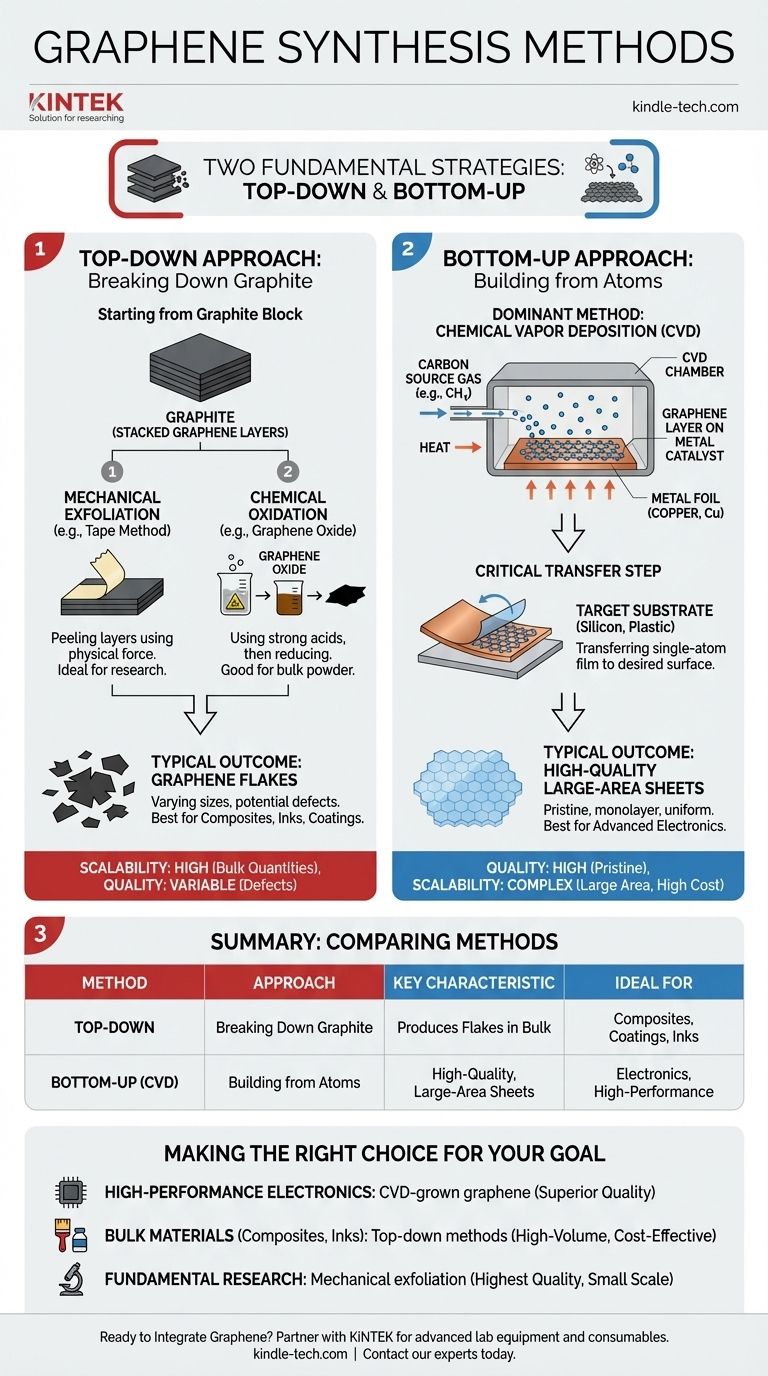
At its core, the synthesis of graphene is divided into two fundamental strategies. These are the "top-down" approach, where graphene is derived by breaking down graphite, and the "bottom-up" approach, which involves building the graphene sheet atom by atom from carbon-containing sources.
The choice between synthesis methods is a critical decision driven by your end goal. Top-down methods are generally suited for producing large quantities of graphene flakes, while bottom-up methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) are the standard for creating high-quality, large-area sheets for electronics.

The "Top-Down" Approach: Starting from Graphite
The top-down strategy is conceptually straightforward: take a block of graphite, which is essentially a stack of countless graphene layers, and separate those layers.
