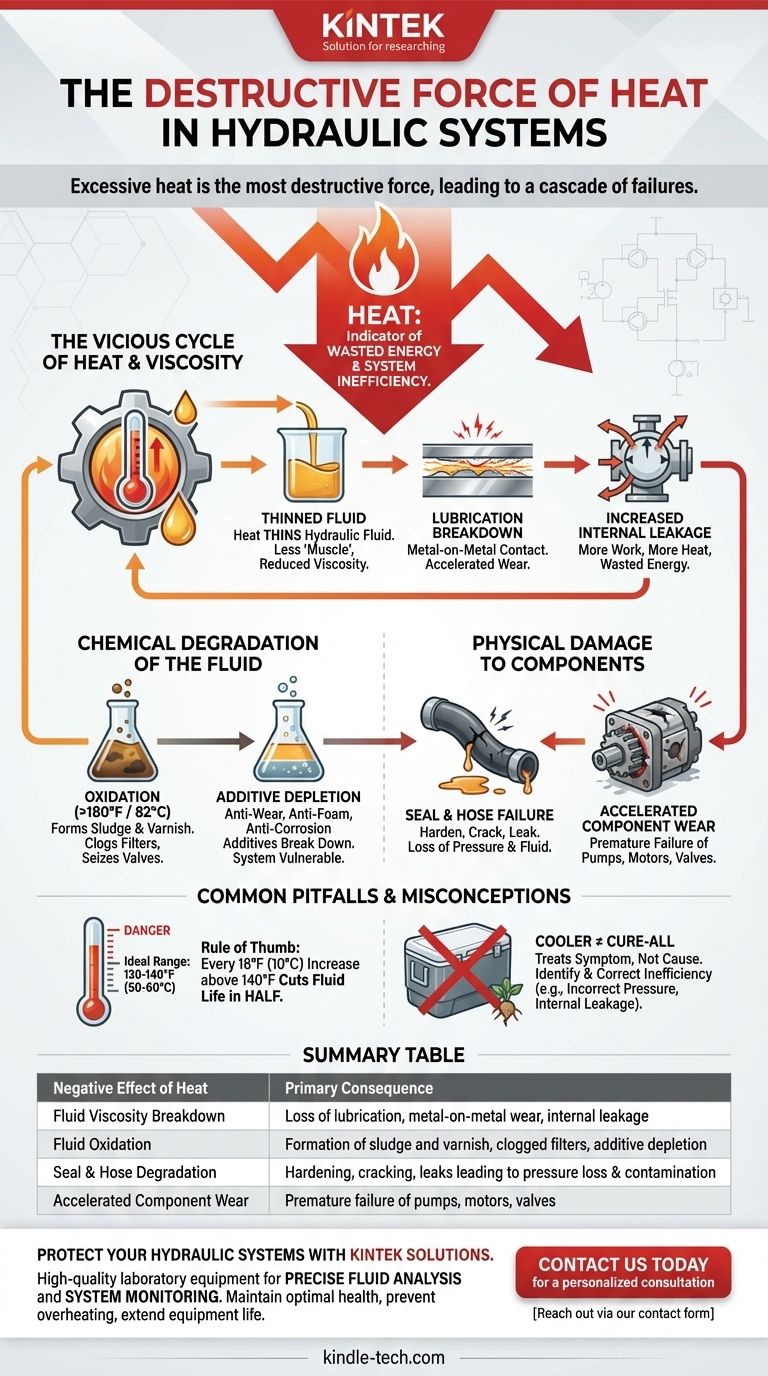
Excessive heat is the most destructive force in a hydraulic system. It directly attacks the hydraulic fluid, the lifeblood of the machine, leading to a cascade of failures. The primary negative effects are the rapid degradation of the fluid, the destruction of seals and hoses, and a critical loss of lubrication that accelerates wear on every component.
Heat is not just a byproduct of operation; it is a direct indicator of wasted energy and system inefficiency. Understanding and controlling heat is the single most important factor in ensuring the reliability, longevity, and performance of any hydraulic system.

The Vicious Cycle of Heat and Viscosity
The most immediate and damaging effect of heat is its impact on the hydraulic fluid's viscosity. This creates a destructive feedback loop that can quickly compromise an entire system.
How Heat Thins Hydraulic Fluid
Viscosity is a fluid's resistance to flow—think of it as the oil's thickness or "muscle." All hydraulic fluids are designed to operate within a specific viscosity range.
As temperature increases, the fluid's viscosity decreases, causing it to become thin and watery. This is the first step in a chain reaction of failures.
The Lubrication Breakdown
The primary job of hydraulic fluid, besides transmitting power, is to lubricate moving parts. This relies on maintaining a strong, microscopic film of oil between metal surfaces.
