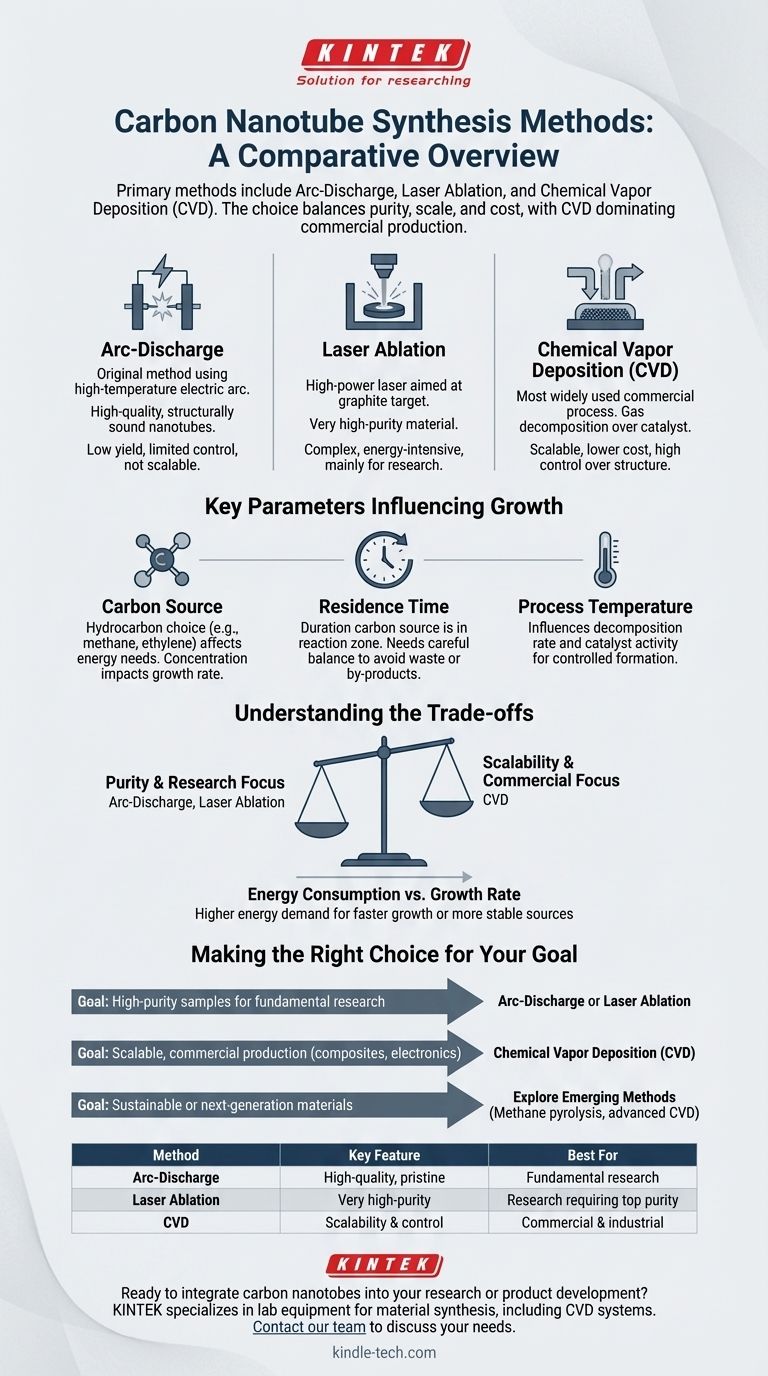
The primary methods for synthesizing carbon nanotubes are arc-discharge, laser ablation, and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). While arc-discharge and laser ablation are traditional techniques known for producing high-purity material, CVD has become the dominant commercial process due to its superior scalability and control over the final product's structure.
The choice of a synthesis method is a critical decision based on a trade-off between the desired nanotube quality, production scale, and cost. While older methods excel at creating pristine samples for research, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) offers the control and efficiency required for most modern industrial and electronic applications.

The Three Core Synthesis Methods
Understanding the fundamental differences between the main production techniques is the first step in selecting the right process. Each method offers a distinct balance of purity, yield, and complexity.