Core Principle
These methods rely on overcoming the weak van der Waals forces that hold the graphene layers together within the graphite structure. The goal is to isolate individual or few-layer sheets.
Common Methods
The most prominent top-down techniques include mechanical exfoliation (famously using adhesive tape to peel off layers) and chemical oxidation, which uses strong acids to create graphene oxide, a precursor that can then be chemically reduced back to graphene.
Typical Outcome
Top-down methods typically yield graphene flakes of varying sizes and quality. While they are often effective for producing bulk quantities of graphene powder for use in composites, inks, and coatings, they can introduce defects into the crystal structure.
The "Bottom-Up" Approach: Building from Atoms
The bottom-up approach is a more controlled process of atomic assembly. Instead of breaking down a larger structure, you are constructing the graphene lattice from individual carbon atoms.
Core Principle
This strategy involves providing a source of carbon atoms and a suitable surface, or substrate, where these atoms can arrange themselves into the characteristic hexagonal lattice of graphene.
The Dominant Method: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the most popular and commercially significant bottom-up method for producing high-quality graphene. It has become the industry standard for applications requiring pristine, large-area films.
How CVD Works
The CVD process involves heating a metal catalyst foil, such as copper (Cu), to high temperatures inside a chamber. A carbon-containing gas, like methane (CH4), is then introduced. The high temperature breaks down the gas, releasing carbon atoms that deposit onto the surface of the metal foil and assemble into a continuous, single layer of graphene.
The Critical Transfer Step
A key characteristic of CVD is that the graphene is grown on a metal substrate. To be used in most applications, this single-atom-thick film must then be carefully transferred to a target substrate, such as silicon or flexible plastic.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single synthesis method is universally superior. The optimal choice depends entirely on the requirements of the final application, balancing quality, quantity, and cost.
Quality vs. Scalability
CVD excels at producing high-quality, monolayer graphene sheets over large areas, which is essential for advanced electronics. Top-down methods, while capable of producing massive quantities, often result in a wider distribution of flake sizes and a higher density of defects.
Complexity and Cost
The CVD process requires specialized high-temperature equipment and precise control over gas flow and pressure, making it a more complex and costly technique. Furthermore, the post-growth transfer process adds another layer of technical challenge.
Purity and Contamination
Top-down chemical methods can leave behind residual chemicals or introduce structural defects during the oxidation and reduction steps. CVD, while cleaner, requires careful optimization to minimize defects and control the nucleation and growth of graphene crystals for a flawless film.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application dictates the most appropriate synthesis method.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics: The superior quality and uniformity of CVD-grown graphene is the necessary choice.
- If your primary focus is bulk materials like composites, coatings, or conductive inks: The high-volume output of top-down methods like chemical oxidation is more practical and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research on pristine graphene: The original mechanical exfoliation method remains a valuable tool for producing the highest-quality, defect-free flakes, albeit on a very small scale.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental difference between building graphene up and breaking it down is the key to selecting the right tool for the job.
Summary Table:
| Method | Approach | Key Characteristic | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top-Down | Breaking down graphite | Produces flakes in bulk quantities | Composites, coatings, conductive inks |
| Bottom-Up (CVD) | Building from carbon atoms | Creates high-quality, large-area sheets | Electronics, high-performance applications |
Ready to Integrate Graphene into Your Research or Product?
Navigating the complexities of graphene synthesis is the first step. The next is equipping your lab with the right tools for success. Whether you are scaling up production with a robust CVD system or require precise thermal processing for material development, KINTEK is your partner in innovation.
We specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to advanced material science needs. Our expertise ensures you have the reliable technology to achieve consistent, high-quality results in your graphene projects.
Let's discuss your specific requirements. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the examples of CVD method? Discover the Versatile Applications of Chemical Vapor Deposition
- What are the advantages of PECVD over CVD? Achieve High-Quality Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- What is the difference between CVD and PVD process? A Guide to Choosing the Right Coating Method
- How plasma is generated in PECVD? A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Process
- Why is PECVD better than CVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















