons of steel or analyzing milligrams of a chemical compound.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial production: You need a high-tonnage, often automated press designed for a specific task like deep drawing, forging, or molding.
- If your primary focus is laboratory analysis or R&D: A smaller manual or "mini" hydraulic press provides the precision and control needed for preparing high-quality spectroscopic pellets or performing material compression tests.
Ultimately, the hydraulic press is a foundational tool that translates fluid pressure into the precise, powerful force that shapes the modern world.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Examples | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Manufacturing | Metal Forming & Forging, Plastics/Composite Molding, Scrap Metal Compacting | Shaping, assembling, and recycling materials with high force. |
| Scientific & Laboratory | FTIR/XRF Sample Preparation, Material Strength Testing | Creating precise samples for analysis and performing quality control. |
Need a Hydraulic Press Tailored to Your Specific Application?
Whether you are forging metal components or preparing delicate lab samples for spectroscopic analysis, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment ensures you get the precise force and control your work demands. Our hydraulic presses are designed for reliability and accuracy across industrial and research environments.
Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and find the perfect hydraulic press solution for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press for XRF KBR FTIR Lab Applications
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the use of manual hydraulic press? A Cost-Effective Tool for Lab Sample Preparation
- How does a laboratory manual hydraulic press facilitate the FT-IR characterization of catalysts? Master Sample Prep.
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in preparing solid model materials? Standardize for Precise Data.
- What is the function of a laboratory hydraulic press for Li10GeP2S12 pellets? Optimize Solid-State Battery Performance
- How is a laboratory hydraulic press used for LLZTO pellets? Achieve 93% Density in Solid-State Battery Research



