Arc-Discharge
The arc-discharge technique is one of the original methods for producing carbon nanotubes. It involves creating a high-temperature electric arc between two carbon electrodes, which vaporizes the carbon and allows it to re-condense into nanotubes.
This method is valued for producing high-quality, structurally sound nanotubes but generally offers low yield and limited control over the growth process, making it less suitable for large-scale production.
Laser Ablation
In laser ablation, a high-power laser is aimed at a graphite target in a high-temperature furnace. The laser vaporizes the carbon, which is then swept by an inert gas onto a cooler collector where the nanotubes grow.
Similar to arc-discharge, laser ablation can produce very high-purity carbon nanotubes. However, the process is complex and energy-intensive, limiting its use primarily to research settings where material quality is the absolute priority.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is the most widely used method for the commercial production of carbon nanotubes. The process involves introducing a carbon-containing gas (a hydrocarbon like methane or ethylene) into a high-temperature chamber, where it decomposes over a catalyst, allowing nanotubes to grow.
The dominance of CVD stems from its scalability, relatively lower cost, and the high degree of control it offers over nanotube length, diameter, and alignment.
Key Parameters That Influence CNT Growth
Regardless of the method, the final properties of carbon nanotubes are dictated by a few critical operating parameters. Mastering these variables is essential for optimizing production.
The Carbon Source
The choice of carbon-containing gas is a crucial factor, especially in CVD. Different hydrocarbons require different amounts of energy to break down into the carbon precursors needed for nanotube growth.
For example, acetylene can act as a direct precursor, while methane and ethylene require more energy for thermal conversion. Managing the concentration of the carbon source is also key; higher concentrations can increase growth rates but also lead to higher energy consumption.
Residence Time
Residence time refers to how long the carbon source remains in the reaction zone. This parameter must be carefully balanced.
An insufficient residence time wastes the carbon source, as it doesn't have enough time to accumulate and contribute to growth. Conversely, an excessive residence time can lead to the accumulation of by-products that hinder the process.
Process Temperature
Temperature is a critical lever in CNT synthesis. It directly influences the decomposition rate of the carbon source and the activity of the catalyst used in the CVD process. The optimal temperature ensures efficient breakdown of the precursor gas and facilitates controlled nanotube formation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a synthesis method is not about finding a single "best" option but about understanding the inherent compromises and aligning them with your goals.
Purity vs. Scalability
The most fundamental trade-off is between material purity and production volume. Arc-discharge and laser ablation excel at creating small batches of highly pure nanotubes, ideal for scientific research.
CVD, on the other hand, delivers good-to-high purity at a scale suitable for industrial applications, making it the workhorse of the industry.
Energy Consumption vs. Growth Rate
There is a direct relationship between the energy put into the system and the speed of nanotube growth. Using a more stable carbon source like methane requires more energy to break down, and increasing the concentration of precursors to accelerate growth also increases overall energy demand.
Optimizing a process involves finding the sweet spot that delivers an acceptable growth rate without incurring prohibitive energy costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final application dictates the ideal synthesis strategy. By defining your primary objective, you can navigate the trade-offs effectively and select the appropriate pathway.
- If your primary focus is high-purity samples for fundamental research: Arc-discharge or laser ablation will provide the highest quality material, despite lower yields and higher costs.
- If your primary focus is scalable, commercial production for composites or electronics: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the industry standard, offering the best balance of control, cost, and output.
- If your primary focus is sustainable or next-generation materials: Explore emerging methods like methane pyrolysis or advanced CVD processes designed to create novel, highly conductive, or hybrid products.
Ultimately, mastering the synthesis of carbon nanotubes lies in carefully aligning the chosen method and its operating parameters with your specific application and economic goals.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Arc-Discharge | High-quality, pristine nanotubes | Fundamental research |
| Laser Ablation | Very high-purity material | Research requiring top purity |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Scalability and process control | Commercial & industrial production |
Ready to integrate carbon nanotubes into your research or product development? The right synthesis method is critical for success. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables needed for advanced material synthesis, including CVD systems. Our experts can help you select the ideal setup to achieve your goals for purity, yield, and scale. Contact our team today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating



















