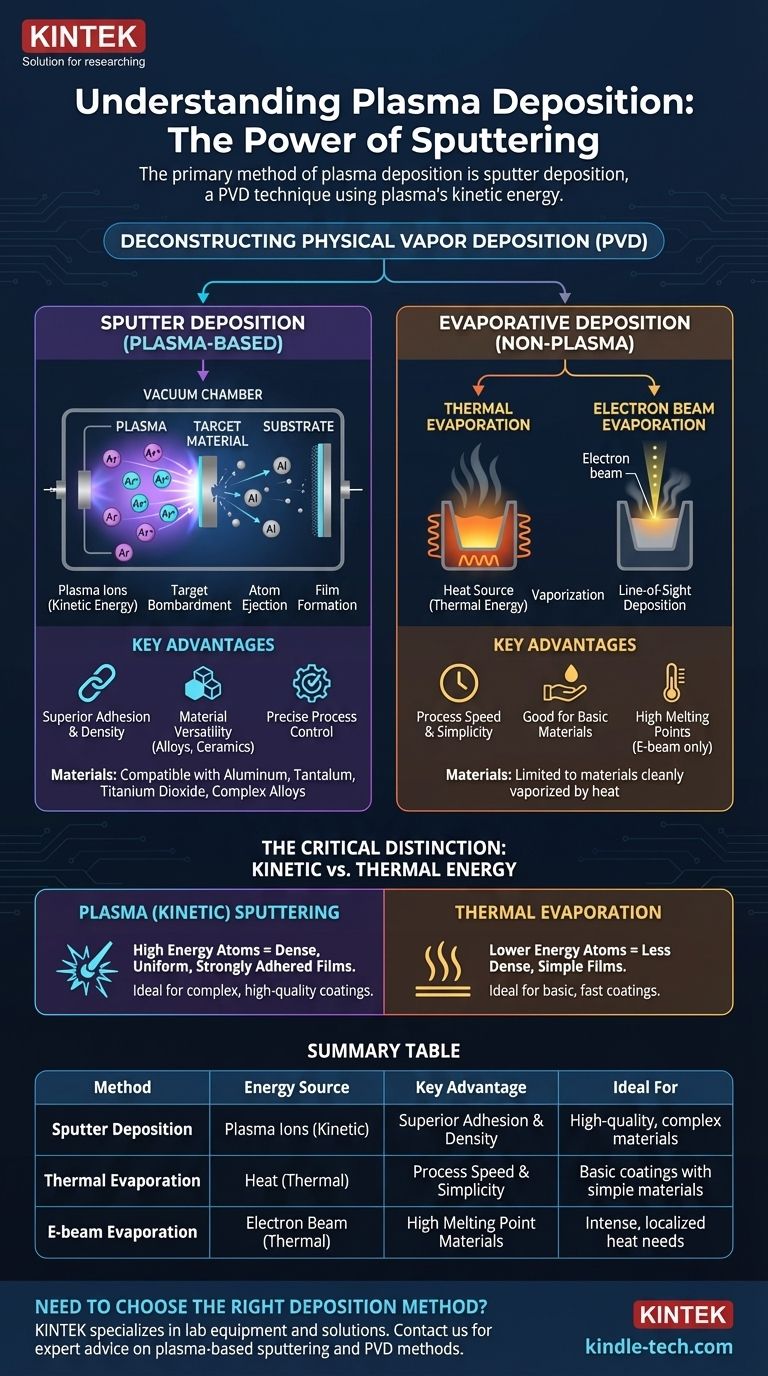
The primary method of plasma deposition is sputter deposition, a technique that uses an energized plasma to bombard a source material, ejecting atoms that then deposit as a thin film onto a substrate. While often grouped with other methods under the umbrella of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), sputtering is distinct because it relies on the kinetic energy of plasma ions, not thermal energy, to vaporize the source material.
The critical distinction to understand is that plasma isn't just one method; it's the enabling tool for a specific category of deposition. Sputtering uses plasma to physically knock atoms loose, while other common techniques like thermal evaporation simply use heat, offering fundamentally different outcomes in film quality and material compatibility.

