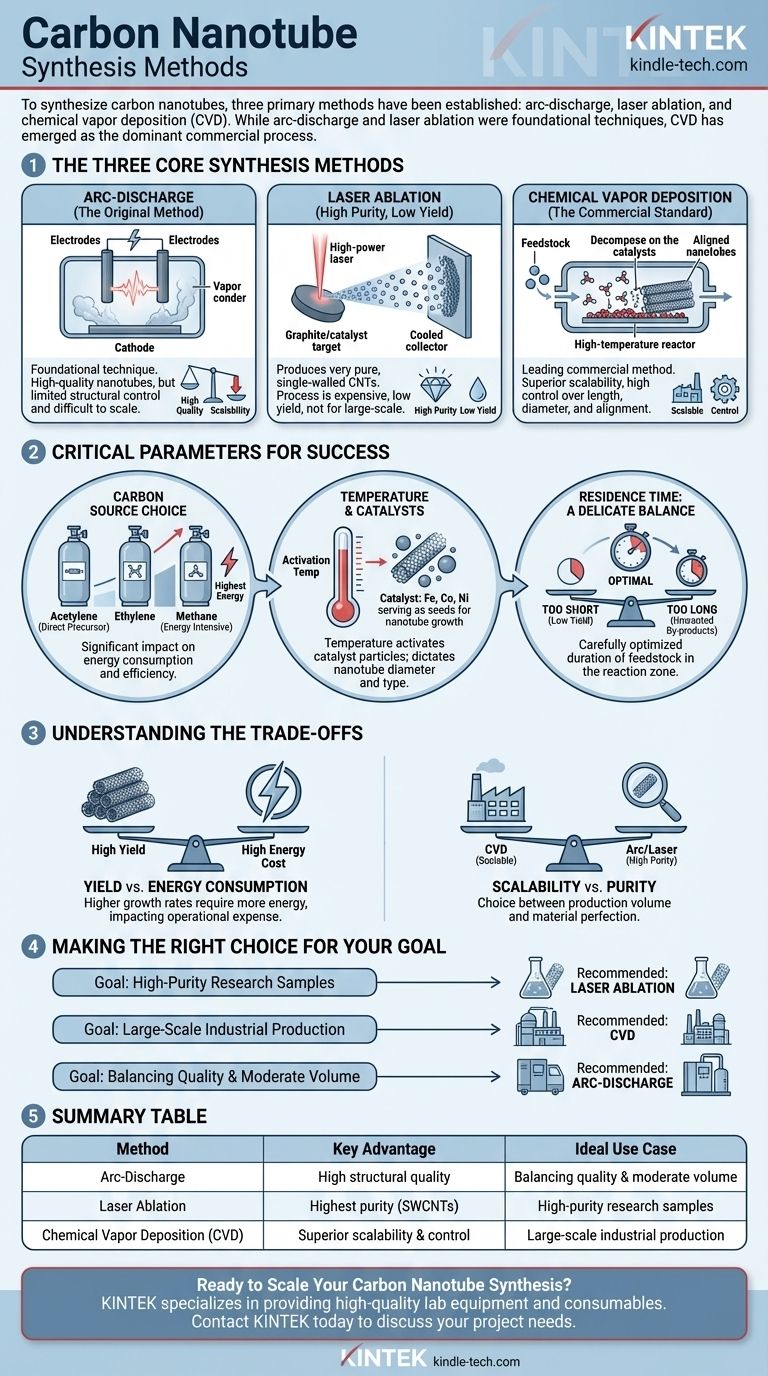
To synthesize carbon nanotubes, three primary methods have been established: arc-discharge, laser ablation, and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). While arc-discharge and laser ablation were foundational techniques for producing high-quality material, CVD has emerged as the dominant commercial process due to its superior scalability and control over the final product's characteristics.
While several methods exist, chemical vapor deposition (CVD) dominates commercial production due to its scalability and granular control. The success of any method hinges on mastering the trade-offs between temperature, carbon source, and time to achieve the desired nanotube structure and yield.

The Three Core Synthesis Methods
Understanding the fundamental differences between the main production techniques is the first step in choosing the right approach for a specific goal, whether it's for fundamental research or industrial-scale manufacturing.
Arc-Discharge (The Original Method)
The arc-discharge technique was one of the first methods used to produce carbon nanotubes. It involves creating a high-voltage electric arc between two carbon electrodes in the presence of an inert gas.
This intense heat vaporizes the carbon from the positive electrode (anode), which then condenses on the cooler negative electrode (cathode), forming nanotubes. While capable of producing high-quality nanotubes, this method offers limited control over their structure and is difficult to scale.