When heat thins the fluid, this protective film weakens and can break down entirely. This leads to direct metal-on-metal contact, causing friction and accelerated wear in pumps, motors, and valves. This increased friction, in turn, generates even more heat.
Increased Internal Leakage
Precision components like pumps, motors, and spool valves depend on tight tolerances to prevent fluid from leaking internally.
Thinner, low-viscosity fluid bypasses these seals more easily. This internal leakage means the component must work harder to produce the same output, generating significant heat and wasting energy without performing any useful work.
Chemical Degradation of the Fluid
Heat acts as a catalyst, accelerating harmful chemical reactions within the hydraulic fluid that permanently damage its properties.
Oxidation and Sludge Formation
At temperatures above 180°F (82°C), the rate at which hydraulic fluid reacts with oxygen (oxidation) increases dramatically. This process is the primary cause of fluid degradation.
Oxidation creates byproducts like varnish and sludge. Varnish forms a sticky film on internal surfaces, causing valves to seize, while sludge clogs filters, strainers, and small orifices, starving the system of clean fluid.
Additive Depletion
Hydraulic fluids are complex formulas containing vital additives for anti-wear, anti-foam, and anti-corrosion properties. High temperatures cause these additives to break down and deplete at a much faster rate.
Once the additives are gone, the base oil is left unprotected and unable to perform its critical functions, leaving the system vulnerable to catastrophic failure.
Physical Damage to System Components
The consequences of degraded fluid and high temperatures extend to the physical hardware of the system.
Seal and Hose Failure
Hydraulic seals and hoses are typically made from specific elastomeric compounds designed for a limited temperature range.
Excessive heat causes these materials to harden, become brittle, and crack. This leads to both internal and external leaks, which can result in fluid loss, contamination, and a loss of system pressure.
Accelerated Component Wear
The combination of poor lubrication, fluid contamination from sludge, and thermal expansion of metal parts creates a perfect storm for premature wear.
Pumps and motors, which operate under the highest pressure and tightest tolerances, are often the first components to fail in an overheated system.
Common Pitfalls and Misconceptions
Understanding the true nature of heat is critical to effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
The Dangers of "Normal" Operating Temperatures
Many operators assume a "warm" system is a "working" system. However, the ideal operating temperature for most industrial hydraulic systems is 120-140°F (50-60°C).
A widely accepted rule of thumb is that for every 18°F (10°C) increase in temperature above this ideal range, the service life of the hydraulic fluid is cut in half.
A Cooler Is Not a Cure-All
Installing a larger heat exchanger or cooler treats the symptom (excess heat) but not the cause (system inefficiency).
While a properly sized cooler is essential, relying on it to manage extreme heat often masks underlying problems like incorrect pressure settings, internal component leakage, or poor circuit design. The root cause of the inefficiency must be identified and corrected.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to heat management should be guided by your primary objective for the system.
- If your primary focus is reliability and long-term lifespan: Prioritize keeping the fluid cool and clean by maintaining an operating temperature below 140°F (60°C) and adhering to a strict fluid analysis and filter change schedule.
- If your primary focus is peak system efficiency: Treat heat as a direct measurement of wasted energy and use an infrared thermometer to locate the specific components that are generating excess heat to diagnose and fix the inefficiency.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting an overheating system: Do not simply add cooling capacity; first, identify the source of the inefficiency, as this is where energy is being lost and components are being damaged.
Ultimately, managing heat in a hydraulic system is the most effective way to manage its efficiency and secure its long-term health.
Summary Table:
| Negative Effect of Heat | Primary Consequence |
|---|---|
| Fluid Viscosity Breakdown | Loss of lubrication, metal-on-metal wear, internal leakage |
| Fluid Oxidation | Formation of sludge and varnish, clogged filters, additive depletion |
| Seal & Hose Degradation | Hardening, cracking, and leaks leading to pressure loss and contamination |
| Accelerated Component Wear | Premature failure of pumps, motors, and valves due to friction and contamination |
Protect your hydraulic systems from the destructive power of heat. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables that support precise fluid analysis and system monitoring. By partnering with us, you gain access to the tools needed to maintain optimal hydraulic fluid health, prevent overheating, and extend the life of your critical equipment. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your system's reliability and efficiency. Reach out via our contact form for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 100L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 10L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
- 80L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Circulator for Water Bath Cooling and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- 10L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
People Also Ask
- How does a water bath work? Master Precise and Gentle Heating for Your Lab
- What are the performance advantages of using a recirculating cooling system for EK-181 steel? Maximize Yield Strength
- What is the function of a constant temperature water bath in CO2 absorption kinetics? Achieve High-Precision Research
- How do circulating cooling systems ensure accuracy in adsorption tests? Stabilize Thermal Variables for Precise Data
- How does a high-precision constant temperature circulator contribute to mineral dissolution kinetic studies?


