Deconstructing Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
To understand plasma deposition, you must first understand its place within the broader category of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
The Core Principle of PVD
PVD describes a family of processes where a solid material is converted into a vapor, transported through a vacuum or low-pressure environment, and condensed onto a substrate as a solid thin film. The goal is to create a highly pure, functional coating.
The Two Main Pathways: Evaporation vs. Sputtering
Within PVD, there are two dominant approaches to creating the vapor. The method chosen dictates the energy of the depositing particles and, ultimately, the properties of the final film.
Sputter Deposition: The Primary Plasma Method
Sputtering is the quintessential plasma deposition technique. It is a highly controlled process valued for its versatility and the high quality of the films it produces.
How Sputtering Works
The process involves creating a plasma, typically from an inert gas like argon. A strong electric field accelerates the positive ions from this plasma, causing them to collide with a "target," which is made of the material you wish to deposit.
This high-energy bombardment physically knocks atoms loose from the target. These ejected atoms travel through the vacuum chamber and deposit onto the substrate, gradually building a thin, uniform film.
The Role of Plasma
The plasma is the engine of the sputtering process. It serves as the source of the energetic ions that provide the momentum for ejecting material from the target. Without the plasma, there would be no bombardment and no deposition.
Materials Compatible with Sputtering
Sputtering is exceptionally versatile and can be used to deposit a wide range of materials, including pure metals like aluminum and tantalum, as well as complex compounds like titanium dioxide.
Evaporative Deposition: The Non-Plasma Alternative
It's crucial to contrast sputtering with evaporative methods to understand why plasma is used. These techniques are also PVD but do not involve plasma.
Thermal Evaporation
This is the simplest PVD method. The source material is heated in a high vacuum until its atoms gain enough thermal energy to vaporize. This vapor then travels in a line-of-sight path and condenses on the cooler substrate.
Electron Beam Evaporation
A more controlled version of thermal evaporation, this method uses a high-energy beam of electrons to heat and vaporize the source material. It allows for the deposition of materials with very high melting points that are inaccessible with simple thermal heating.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Sputtering vs. Evaporation
Choosing between a plasma-based method and an evaporative one depends entirely on the requirements of the final film.
Adhesion and Film Density
Sputtered atoms arrive at the substrate with significantly more kinetic energy than evaporated atoms. This results in films that are denser, more uniform, and have superior adhesion to the substrate.
Material Versatility
Evaporation is limited to materials that can be cleanly vaporized by heat. Sputtering can deposit virtually any material that can be made into a target, including complex alloys and compounds that would decompose if heated.
Process Control
Sputtering offers more precise control over film thickness, uniformity, and composition. However, it is generally a slower and more complex process than thermal evaporation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a plasma-based process comes down to the performance you need from your thin film.
- If your primary focus is superior film quality, density, and adhesion: Sputter deposition is the clear choice due to the higher energy of the depositing atoms.
- If your primary focus is process speed and simplicity for basic materials: Thermal evaporation can be a more straightforward and rapid method for creating simple coatings.
- If you are depositing complex alloys or high-melting-point materials: Sputter deposition provides the robust capability that evaporative methods often lack.
Understanding the fundamental difference between energetic plasma sputtering and passive thermal evaporation is the key to selecting the right deposition process for your application.
Summary Table:
| Method | Energy Source | Key Advantage | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sputter Deposition | Plasma Ions (Kinetic) | Superior Adhesion & Density | High-quality, complex materials (alloys, ceramics) |
| Thermal Evaporation | Heat (Thermal) | Process Speed & Simplicity | Basic coatings with simple materials |
| E-beam Evaporation | Electron Beam (Thermal) | High Melting Point Materials | Materials that require intense, localized heat |
Need to choose the right deposition method for your project? The quality of your thin film depends on selecting the correct technique. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with expert advice and reliable solutions. Our team can help you determine if plasma-based sputtering or another PVD method is best for your application's requirements for adhesion, material compatibility, and film uniformity.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific needs and ensure optimal results for your research or production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between CVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What materials are deposited in PECVD? Discover the Versatile Thin-Film Materials for Your Application
- What is PECVD silicon deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is meant by vapor deposition? A Guide to Atomic-Level Coating Technology



