Laser Ablation (High Purity, Low Yield)
In this method, a high-power laser is aimed at a graphite target that is mixed with a metal catalyst. The process takes place in a high-temperature furnace under a flow of inert gas.
The laser vaporizes the target, creating a plume of carbon and catalyst atoms that condense into nanotubes on a cooled collector. Laser ablation is known for producing very pure, single-walled carbon nanotubes, but the process is expensive, has a low yield, and is not suited for large-scale production.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (The Commercial Standard)
CVD is the leading method for commercial and industrial-scale CNT production. This process involves introducing a carbon-containing gas (feedstock) into a high-temperature reactor containing a substrate coated with catalyst nanoparticles.
At high temperatures, the gas decomposes, and carbon atoms deposit onto the catalyst particles, where they self-assemble into nanotube structures. The primary advantage of CVD is its scalability and the high degree of control it offers over nanotube length, diameter, and alignment.
Critical Parameters That Dictate Success
Regardless of the method, the final output is governed by a few critical operating parameters. Controlling these variables is the key to efficient and effective synthesis.
The Choice of Carbon Source
The type of carbon-containing gas used as a feedstock significantly impacts energy consumption and efficiency.
For example, acetylene can act as a direct precursor for nanotube growth without needing extra energy for thermal conversion.
Ethylene and methane, on the other hand, require more energy to break their chemical bonds before carbon can be used for synthesis, with methane being the most energy-intensive of the three.
The Role of Temperature and Catalysts
Temperature is a critical factor. It must be high enough to decompose the carbon feedstock and activate the metal catalyst particles that serve as the "seeds" for nanotube growth.
The choice of catalyst—typically metals like iron, cobalt, or nickel—and the temperature directly influence the diameter and type (single-walled vs. multi-walled) of the nanotubes produced.
Residence Time: A Delicate Balance
Residence time is the duration the carbon feedstock spends in the reaction zone. This parameter must be carefully optimized.
If the residence time is too short, the carbon source doesn't have enough time to accumulate and react, leading to low yield and wasted material.
If the residence time is too long, the feedstock supply can become limited, and unwanted by-products can accumulate, hindering further nanotube growth.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a synthesis method is not about finding a single "best" option, but about balancing competing priorities like cost, quality, and volume.
Yield vs. Energy Consumption
Increasing the concentration of the carbon source and hydrogen can lead to higher growth rates and greater yield. However, this comes at a cost.
This approach requires significantly more energy to maintain reaction conditions, creating a direct trade-off between productivity and operational expense that must be managed for commercial viability.
Scalability vs. Purity
The different methods present a clear choice between production volume and material perfection.
Arc-discharge and laser ablation excel at producing nanotubes with very few structural defects, making them ideal for high-end electronics or research. However, these methods are notoriously difficult to scale up.
CVD, while highly scalable for industrial needs, often produces nanotubes with a wider range of purities and structures, which may require additional purification steps depending on the application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of synthesis method should be dictated entirely by your end-goal. A technique that is ideal for a research lab is often impractical for a factory floor.
- If your primary focus is high-purity research samples: Laser ablation is your best option, as it produces exceptionally high-quality single-walled CNTs, despite its high cost and low yield.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial production: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the only practical choice due to its proven scalability, lower cost, and precise process control.
- If your primary focus is balancing quality and moderate volume: Arc-discharge can serve as a middle ground, offering better structural quality than bulk CVD without the extreme expense of laser ablation.
Ultimately, selecting the right synthesis method is about aligning the process capabilities with your specific application and economic goals.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Advantage | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Arc-Discharge | High structural quality | Balancing quality and moderate volume |
| Laser Ablation | Highest purity (SWCNTs) | High-purity research samples |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Superior scalability & control | Large-scale industrial production |
Ready to Scale Your Carbon Nanotube Synthesis?
Choosing the right synthesis method is critical for achieving your research or production goals. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables needed for advanced material synthesis, including carbon nanotubes. Our expertise can help you optimize your process parameters for maximum yield and efficiency.
Let our team help you select the perfect solution for your specific application. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project needs and discover how our products can enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is direct current DC magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- What is the process of coating deposition? A Step-by-Step Guide to Thin Film Engineering
- How do you calculate coating coverage? A Practical Guide to Accurate Material Estimation
- How do CVD diamonds grow? A Step-by-Step Guide to Lab-Grown Diamond Creation



















